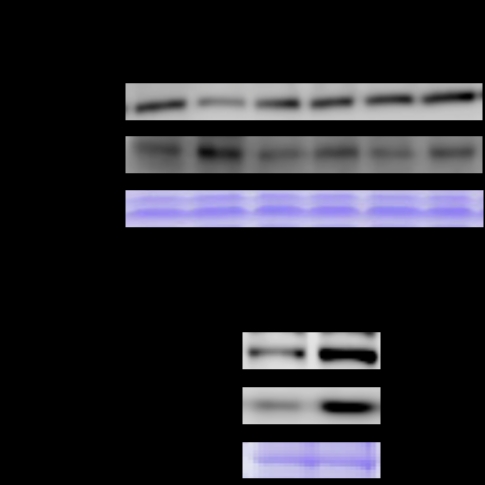
Title Effects of Acute and Chronic High intensity muscle contractions on the expression of irisin and related factors in mice skeletal muscle Riku Tanimura1, Kazuki Uemichi1, Katsuyuki Tokiunoya2,3, Takanaga Shirai1,3, Tohru Takemasa1 1Graduate School of Comprehensive Human Sciences, University of Tsukuba, ,2Graduate School of Human Health Sciences, Tokyo Metropolitan University, 3Japan society for the promotion of science Introduction Irisin is an exercise-induced myokine which regulates adipocyte browning and thermogenesis (Boström et al., 2012). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), which plays a central role in oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle, leads to the processing of irisin from its precursor, fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5) (Reza et al., 2017). It is known that blood irisin concentrations in mice are increased by endurance exercise (Fatouros et al., 2017), but it is unclear what type of exercise is effective for irisin expression in skeletal muscle. The aim of this study was to investigate changes in the expressions of irisin signals in mouse skeletal muscle following acute and chronic high intensity muscle contractions. Methods All experimental procedures performed in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Experiment Committee of the University of Tsukuba (20-407). Male ICR mice aged 7 weeks were used in this study. We conducted electrical stimulation (ES) as a model to induce high intensity muscle contractions (Shirai et al., 2020). Gsatrocnemius muscle was obtained 0, 1, and 3 h after single bout of ES, or 48 h after chronic ES (3 times a week for 4 weeks) (n = 5-6 in each time point). All tissues were rapidly frozen with liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until use. We used Western blotting as the method of analysis for protein expressions in skeletal muscle. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using the SPSS software (IBM Corp., New York, NY, USA) to determine whether a significant interaction exists between two paired factors. Results We found that the expression of irisin was significantly increased by acute and chronic ES (p<0.05). The expression of PGC-1α was significantly increased by chronic ES (p<0.05), but we found no significant difference in acute ES groups compared with that in control (no ES) legs. Conclusion We demonstrated that acute and chronic high intensity muscle contractions increased the expression of irisin in skeletal muscle, but the expression of PGC-1αshowed different results between acute and chronic ES. These results may suggest that acute high intensity muscle contractions augment the expression of irisin through a PGC-1α-independent pathway.
Physiology 2021 (2021) Proc Physiol Soc 48, PC096
Poster Communications: Effects of Acute and Chronic High intensity muscle contractions on irisin and related factor expression in mice skeletal muscle
Riku tanimura1, Kazuki Uemichi1, Katsuyuki Tokinoya2, 3, Takanaga Shirai3, Tohru Takemasa1
1 University of Tsukuba, Ibaraki/Tsukuba, Japan 2 Tokyo Metropolitan University, Ibaraki/Tsukuba, Japan 3 Japan society for the promotion of science, tokyo, Japan
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.