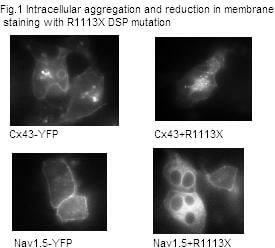
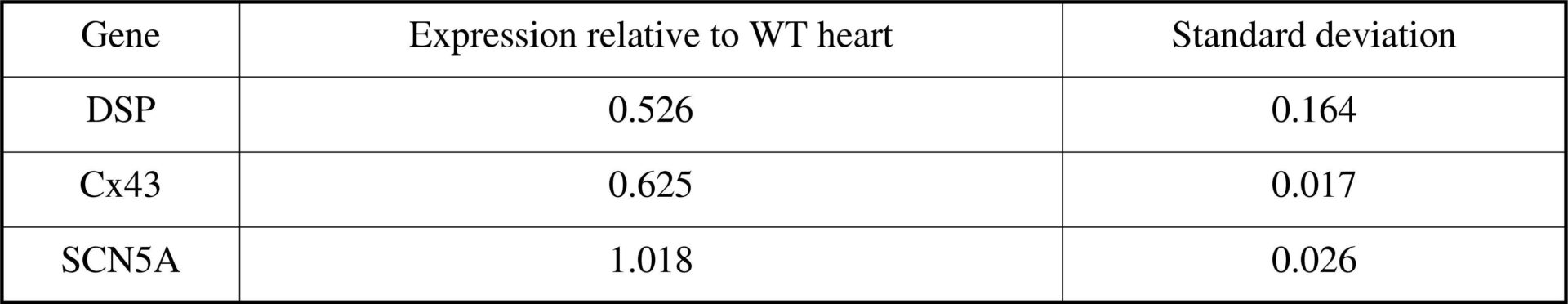
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is responsible for up to 20% of sudden cardiac deaths in the young and has been linked to mutations in desmoplakin(1). We have examined the arrhythmic substrate by performing electrophysiological studies (EP) on a cardiac restricted desmoplakin (DSP) heterozygous knockout mouse (hetKO), as a model of ARVC(2). Real time polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR) and immunostaining were performed to examine the expression level of connexin 43 (Cx43)and the alpha subunit of the sodium channel (Nav1.5). HL-1 cells (a cardiac cell line) were transfected with a mutation identified in our patient group and the expression of Cx43 and Nav1.5 observed. ECGs were recorded from hetKO and wild type (WT) DSP mice and a standard EP study was performed under 1.5% inhaled isoflurane. HL-1 cells were transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 with the R1113X DSP mutant and either YFP tagged Nav1.5 (Nav1.5-YFP) or Cx43 (Cx43-YFP). Immunostaining was performed on frozen sections of mouse hearts in triplicate using Cx43 and β catenin antibodies. RTPCR was performed on mouse heart lysate using Taqman assays. Genes were assayed in triplicate relative to GAPDH using the 2-ΔΔCt method. In vivo: Apart from sinus node recovery time (SNRT), no significant differences in ECG parameters or EP measurements between WT and hetKO mice were identified (SNRT WT 0.133s, hetKO 0.108s (p<0.05); AV node effective refractory period WT 0.055s, hetKO 0.050s; ventricular effective refractory period WT 0.037s, hetKO 0.034s, n=7 WT, n=9 het KO, Mann-Whitney test). However, only hetKO mice developed ventricular tachycardia (VT) on pacing (0/7 WT; 6/9 het KO, p<0.05, Fisher’s exact test). In vitro: Cx43 expression was reduced by 37% (table 1), but SCN5A expression was not reduced by RTPCR. Immunostaining showed that Cx43 expression was reduced and mislocalized away from the intercalated disk. HL-1 cells transfected with the R1113X mutant showed intracellular aggregation of Nav1.5 and Cx43 (fig.1). The DSP hetKO mouse reproduces the arrhythmic phenotype seen in ARVC. Reduction of DSP in the mouse model reduces Cx43 transcription and leads to mislocalization of Cx43 – leading to gap junction dysfunction and reduction in arrhythmia threshold. DSP mutations lead to aggregation of the Nav1.5 and Cx43 in cells. Nav1.5 mislocalization could reduce the depolarizing current, promote conduction delay and VT. Further work is needed to establish a reduction in sodium current by patch clamping in the murine model.
University of Manchester (2010) Proc Physiol Soc 19, C3
Oral Communications: Role of desmoplakin in the development of arrhythmogenesis in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
J. Gomes1,2, P. Syrris3, P. Lambiase2, A. Tinker1
1. Metabolism and Experimental Therapeutics, Division of Medicine, UCL, London, United Kingdom. 2. Heart Hospital, UCL, London, United Kingdom. 3. Centre for Cardiology in the Young, UCL, London, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1 Cx43 but not Nav1.5 shows reduced expression in hetKO DSP hearts by RTPCR<#13>
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.