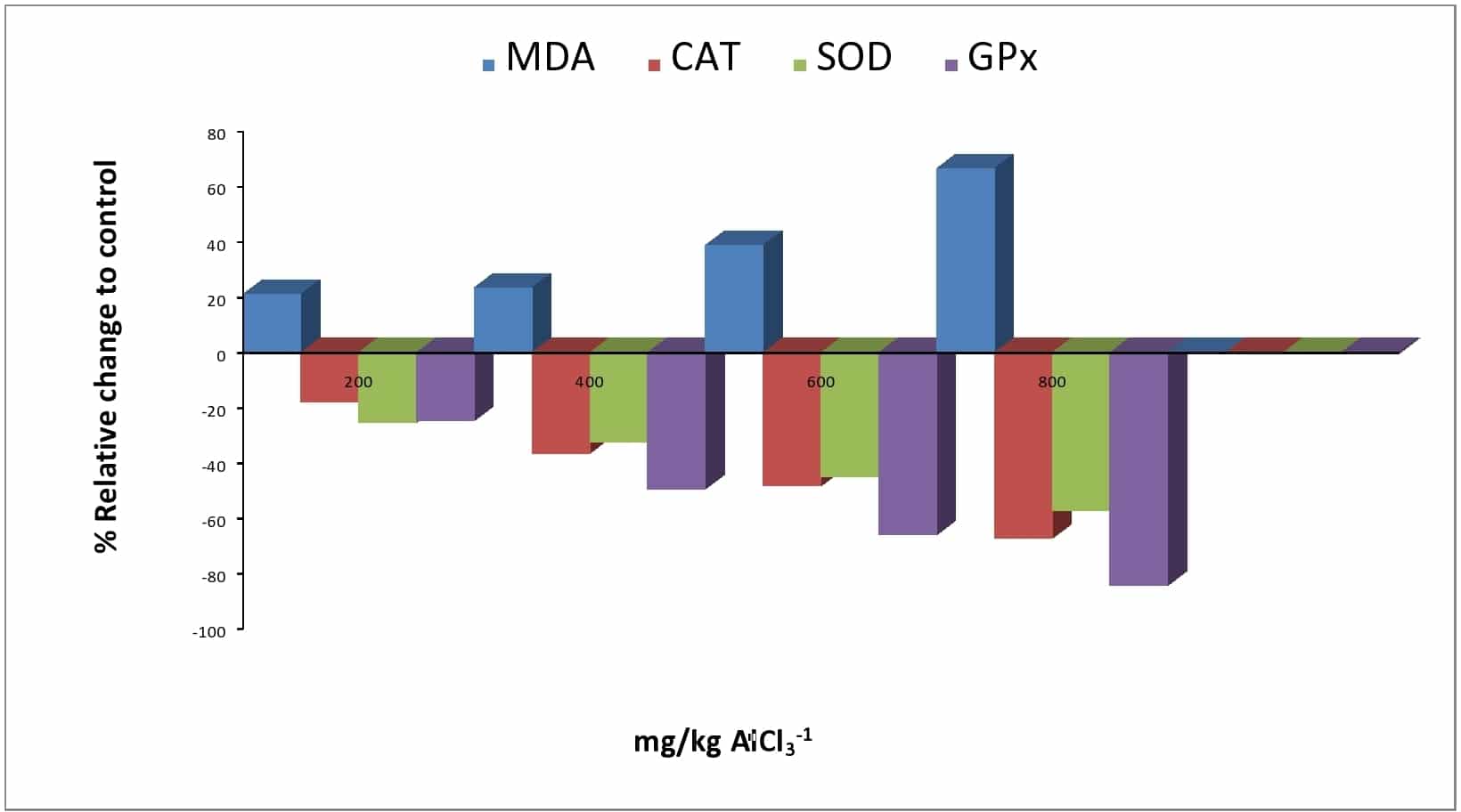
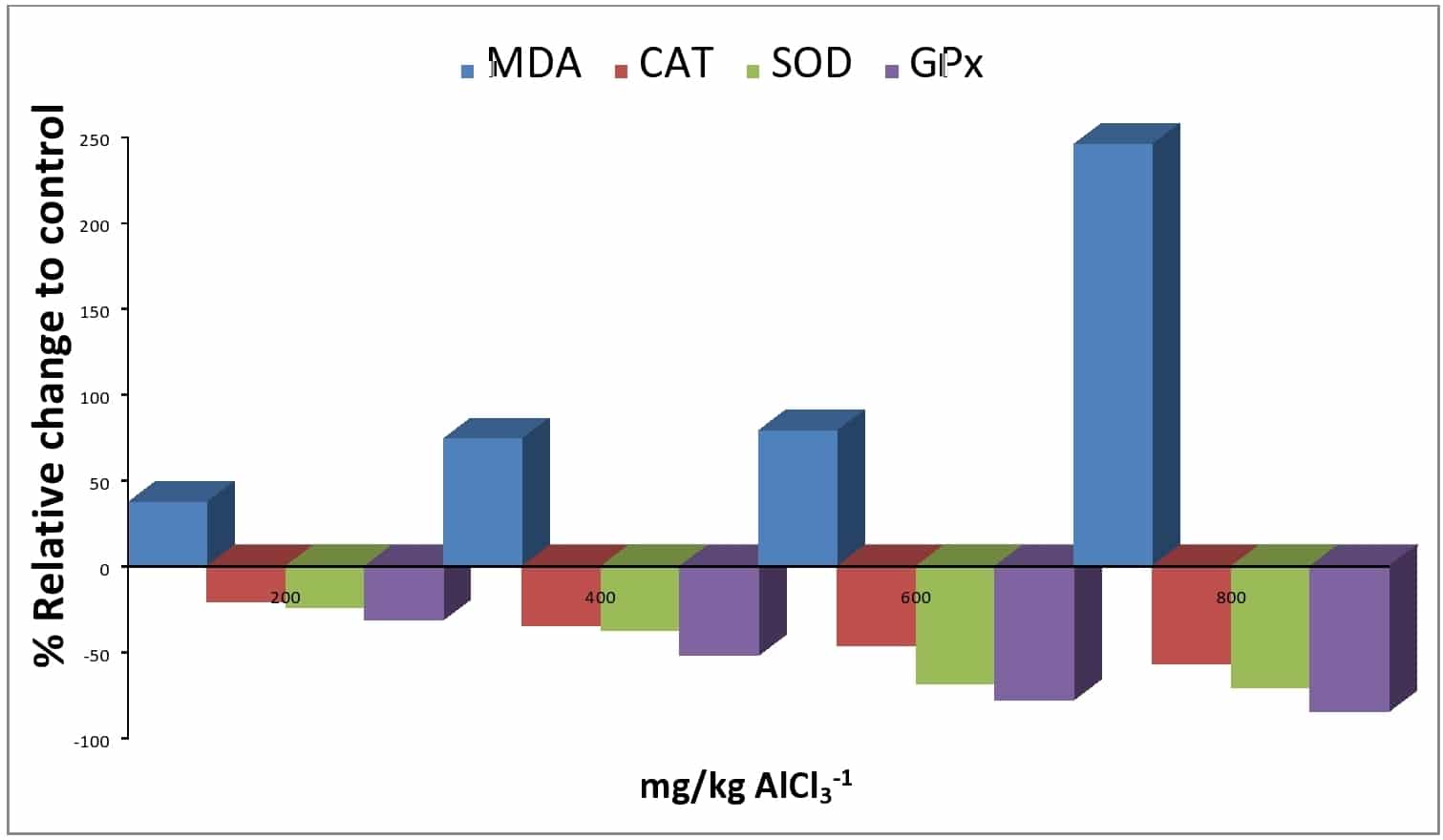
Aluminum is one of the most widely distributed elements in the environment and the third most prevalence and bioavailability metal comprising 8% of the earth’s crust. Its adverse effect on body organs is incompletely understood. This study aims to evaluate the possible mechanistic-link of prolonged exposure to aluminum tainted drinking water (AlCl3) on the perturbation of oxidative stress as assessed by alterations in pro-oxidant/antioxidant in the heart and kidney. Five groups of 10 healthy male wistar rats were used for the study. Normal control group received drinking water, while the cases were administered 200-800mg/kg-1 AlCl3, orally once daily for 28 consecutive days. Thereafter, the heart and kidney oxidative markers were studied. Result showed that AlCl3 up regulated heart and kidney lipid peroxidation significantly (<0.05) in a dose-response-organ specificity as reflected by marked increased malondialdehyde(MDA) with a concomitant diminution of glutathione peroxidase(GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities. Correlation studies revealed that oxidative stress contributes to AlCl3 induced cardio-renal toxicity in increasing other respectively upon comparing in both AlCl3 and control groups. Our data indicated and confirmed that aluminum tainted drinking water can induce differential pathophysiology risk to heart and kidney oxidative damage.
Physiology 2019 (Aberdeen, UK) (2019) Proc Physiol Soc 43, PC038
Poster Communications: Aluminum Tainted Drinking Water Impacts Negatively and Differently on Antioxidant Status of Cardio-Renal Systems
P. Akangbou1, A. N. CHUEMERE1, D. V. Dapper1, O. Ilochi2, M. Anyiyeloye3
1. human physiology, university of port harcourt, Port Harcourt, Rivers State, Nigeria. 2. Department of Human Physiology, Madonna University, Port Harcourt, Nigeria. 3. Department of Pharmacology, University of Port Harcourt, Port Harcourt, Nigeria.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1: Effect of AlCl3 induced oxidative stress in the heart
Figure 2: Effect of AlCl3 induced oxidative stress in the kidney
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.