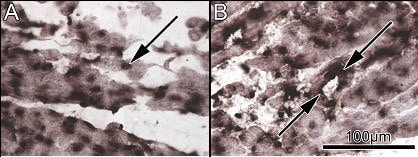
ATP and its derivatives are known to exert profound electrophysiological effects on the heart. Recent studies have revealed the expression of various P2 receptors, both ligand-gated P2X receptors and G-protein coupled P2Y receptors, throughout the heart. Although it is possible that they play a significant role in pacemaker activity (Ju et al., 2003), there are no detailed reports on the expression of the P2 family in the sinoatrial node (SAN). To investigate the expression profile of P2 receptors, we used quantitative PCR (qPCR) to measure the abundance of P2 receptor mRNA in the sinoatrial node (and also atrium and ventricle) of Wistar-Hannover rats (n=7). qPCR was carried out using an ABI 7900HT instrument together with ABI Taqman probe assays. In addition, we confirmed P2 receptor mRNA expression using in situ hybridisation (ISH) and measured protein expression using Western blotting. ISH was performed with a transcript specific riboprobe and Western blotting was performed with a transcript specific antibody (Alomone Labs). qPCR revealed the presence of mRNA for P2X receptors 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 (6 was not expressed) and P2Y receptors 1, 2, 4, 6, 12, 13 and 14 (11 was not tested) in the three areas of the heart. Of the transcripts investigated, P2X5 mRNA was 10 fold more abundant than any other transcript, in all tissue areas. P2X5 mRNA abundance was approximately the same as HCN4 (the primary alpha-subunit for the pacemaker current If) mRNA in the SAN. ISH was performed to confirm that the P2X5 mRNA was expressed in myocytes (rather than intra-cardiac neuronal tissue for example): a P2X5 specific riboprobe revealed strong specific labelling around the nuclei (site of the rough endoplasmic reticulum) in the sinoatrial node (Fig. 1A, arrow) and the atrial muscle (Fig. 1B); labelling was similar in the two regions, in agreement with the qPCR data. Labelling was also present within blood vessels (Fig. 1B, arrows). Finally, Western blot was carried out to determine whether the protein is present: a P2X5 specific antibody produced a single band at the expected molecular weight (51 kD) in all tissues. These data show the presence of mRNA for various P2 receptors in the sinoatrial node (and also atrium and ventricles). Whether P2X5 (the most abundant of the receptors) plays a significant role in pacemaking in the sinoatrial node remains to be elucidated.
University of Manchester (2007) Proc Physiol Soc 8, PC11
Poster Communications: ATP (P2) receptor expression in the sinoatrial node
H. Musa1, J. O. Tellez1, I. D. Greener1, H. Dobrzynski1, M. R. Boyett1
1. School Of Medicine, University Of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1. A, P2X5 mRNA expression in the sinoatrial node. B, P2X5 mRNA expression in the atrial muscle of the crista terminalis.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.