Microglial cells are the key immunogenic cells in the CNS, and significantly contribute to overall brain function by participating in phagocytosis during development, homeostasis, and diseased states. It has been demonstrated that oxygen levels have significant impacts on microglial morphology and behaviour. Hypoxia is reported to either induce, or attenuate externally induced, inflammatory signalling. This study aimed to characterise the LPS induced inflammatory response, including its potential dose dependency, of BV-2 cells, and discover how this response is altered when stimulation occurs during hypoxia. BV-2 cells between passage 3-11 were exposed for 24h to LPS, at 1, 10, 100, 1000, or, 10,000 ng/mL, in normoxia (21% O2), or hypoxia (1% O2). Media samples were collected and assessed for inflammatory response, via TNF-α ELISA assay. Cell viability, via LDH assay, and metabolic activity, via MTT assay, were also determined. Lastly expression of inflammation and hypoxia associated genes was analysed via qPCR, using only 100ng/ml LPS as a dosage.
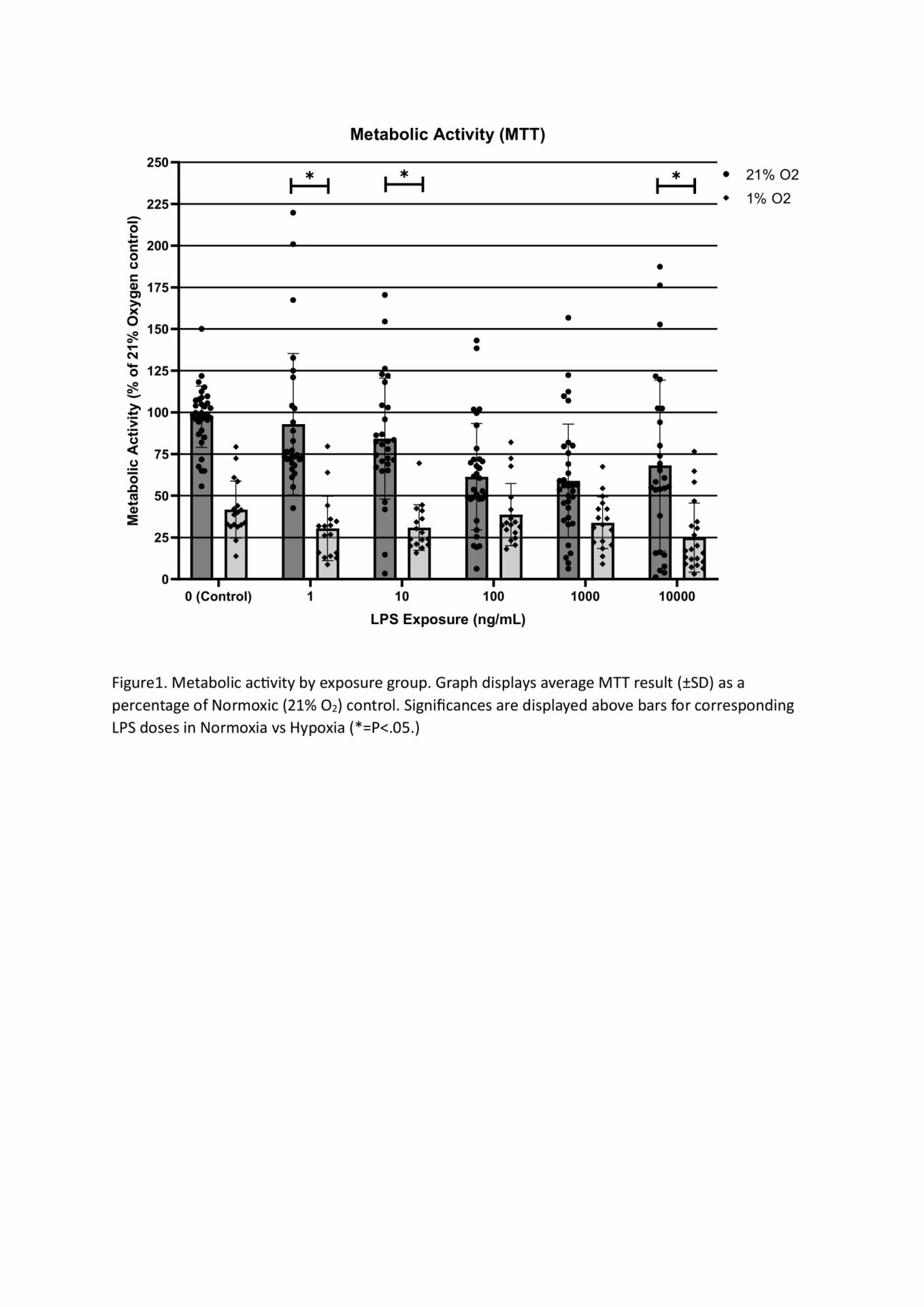
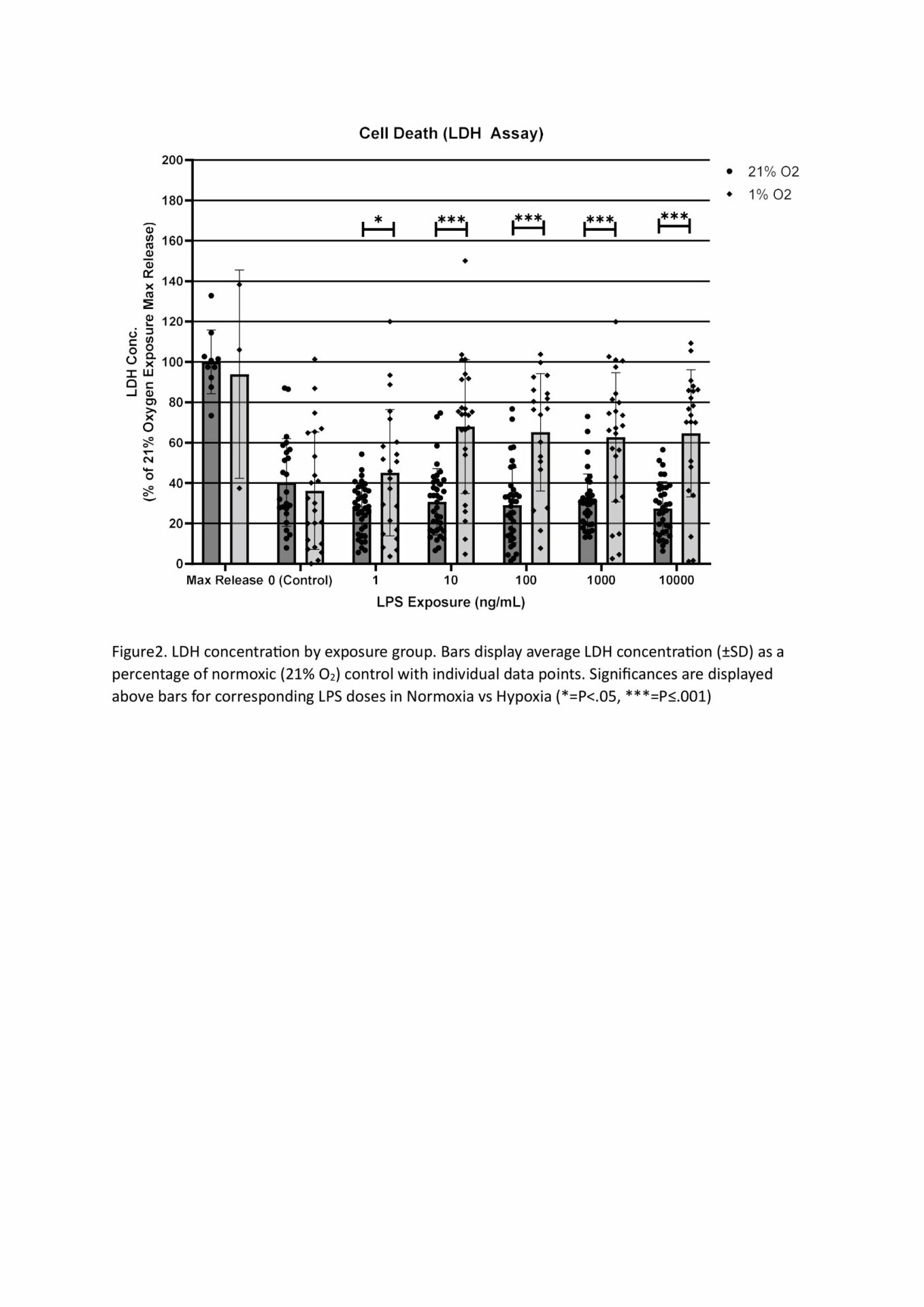
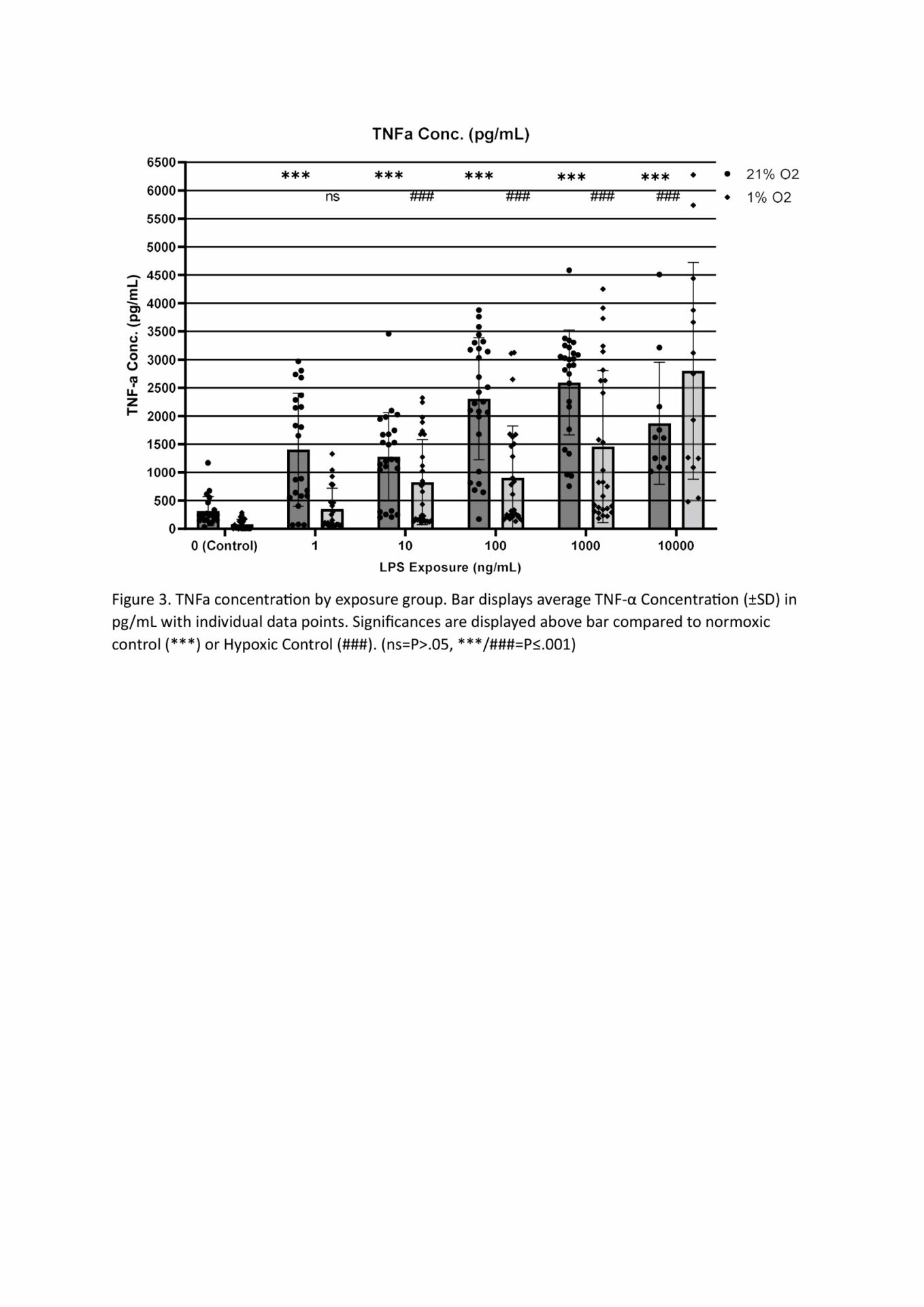
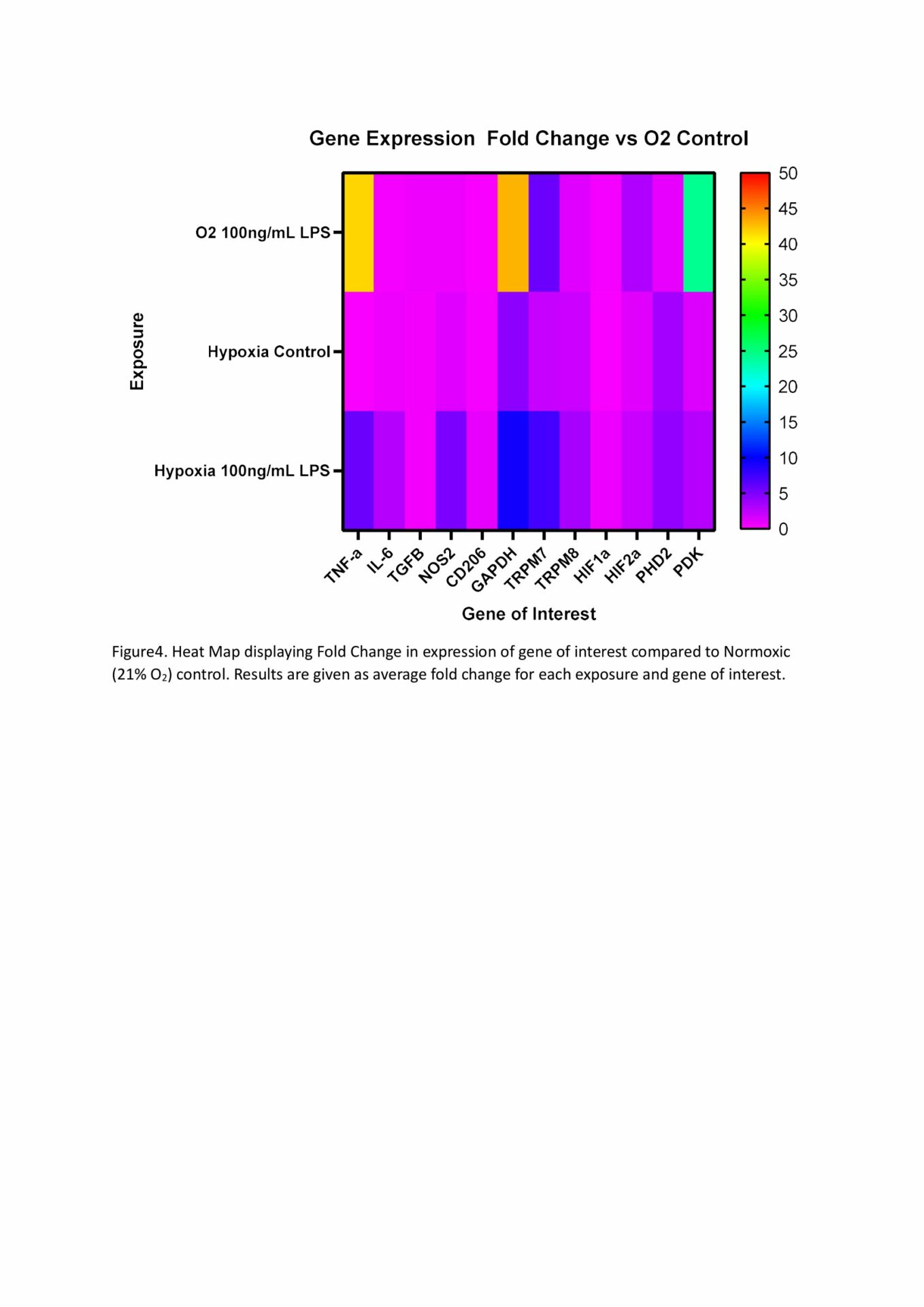
MTT assays demonstrated decreased metabolic activity in hypoxia at all LPS doses, with 10,000, 10 and 1ng/mL being significant at p<.05, n=4 (Figure 1). This decrease is likely the reduced oxygen limiting aerobic respiration, though cell death from hypoxia, suggested from our LDH results, may also be responsible. LDH concentration was significantly increased by hypoxia compared to normoxic cells when LPS was present, but not by hypoxia alone. All LPS doses 10ng/mL or higher showed significantly increased LDH concentration