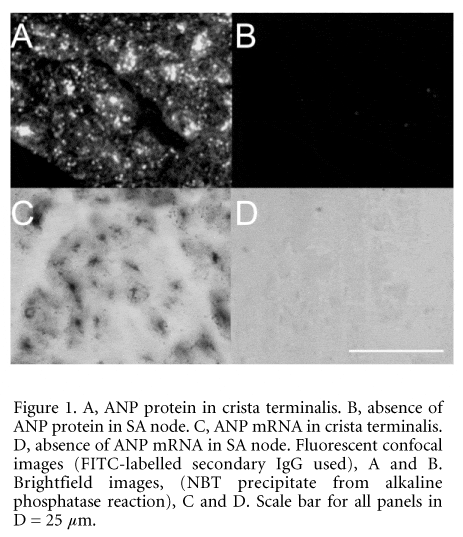
Atrial natriuteic peptide (ANP) is produced mainly by the cardiac atria and has been shown to be involved in sodium and volume homeostasis (de Zeeuw et al. 1992). The aim of the study was to determine whether ANP is expressed in the sinoatrial (SA) node, the pacemaker of the heart, of the rabbit. Rabbits were killed humanely (UK Home Office Schedule 1 method) and the SA node was isolated. Ten micrometre serial sections through the SA node (approximately at the level of the leading pacemaker site) and surrounding atrial muscle of the crista terminalis were cut. Adjacent SA node sections were examined for ANP protein and mRNA. ANP protein was detected using immuno-histochemistry, with a suitable anti-ANP monoclonal IgG (1:100, Biogenesis Ltd, Poole, UK). This showed ANP protein to be present throughout the surrounding atrial muscle, but absent in the SA node (Fig. 1A and B). Similar results were seen in sections from three rabbits. ANP mRNA was localised using in situ hybridisation (ISH). Antisense and sense digoxigenin-labelled riboprobes (385 nt) were designed specifically for rabbit ANP mRNA. Signal for ANP mRNA was obtained throughout the atrial muscle using the antisense riboprobe (Fig. 1C). The specificity of the signal was confirmed by the lack of binding of sense riboprobe. With the antisense riboprobe, the ANP mRNA signal was absent from the SA node (Fig. 1D).
Similar results were seen in sections from two rabbits. When the negative regions for ANP protein and mRNA were compared on adjacent sections, they were shown to occupy the same area. High magnification imaging of the ISH staining showed ANP mRNA to be localised in the perinuclear region (presumably in the rough endoplasmic reticulum; Fig. 1C), while immunolabelling showed ANP protein to be present in granules within the cell (Fig. 1A).
It is concluded that (i) ANP is not expressed in the rabbit SA node, (ii) in the SA node expression of ANP is regulated at the level of transcription, and (iii) ANP can be used as a negative marker for rabbit SA node at the level of both mRNA and protein.
This work was supported by the British Heart Foundation and the Medical Research Council.
All procedures accord with current UK legislation.