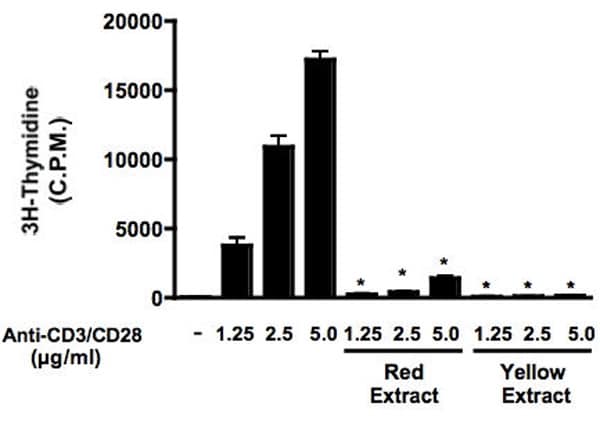
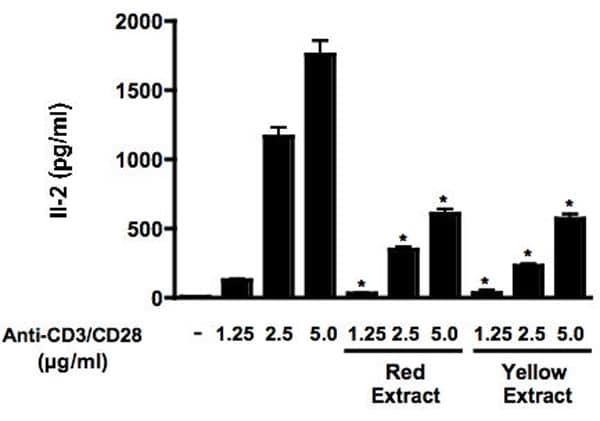
Introduction Cactus pear (Opuntia Ficus Indica) has recently been acknowledged as a source of bioactive compounds able to act as antioxidants in vitro and to decrease oxidative stress in vivo (1). Here we investigated the effects of extracts from fruits of Red and Yellow cactus pear cultivars on naïve murine lymphocytes, activated by the simultaneous engagement of TCR/CD3 and CD28 receptors. Material and Methods Cactus pear fruit extracts were obtained as previously reported (1). Naïve lymphocytes purification and treatment, proliferation assays, IL-2 production and CD69 expression assays were conducted as described by D’Acquisto et al. (2). Results Naïve T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 either in the absence, or in the presence, of cactus pear fruit extracts. Anti-CD3/CD28 treatment (1.25 to 5.0 μg/ml) induced a dose-dependent increase of cell proliferation (Fig.1) as well as IL-2 production (Fig.2). Co-incubation with either Red or Yellow cactus pear fruit extract (330 and 110 mg fresh fruit/ml, respectively) almost abolished cell proliferation, and significantly decreased IL-2 levels at all anti-CD3/CD28 concentrations (Figs. 1, 2). In addition, the expression of CD69, a marker of T cell activation, induced by anti-CD3/CD28 at 5.0 μg/ml, was reduced by 41.7 ± 4.5 and 42.3 ± 4.3%, n=3, P<0.01, when lymphocytes where stimulated the presence of either the red or the yellow extracts, respectively. Conclusions Extracts from cactus pear fruits significantly counteract the TCR-mediated activation of naïve lymphocytes. A potential use of these natural, non toxic extracts in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, is therefore suggested. In addition, the anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-stimulated macrophages (manuscript in preparation), and the antioxidative protection on human LDL by the betalain components (3), suggest these extracts beneficial in diseases such as atherosclerosis where inhibition of LDL oxidation and modulation of macrophage and lymphocyte response has been proven to be crucial.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC496
Poster Communications: Inhibition of the TCR-mediated activation of naïve murine T cells by Cactus Pear Fruit Extracts
M. Allegra1, L. Tesoriere1, F. D'Acquisto2, M. Perretti2, M. A. Livrea1
1. Farmacochimico, Tossicologico e Biologico, Universita' di Palermo, Palermo, Italy. 2. Centre for Biochemical Pharmacology, William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Effects of cactus pear fruit extracts either red or yellow (330 and 110 mg fresh fruit/ml respectively) on anti-CD3/CD28-induced T cell proliferation. Results are the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. *Significantly different from anti-CD3/CD28 treated cells with a P < 0.01.
Effects of cactus pear fruit extracts either red or yellow (330 and 110 mg fresh fruit/ml respectively) on anti-CD3/CD28-induced Il-2 production. Results are the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. *Significantly different from anti-CD3/CD28 treated cells with a P < 0.01.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.