compared to hypoxic control (min sig .05), n=4 (Figure 2). Predictably, all normoxic LPS dosages, and all doses above 1ng/mL in hypoxia, showed significantly higher TNF- α than control, n=4 (Figure 3). Not all doses differed significantly, however increasing TNF- α release trended with increasing LPS concentration. The exception was normoxic 10,000ng/mL LPS where a biphasic high (1000-3000pg/mL,) or low response (<50pg/mL, excluded herein) appeared between technical replicates. We suspect this results from the cytotoxic effect of LPS at high dosages limiting TNF- α production. qPCR analysis showed LPS 100ng/mL induced increases in TNF-α (x41.58), GAPDH (x42.86), and PDK (x24.32) expression at 21% O2, which were reduced when combined with Hypoxia (x5.62, x4.42, x1.30 respective) n=4 (Figure 4). TNF-α (x30.58) and IL-6 (x25.64) were also notably increased in LPS dosed hypoxia samples compared to hypoxic controls. This indicates that while LPS promotes a proinflammatory response, 24h of hypoxia suppressed this induction.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates LPS stimulates TNF-α gene expression in both normoxia and hypoxia and TNF-α release shows evidence of dose dependency, with a potency threshold as low as 1ng/mL regardless of hypoxic status. This work further shows the combination of LPS and Hypoxic stimulation may induce cell death where LPS stimulation alone does not. Lastly, we demonstrated that 24h hypoxia (1% O2) reduced BV-2 cell metabolism, including reduced expression of metabolically associated genes and reducing the inflammatory response of BV-2 cells induced by LPS at some concentrations. With these results, this study furthers our understanding of neuroinflammation under hypoxic conditions.