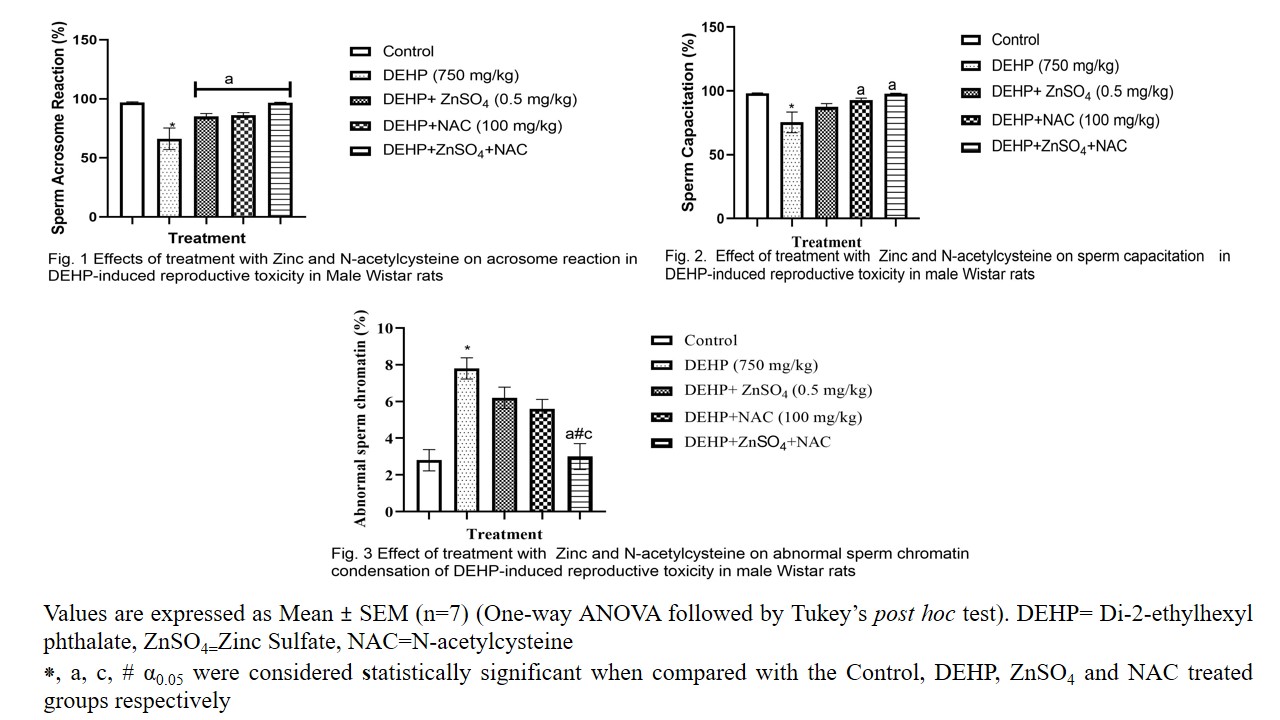
Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), as a low molecular weight phthalate has been used as a plasticizer in many products, especially medical devices, food packaging, cosmetics, and personal care products (Sai and Jiaxiang, 2018). Unfortunately, Consistent experimental evidence shows that some phthalates are developmental and reproductive toxicants in animals. Therefore, reduction of these side effects is necessary. The present study was aimed to explore the ameliorative effect of combined treatment with zinc sulfate (ZnSO4) and n-acetylcysteine (NAC) on sperm acrosome reaction, capacitaion and chromatin integrity in DEHP-induced reprotoxicity in male wistar rats. The study included thirty five (35) Male Wistar rats randomly assigned into five groups (n=7). Group A served as untreated control, group B served as treated control and received Phthalate (750 mg/kgbw) only for 21 days, group C received phthalate (750 mg/kgbw) + 0.5mg of Zinc per kgbw for 21 days, group D received phthalate (750 mg/kgbw) + 100mg of N-acetylcysteine per kg bw for 21 days and group E received Phthalate (750 mg/kg/day) + N-acetylcysteine (100mg/kgbw) + Zinc (0.5mg/kgbw) for 21 days. At the end of the experimental period, the animals were fasted overnight and sacrificed by cervical dislocation followed by laparotomy. The epididymis were carefully dissected out and sperm sample was collected by perfusing the caudal epididymis of the rats through the distal end of the vas deferens into a pre-warmed modified sperm capacitation medium (SCM) as modified from the method of Morakinyo et al., (2011) for sperm capacitation; and acrosome reaction evaluation was done using Coomassie brilliant blue staining technique (Feng et al., 2007) while sperm chromatin integrity was evaluated by toluidine blue method as explained by Talebi et al., 2013. Data were analysed using ANOVA and differences in mean values were considered significant at p<0.05. The result showed that DEHP significantly decrease the percentage acrosome intact reacted sperm after incubation in sperm capacitation medium when compared to control groups (Fig.1). This was ameliorated in ZnSO4, NAC and Zn+NAC treated groups. Sperm capacitation was also significantly reduced in DEHP treated group but this was significantly ameliorated in NAC and Zn+NAC treated groups when compared with the DEHP treated group respectively (Fig.2). Numbers of abnormal sperm chromatin was seen to be high in DEHP treated group which was also significantly reduced in Zn+NAC treated groups when compared with the DEHP, Zn and NAC treated groups respectively (Fig.3). It was therefore concluded that combination of zinc sulfate and n-acetylcysteine has the capacity to ameliorate the reprotoxic effects DEHP on the examined parameters. Keywords: Phthalate, DEHP, Sperm capacitation, Acrosome reaction, Sperm chromatin integrity
Future Physiology 2020 (Virutal) (2020) Proc Physiol Soc 46, PC0088
Poster Communications: AMELIORATIVE EFFECT OF COMBINED TREATMENT WITH ZINC SULFATE AND N-ACETYLCYSTEINE ON SPERM ACROSOME REACTION, CAPACITAION AND CHROMATIN INTEGRITY IN DEHP-INDUCED REPROTOXICITY IN MALE WISTAR RATS
Victor EMOJEVWE1, Alexander Obidike NAIHO 2, Eze Kingsley NWANGWA2, Mega Obukohwo OYOVWI3
1 Department of Physiology, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria 2 Department of Physiology, Delta State University, Abraka, Nigeria 3 Department of Basic Medical Sciences (Physiology Unit), Achiever University, Owo, Nigeria
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.