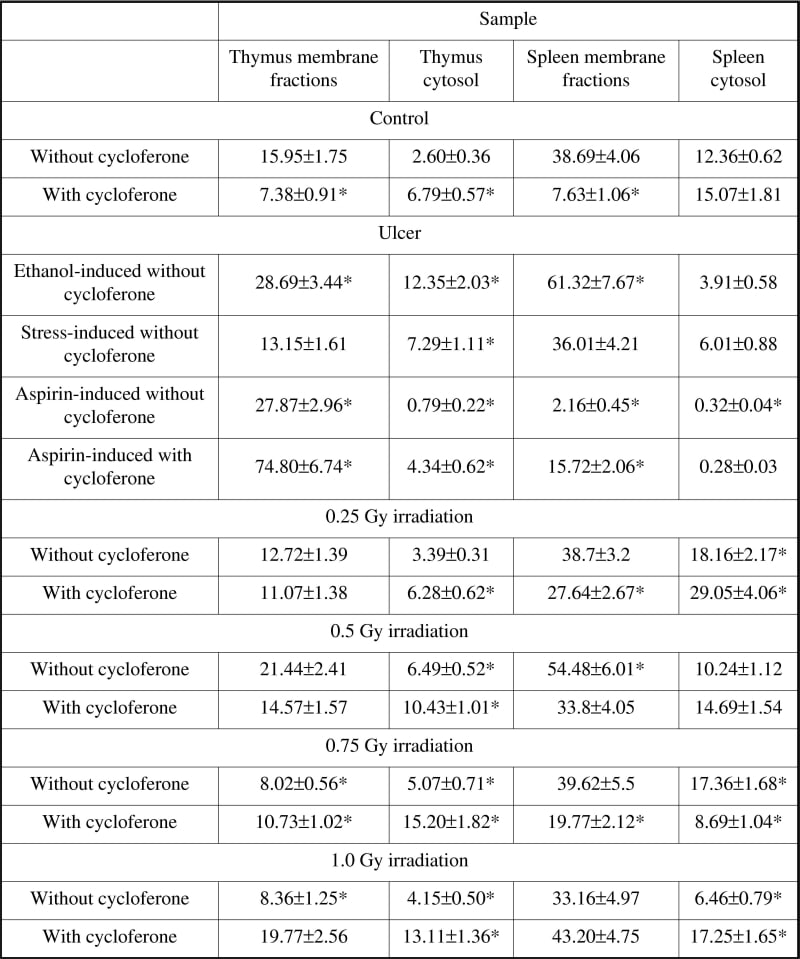
The levels of protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) activities in cytoplasmic membrane and cytosol of rat spleen and thymus lymphocytes under conditions of development of different models of stomach ulcer and whole body irradiation of rats at doses of 0.25-1 Gy were investigated. The effect of cycloferone administration on these parameters was evaluated. Three models of stomach ulcer disease were used: aspirin-, stress- and ethanol-induced. It was shown that ethanol-induced stomach ulcer was accompanied by stimulation of PTP activities in membrane fractions of spleen and thymus lymphoid cells. A significant increase of thymocyte cytosol PTP activity and decrease of spleenocyte cytosol PTP activity were observed (Table 1). Development of a stress-induced ulcer leads to thymocyte cytosol PTP activity stimulation and spleenocyte cytosol PTP activity inhibition. No changes were found in the activity of membrane PTP. Inhibition of PTP activities under conditions of aspirin-induced ulcer development was shown in most cases, except with thymus membrane-associated enzymes (Table 1). These data confirmed that different processes were involved in immune dysfunction accompanied ulcers with various aetiologies. An increase of intracellular PTP activity and a decrease of membrane-associated activity was observed after addition of cycloferone, a synthetic interferon inducer (injections twice a day at a dose of 62 mg/kg for 5 days) (Table 1). Cycloferone application on rats with aspirin-induced ulcer leads to an increase in PTP activity in most cases (Table 1). Cycloferone treatment before exposure to X-ray irradiation results in a shift of maximal increasing PTP activity levels to hither doses of irradiation in thymus and more potent activation of PTP activities in spleen (Table 1). Radioprotective features of the drug were confirmed also by cyclic nucleotide level measurement under the same conditions.
University of Bristol (2005) J Physiol 567P, PC122
Poster Communications: Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in lymphoid cells under conditions of different models of ulcer development and ionizing irradiation treatment, combined with cycloferone application
Bogdanova, Olena Viktorivna; Kuzmenko, Larysa Ivanivna; Prokopova, Kateryna Vasylivna; Gavrysh, Larysa Ivanivna; Drobinska, Olesya Vadymivna; Ostapchenko, Ludmyla Ivanivna;
1. Biochemistry, Taras Shevchenko Kyiv National University, Kyiv, Kyiv, Ukraine.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity (nmol Pi / (min x mg)) in membrane fractions and cytosol of thymus and spleen lymphoid cells under conditions of stomach ulcer development and radiation treatment combined with cycloferone injections.Values are means±S.E.M.; n=6. *P±0.5 compared with the control.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.