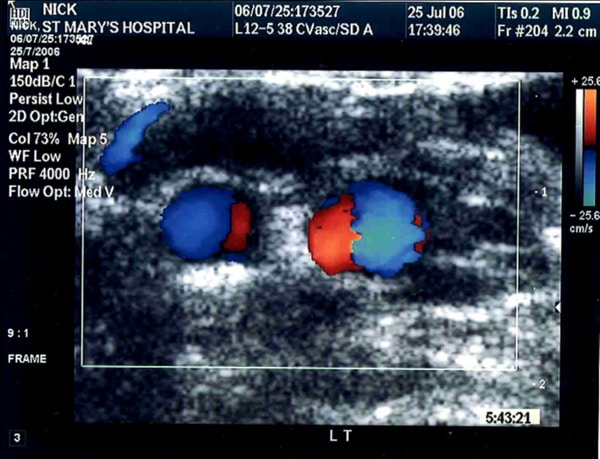
The pattern of blood flow in arteries influences their biology and development of disease. Arterial geometry is commonly non planar1 generating blood flow fields that often include secondary flows. Model studies show that mixing, resulting from such geometries, can render the distribution of wall shear stress more uniform and enhance blood-wall mass transport of lower molecular weight fluid phase controlled materials2. Doppler ultrasound is widely used clinically to visualize axial flows. By setting the ultrasound probe in a plane perpendicular to the vessel, Frazin et al3 detected secondary flows in a model and also in-vivo, showing the presence of swirling flow in the thoracic aorta. Hoskins et al4,5 detected swirling flow in the lower limb arteries and also a Dean flow pattern in a model bifurcation. Following the same approach, we have investigated the potential of using an ultrasound scanner to image secondary flows in arterial models with planar and non-planar geometries. The scanner employed was a Philips HDI 5000 colour Doppler with linear array transducers. We visualised both Dean vortices and swirling flow, depending on geometries and flows. We acquired in-vivo measurements in the internal and external carotids (ICA & ECA) and common femoral (CFA) arteries of a 23 year old healthy male volunteer. The patterns of the transverse Doppler scan suggest the presence of swirling flow in both the ICA and ECA. Swirling flows were not visible in the common carotid or the carotid bulb. In the left ICA and ECA, the scan showed the flow to swirl in opposite directions. Looking downstream, the rotation was clockwise in the ICA and anticlockwise in the ECA. Mirror image patterns were found in the right carotids. In the CFA, Dean vortex patterns were visible during systolic flow. Comparison of the scans at two stations, suggests that the Dean pattern rotates along the CFA. Ultrasound scanning may be of value in visualising secondary flows and increasing understanding of the correlation between the flow and vascular biology and disease.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC11
Poster Communications: Ultrasound imaging of secondary flows in blood vessels
N. Foin1, C. G. Caro1, S. Dhanjil2
1. Department of Bioengineering, Imperial College, London, United Kingdom. 2. Irvine Vascular Studies, St Mary's Hospital, Imperial College, London, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Swirling flow pattern in the left (LT) carotid arteries of a 23 yr. old healthy male volunteer. ECG-gated scan in the right common femoral artery (CFA) during systolic flow showing Dean vortices.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.