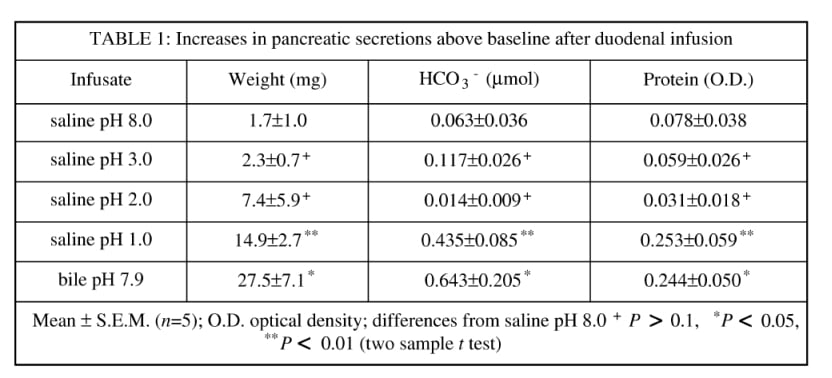
Infusion of bile salts at high concentration into the duodenum has been shown to stimulate pancreatic exocrine secretions in man and cat through release of the hormone secretin (Osnes et al. 1980; Hanssen et al. 1980). In our experiments, we have collected natural bile from fasted rats (weight 250-350 g), which was then infused into the duodenum to determine whether pancreatic secretions were stimulated. Anaesthesia, taken as abolition of the hind limb flexor withdrawal reflex, was induced with 80 mg kg-1 Sagatal I.P. and maintained with 24 mg kg-1h-1 I.M. After the experiments, the animal was killed with 1.0 ml Euthatal I.V. After bilateral vagotomy, the following were cannulated: carotid artery for blood pressure recordings, jugular vein for I.V. injections, duodenum via the pylorus for infusions, pancreatic/bile duct at the duodenum for collection of pancreatic secretions and above the pancreas for collection of bile (Wheeler et al. 1997). Pancreatic secretions were collected over 15 min periods and analyzed for weight, HCO3 and protein content. The effects of infusion of 0.5 ml of test solution at 37oC into the duodenum are presented in Table 1 which shows the increase in secretion above the preceding baseline level, summed over the response duration.Bile which was secreted at a mean rate of 15 mg min-1 was collected for 2 h prior to the experimental procedures. Total cholate concentration assayed by the method of O’Maille et al. (1965) was 18.9 ± 2.8 (S.D.) mM. On infusion into the proximal duodenum, there resulted marked increases in weight, HCO3 content and protein content which were significantly greater than the effects of infusion of saline pH 8.0. Significant increases were also caused by saline pH 1.0 but not by saline pH 2.0 or 3.0. The response duration to saline pH 1.0 was 45 min in contrast to the bile-evoked response which lasted 165180 min. We conclude that natural bile does stimulate rat pancreatic secretions over an extended time course.
University of Glasgow (2004) J Physiol 557P, PC41
Communications: Effects of duodenal bile salts and acidity on pancreatic secretions in anaesthetized rats
N. Kane, J. Overend and J. Morrison
Institute of Biomedical & Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ, UK
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.