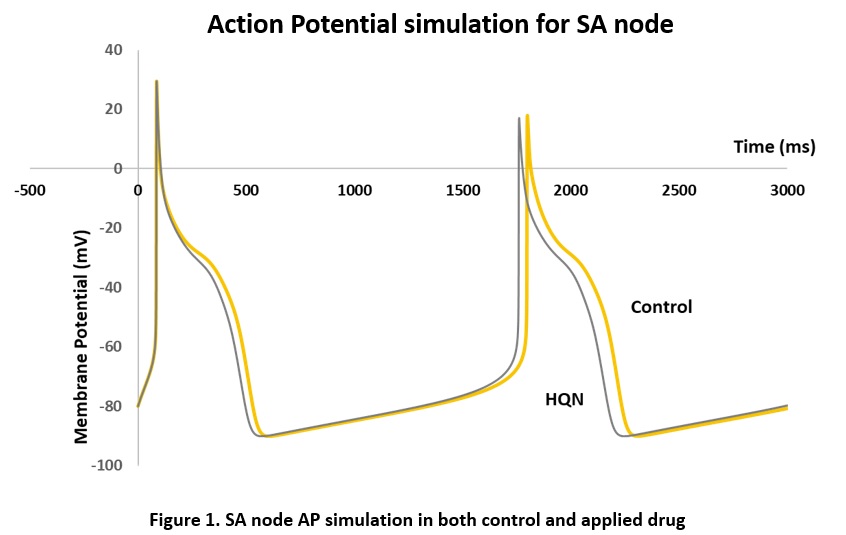
Objectives: The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2/2019-nCoV) poses a serious threat to global public health and local economies. With the heightened interest in the potential use of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) to treat patients with SARS-CoV2, it may be prudent to reflect on the risks of therapy, particularly their cardiac toxicity. This quantitative study investigates the propensity of HCQ in relation to cardiac safety. Methods: The sinoatrial node (SAN) cell is presented as an equivalent electrical circuit comprising nine ion channels. All ionic currents are described by the ordinary differential equations [2 and 3]. The SAN action potential (AP) and respective ionic currents are constructed in silico. A HCQ drug model for the hyperpolarizing-activated current or funny current (if) is simulated after mining data from the experimental studies [1]. Results: The resting membrane potential is set at ─80mV. The HCQ blocked if with IC50 concentration. The steady-state value of the activation parameter of the if is shifted to the positive side after applying HQN of 1 µM. The action potential (AP) timing (shown in Figure 1) is altered when we incorporated the biophysically modified if after the application of HCQ. The results show that the modified if plays an important role in reducing the frequency of the spontaneous AP at the SA node. Conclusions: We simulated the effects of HCQ drug upon funny current and action potential. Our quantitative investigation identifies hydroxychloroquine, a well-established drug used against COVID-19 reduces the frequency rate of the spontaneous action potential firing by inhibiting the funny current. Therefore, we should prevent it as a potential drug for COVID-19.
Physiology 2021 (2021) Proc Physiol Soc 48, PC048
Poster Communications: Computational study of SARS-CoV-2 infection inhibitor Hydroxychloroquine on Cardiac toxicity
Chitaranjan Mahapatra1
1 University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, The United States of America
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.