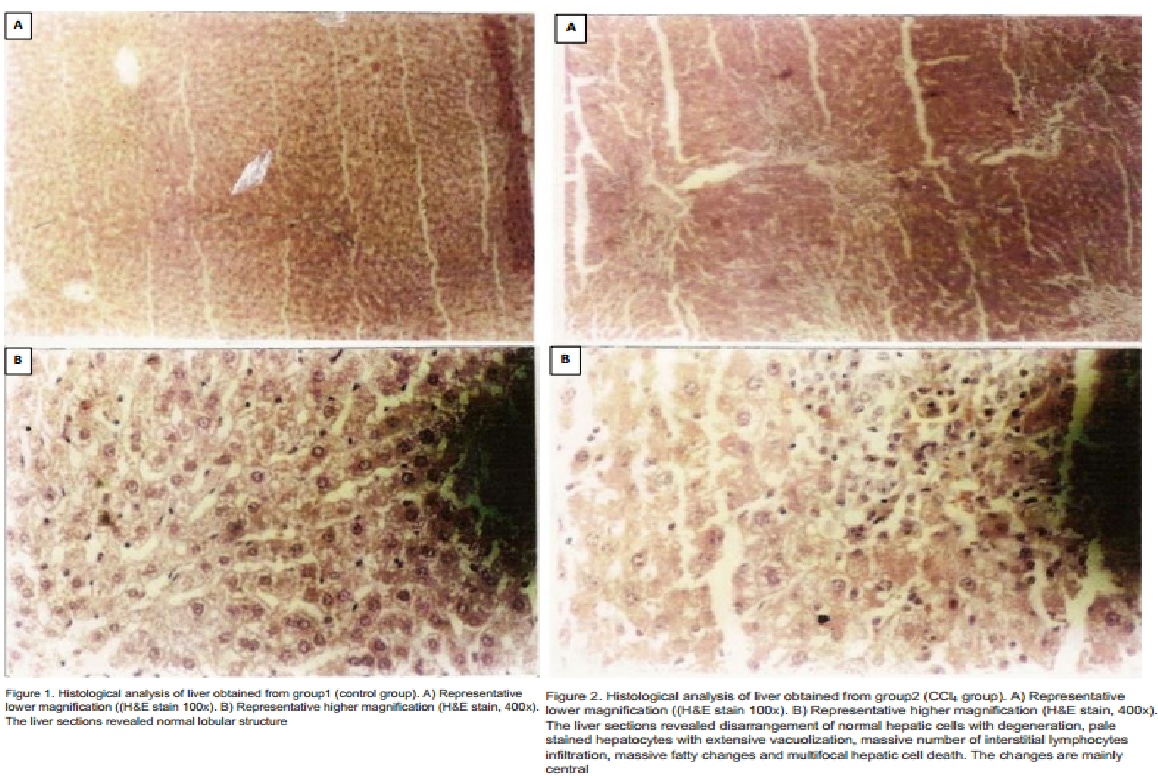
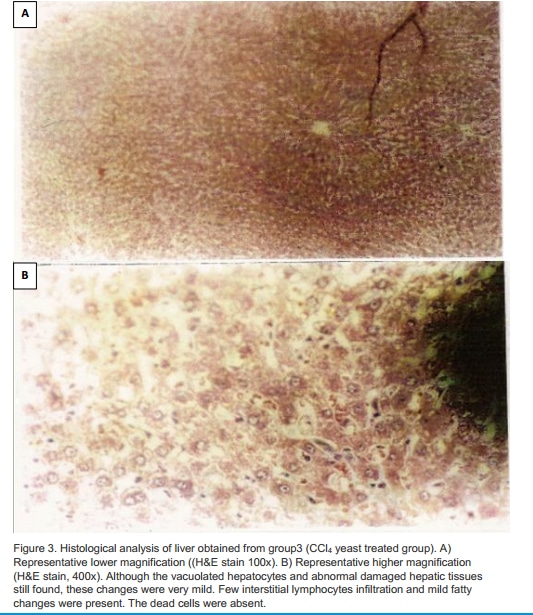
Carbon Tetrachloride [CCl4] can be used as a solvent, rubber cement and insecticides. Furthermore, observation-based methods illustrated continuing emissions of 35 Gg per year of CCl4 into the atmosphere1. CCl4 produce acute and chronic liver injury. Baker’s yeast is an excellent source of vitamins, minerals, and high-quality protein such as glutathione and choline. Glutathione, the most important antioxidant supporting detoxification and strengthing immunity, is present in up to 10 mM in yeast cells2. As well, choline is present in large quantity in Baker’s yeast. Choline promotes phosphatidylcholine Synthesis; a vital for the integrity of the cell membranes3. Choline is also a precursor of betaine which increase the concentrations of hepatic S-adenosylmethionine that prevents CCl4 induced DNA hypomethylation which produces cirrhosis in rats’ liver4. In addition, Betaine as an osmolyte it improves the function of kupffer cells in rat liver macrophages and prevents the reduction of Golgi complexes and mitochondrial induced by the exposures to CCI45. Our aim was to evaluate protective effect of oral Baker’s yeast against CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in rats’ model. 30 male Sprauge Dawley rats [125 -265g] were divided into three groups [n=10]. All rats were fed a normal diet for 2weeks. Then, group1 were injected with intraperitoneal (0.1ml /100g BW) olive oil. Group2 and 3 were injected with (0.1ml /100g BW) CCl4 dissolved on eqi-volume of olive oil. However, group3 received oral yeast (200mg) dissolved in distal water by oral tube along with normal diet for 2 weeks before CCl4 injection. On the 16th day, the rats were humanly killed according to the national guidelines. Blood was collected to measure alanine amino transferase (ALT), aspartate amino transferase (AST) by enzymatic colorimetric method. The livers were weighed and then kept in formalin /saline 10% for histological examination. Exposure to CCl4 significantly (p < 0.05) increase AST to 170±11mg/dl and ALT to 72±6mg/dl as compare to normal group 63±2mg/dl for AST and 21±2mg/dl for ALT. It was noted that yeast significantly reduced the rise in liver enzymes (p < 0.05) to 107±8mg/dl for AST and 35.6±3mg/dl for ALT as compare no-yeast fed CCl4 group . Also, there was an increase in the liver weight in the no-yeast fed CCl4 group (9.7±0.8g) and (7.8±0.1g) for yeast fed CCl4 group as compare to control group (7.25±0.2g). Grossly the liver of the rats were damaged, swollen and yellow in CCl4 group. Microscopically there was perivenular ballooning, hepatocyte fatty degeneration and cell necrosis with many fibrotic septa. All these finding was less evident in yeast fed group. All these data suggest that baker’s yeast could be used as a food supplement to protect against xenobiotic induced hepatotoxicity which possibly due its high nutriotional values.
Extreme Environmental Physiology (University of Portsmouth, UK) (2019) Proc Physiol Soc 44, C48
Oral Communications: Protective Effect of baker’s yeast on Carbon Tetrachloride Induced Hepatotoxicity in rats
A. Alfituri1, I. Busnaina1
1. University of Benghazi, Benghazi, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.