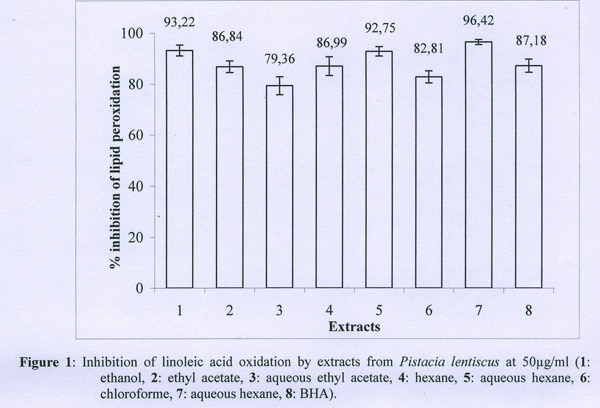
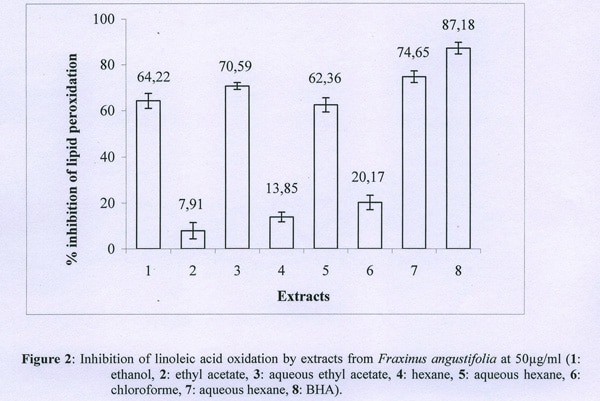
Xanthine oxidase (XO)-inhibitory activity and total antioxidant capacity of extracts from two local medicinal plants, the leaves of Pistacia lentiscus used to treat gastro-intestinal inflammations and the bark of Fraxinus angustifolia used to treat arthritis and gout have been evaluated by various spectrophotometric methods. These include xanthine/XO test, inhibition of linoleic acid oxidation using the ferro-thiocyanate method and the capacity of the extracts to trap the radical 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Our results indicate that aqueous extracts (100 µg/ml) of Pistacia lentiscus and those of Fraxinus angustifolia showed a mixed type inhibition of 70% and 60%, respectively on XO activity. At a concentration of 50 µg/ml, extracts of Pistacia lentiscus inhibited linoleic acid oxidation by up to 97% whereas those of Fraxinus angustifolia showed an inhibition of only 75%, much less than the antioxidant of reference, butylhydroxyanisol (BHA) (87%). With the exception of the chloroform extract of Pistacia lentiscus, all the extracts showed high DPPH radical scavenging activity (90%), whereas Fraxinus angustifolia extracts presented an important activity which, however, remains lower than that of Pistacia lentiscus extracts. Pistacia lentiscus aqueous phases exhibited H2O2 scavenging activity of about 74% while that of Fraxinus angustifolia extracts is around 50%. Antioxidant capacity and scavenging activity against DPPH radical of Pistacia lentiscus are dose-dependant and more significant than many tested standards, including α-tocopherol. Column chromatography using silica gel allowed the isolation of the fractions responsible on inhibition of XO activity and linoleic acid oxidation. A positive correlation between various activities and the contents of total phenols was established for Pistacia lentiscus extracts.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC131
Poster Communications: Anti-xanthine oxidase, antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of selected Algerian plants used in the treatment of inflammatory-related disorders
D. B. Atmani1, D. M. Kilani1
1. Biology, University of Bejaia, Bejaia, Bejaia, Algeria.
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.