Multiple nutritional factors can be related to blood pressure (BP) control. However, their regulatory mechanisms are not yet understood. Fatty acids (FA), mainly essential fatty acids (EFA), and their derivatives such as eicosanoids, can influence BP and be involved in cardiovascular diseases. Low fat diet, with reduced saturated FA, decreases BP substantially (Das, 2001). In contrast, a positive relationship between BP and high intake of saturated FA has been found (Pérez-Jiménez et al. 2002). However, the qualitative effect of different types of fat on BP control is scarcely known.
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is an important regulator of BP and water homeostasis. Polyunsatureted FA inhibit ACE and enhance the synthesis of NO (Kumar & Das 1997). This suggests a close interaction between FA and RAS.
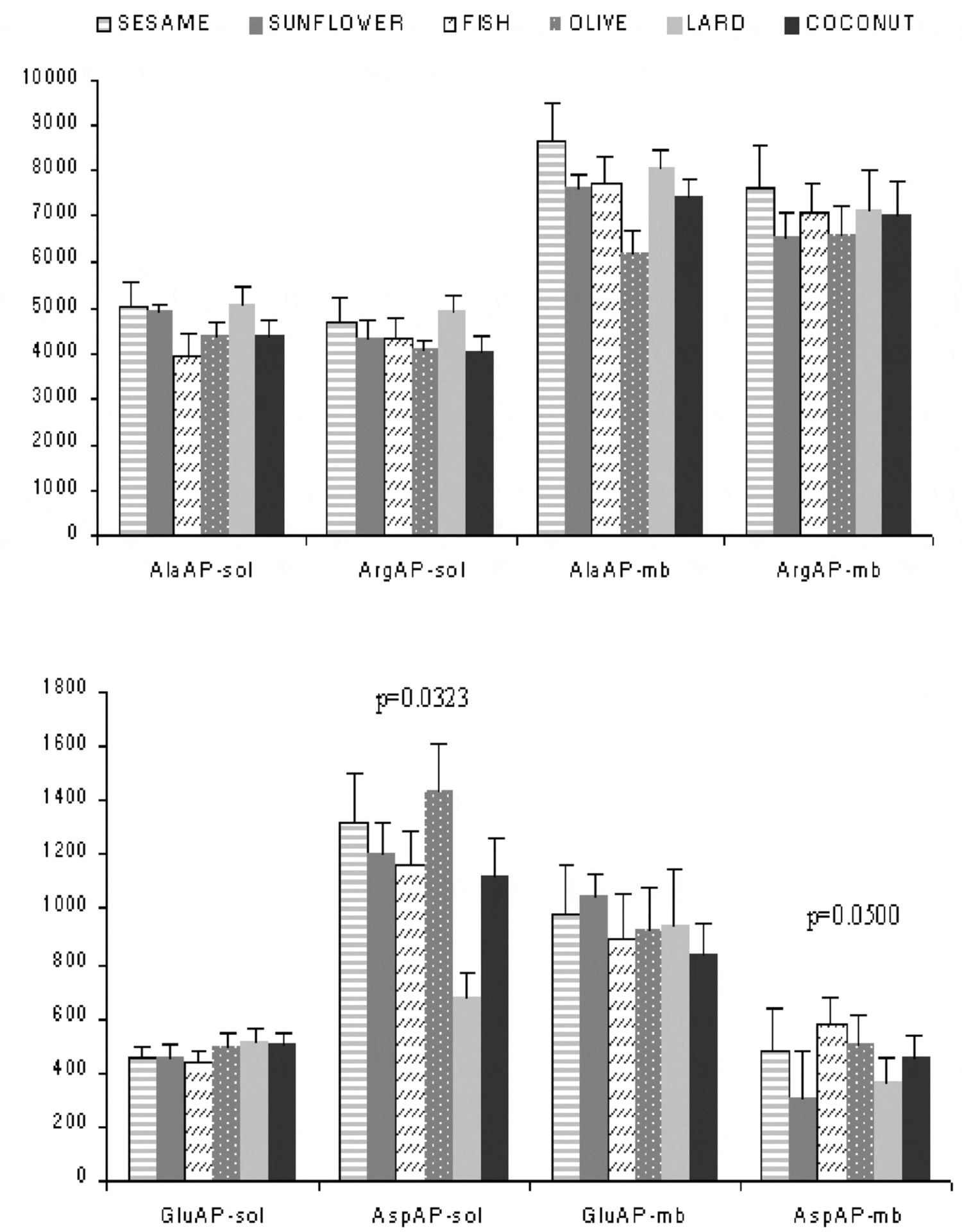
There is evidence that local kidney angiotensins (Ang) serve as important paracrine regulators of renal function (Harris & Cheng, 1996). Aminopeptidases (AP) play a major role in the metabolism of RAS (Barret et al. 1998).
The aim of this study was to analyse the effect of several fats (with different degrees of saturation and EFA composition) used in the diet on renal angiotensinase activities (AlaAP, ArgAP, GluAP and AspAP). The AP activities were assayed in both soluble (sol) and membrane-bound (MB) fractions obtained from the renal cortex and medulla of adult male rats.
Junta De Andalucía through PAI CVI-221 and PAI CTS-438 (Acciones coordinadas) supported this work.