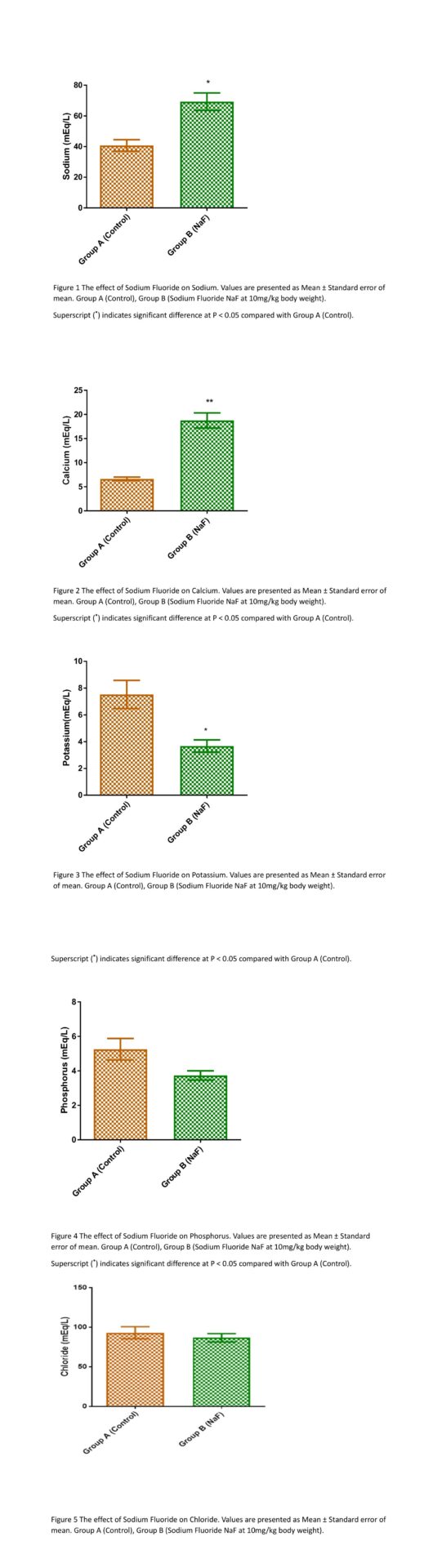
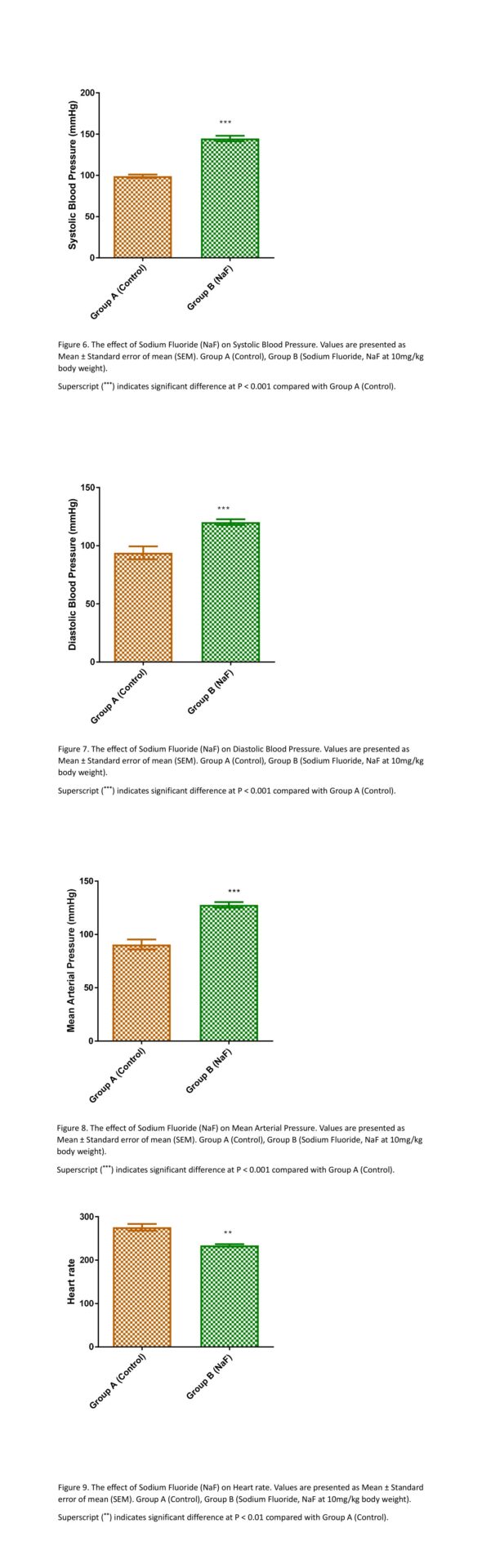
This study investigated the role of sodium fluoride on electrolytes and blood pressure in male Wistar rats. Sodium fluoride and the damage done to human health have been of public concern in recent years. Electrolyte imbalance poses threat and can predispose the body to life-threatening cardiovascular conditions including hypertension. Hypertension has been identified as one of the most significant risk factors for morbidity and mortality worldwide. Ten male adult Wistar rats (150-180g) divided into two groups (n=5) were used for this study. Group 1 was the control group and received distilled water orally for 21 days, group 2 received 10mg/kg sodium fluoride p.o. through oral gauge for 21 days. Twenty-four hours after the last treatment with sodium fluoride, blood pressure indices; systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure and heart rate were determined non-invasively in awake animals by tail plethysmography using an automated blood pressure monitor (CODA S1, Kent Scientific Corporation, CT). The average of no less than nine readings was recorded for each animal at rest during the blood pressure measurements after the acclimatization period. About 3 mL of blood was collected by retro-orbital venous puncture using plain capillary tubes into plain bottles and left to clot. The clotted blood was then centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 10 min. Clear serum was separated using a Pasteur pipette into another plain tube and then stored at 40C. Data collected were expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05 using Student’s t-test analysis. The results from this study showed that sodium fluoride caused a significant increase P<0.001 in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure, and P< 0.01 in heart rate compared to the control group that received distilled water. Also, the administration of sodium fluoride caused a significant increase P<0.05 in serum sodium and calcium when compared to the control group. The oral administration of sodium fluoride caused a significant decrease P<0.05 in potassium and phosphorus when compared to control group. There was no significant difference in chloride level in sodium fluoride-treated rats compared to the control. This study showed that sodium fluoride has hypertensive effects on blood pressure as seen in the significant increase in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure and heart rate. The results from this study also showed that sodium fluoride elevate serum electrolytes that have the potency to lead to increasing blood pressure as seen in sodium and calcium while reducing the electrolytes that have beneficial effects on lowering blood pressure such as potassium and phosphates.
Physiology 2023 (Harrogate, UK) (2023) Proc Physiol Soc 54, PCB005
Poster Communications: The role of Sodium fluoride on electrolytes and blood pressure in male Wistar rats
Olusola Ayegboyin1, Abayomi Ige1, Elsie Adewoye1,
1University of Ibadan Ibadan Nigeria, 2University of Ibadan Ibadan Nigeria, 3University of Ibadan Ibadan Nigeria,
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.