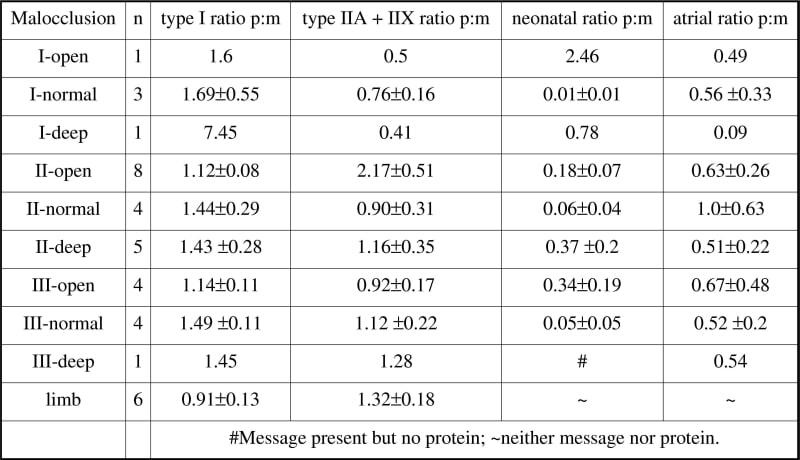
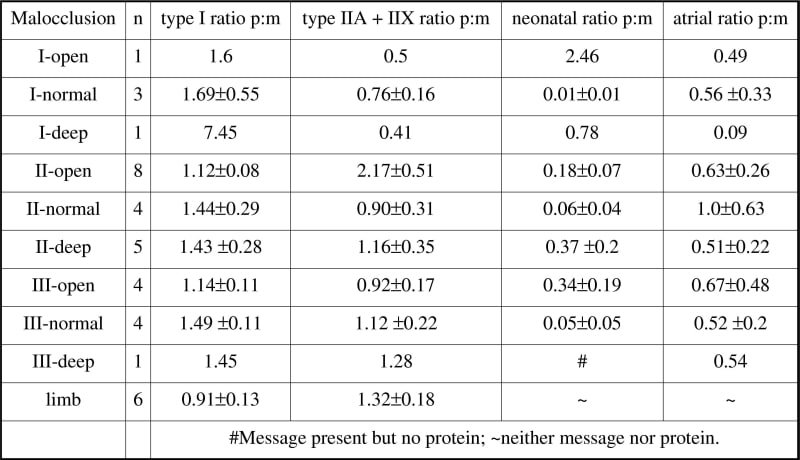
Samples are obtained from masseter of subjects undergoing orthognathic surgery for treatment of malocclusion, snap frozen for myosin immunostaining to identify fibre types and processed in parallel with samples of limb muscle taken from the margin of excised soft tissue tumours. Sample collection from consenting subjects was approved by the local Research Ethics Committees of Guy’s Hospital (limb samples) and Lille (masseter). Cross-sectional areas of typed fibres (identified according to Sciote et al. 1994) are measured to work out their relative ‘occupancy’ (% area) of the biopsy and serial sections are collected for quantification of myosin heavy chain gene expression by RT-PCR using isoform-specific probes. Values of myosin message in each reaction are calculated as pg of amplified DNA per ng of internal 18S RNA, and the relative content of each individual MHC isoform RNA is obtained as a percent of the total of all myosin message in that sample. Malocclusion is diagnosed from sagittal (class I, II and III) and vertical dimensions (Open, Normal and Deep) from lateral cephalograms. The relative abundance of the mRNAs for each isoform was compared with an estimate of the corresponding myosin protein content obtained from the fiber type occupancy values, in the form of a simple ratio (protein:message). The Table shows mean ratios for masseter samples separately for the 9 different craniofacial groups and for the limb muscle samples. Values are close to 1 for limb muscle samples, but show more mismatch in masseter samples where there is generally a ‘deficit’ of type I message (ratios greater than 1) and a very variable ‘excess’ of message for neonatal and atrial isoforms in most cases. We conclude that in subjects with malocclusion, translational control of myosin expression is different in masseter muscle compared with limb muscles.
King's College London (2005) J Physiol 565P, C93
Communications: Expression of myosin isoforms in masseter of human subjects with malocclusions
Horton, M ; Sciote, J J; Ferri, J ; Raoul, G ; Rowlerson, Anthea ;
1. Department of Orthodontics, School of Dental Medicine, Pittsburgh, PA, USA. 2. Service de Stomatologie & Chirurgie Maxillofaciale, CHRU de Lille, Lille, France. 3. Applied Biomedical Research, King's College London, London, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Protein: mRNA (p:m) ratios (± s.e.m.) for myosin heavy chain isoform
Protein: mRNA (p:m) ratios (± s.e.m.) for myosin heavy chain isoform
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.