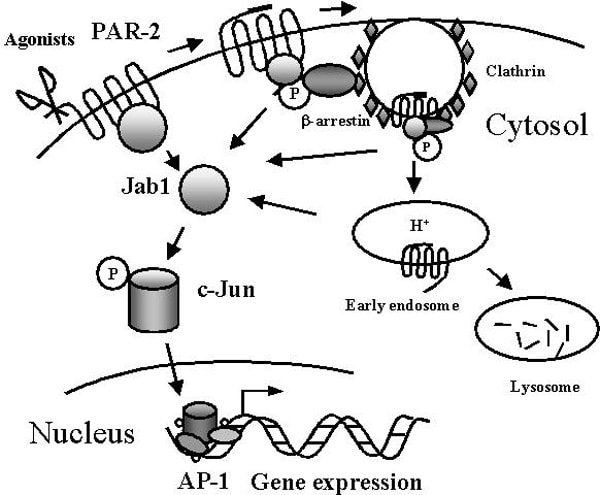
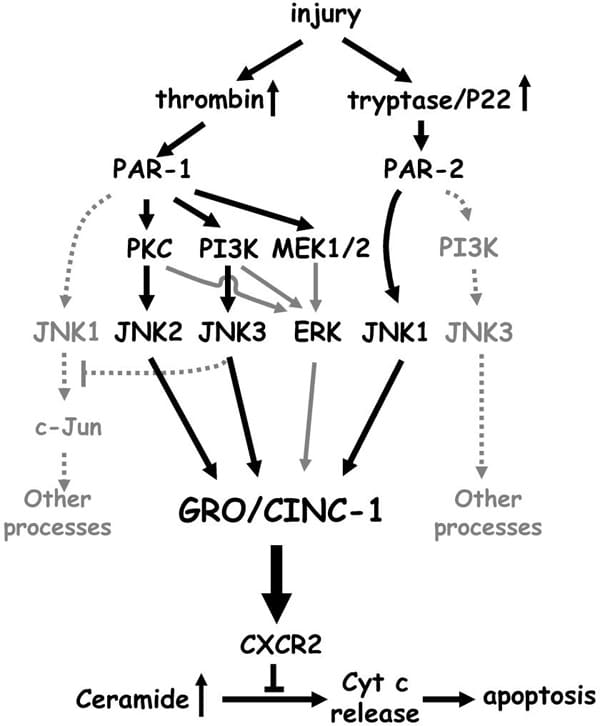
Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2), a receptor for trypsin and tryptase, has important physiological /pathological functions. PAR-2-mediated intracellular signal transductions are hardly known. Here, we identified an interacting partner of human PAR-2, the Jun activation domain-binding protein 1 (Jab1). The interaction was shown by GST pull-down in vitro, and by co-immunoprecipitation assays in vivo. Jab1 was shown to be colocalized with PAR-2 in transfected HEK293 cells and in primary human astrocytes by double immunofluorescence staining. Multiple intracellular domains of PAR-2 are required for the interaction with Jab1. Agonist stimulation of PAR-2 disrupted the interaction, which could be prevented by the inhibitor of receptor endocytosis phenylarsine oxide, but not by the lysosomal protease inhibitor ZPAD. Activation of PAR-2 induced the redistribution of Jab1 from the plasma membrane to the cytosol, but did not influence expression of Jab1. Furthermore, Jab1 mediated PAR-2-induced c-Jun activation, which was followed by increased activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1). Loss-of-function studies, using Jab1 small interfering RNA, demonstrated that Jab1 knockdown blocked PAR-2-induced AP-1 activation. Jab1 is an important effector that mediates a novel signal transduction pathway for PAR-2-dependent gene expression. Activation of PAR-1 and PAR-2 both resulted in release of the chemokine growth-regulated oncogene/cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant-1 (GRO/CINC-1), a functional counterpart of human interleukin-8, from rat astrocytes. PAR-2-induced GRO/CINC-1 release was independent of protein kinase C, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 activation. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) was identified in both signaling pathways to play a pivotal role. By isoform-specific loss-of-function studies using JNK (1-3) small interfering RNA, we found that different JNK isoforms mediated GRO/CINC-1 secretion. JNK2 and JNK3 isoforms were both activated by PAR-1 and essential for chemokine GRO/CINC-1 secretion. PAR-2-induced JNK1 activation, which failed to phosphorylate c-Jun, contributed to GRO/CINC-1 release. JNK-mediated chemokine GRO/CINC-1 release occurred in a JNK isoform-dependent fashion and invoked PAR subtype-specific mechanisms. Activation of PAR-2, as well as PAR-1, rescued astrocytes from ceramide-induced apoptosis via regulating GRO/CINC-1 release. PAR-1 and PAR-2 have overlapping functions, but can activate separate pathways under certain pathological conditions, to rescue neural cells from cell death. This provides functional insights into PAR-JNK signaling and the protective actions of PARs in brain.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, C67
Research Symposium: A protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2)-interacting protein, Jab1, is involved in PAR-2-induced activation of AP-1, and PAR-2-induced release of chemokine GRO/CINC-1 from rat astrocytes via differential JNK activation protects brain tissue
W. Luo1, Y. Wang1, G. Reiser1
1. Institut für Neurobiochemie, Otto-von-Guericke Universität Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany.
View other abstracts by:
Model for Jab1-mediated signaling pathway for PAR-2.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.