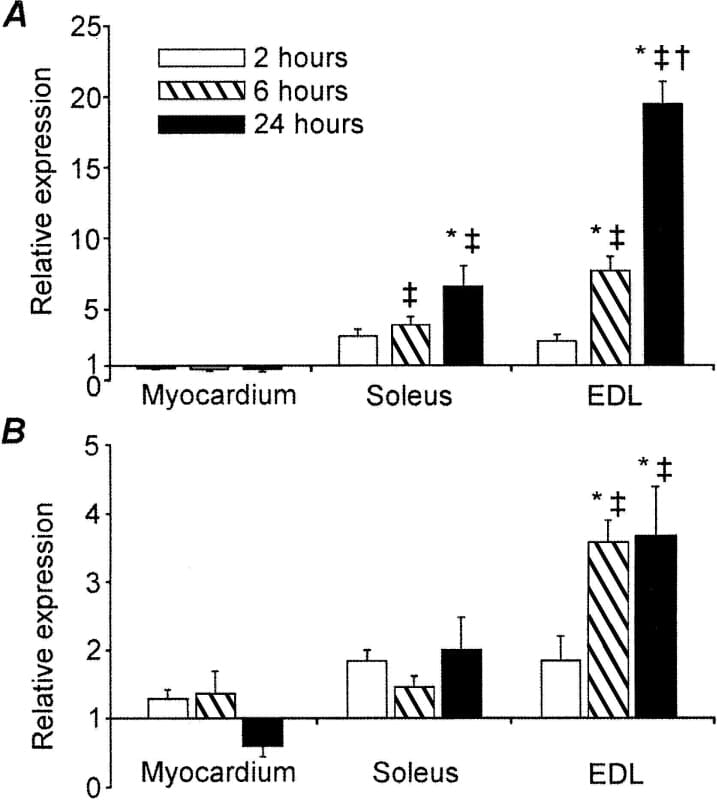
Sepsis induces skeletal muscle atrophy as a consequence of the suppression of muscle protein synthesis and stimulation of protein degradation, with proteins predominantly degraded via the ubiquitin-proteasome system (Hasselgren, 1999). Two muscle-specific ubiquitin ligases, namely, MuRF1 and MAFbx, responsible for the targeting of proteins for proteolysis, have recently been described, and their mRNA levels in fast-twitch muscle shown to increase during atrophy (Bodine et al., 2001). Here, we examined the effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) infusion on MAFbx and MuRF1 mRNA expression in myocardium, and muscles of a slow- and fast-twitch phenotype. Conscious male Sprague-Dawley rats (previously implanted with jugular venous catheters under general anaesthesia (fentanyl and medetomidine, 300 μg kg-1 each i.p.)), were divided into 6 groups and infused with either saline (0.4 ml h-1) for 2h (n=8), 6h (n=7) or 24h (n=8), or LPS dissolved in saline to induce sepsis (E. coli serotype 0127:B8, 150 μg kg-1 h-1) for 2h (n=8), 6h (n=8) or 24h (n=6). At each time point, the myocardium, slow-twitch soleus and fast-twitch extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscles were freeze clamped in situ under terminal anaesthesia (sodium pentobarbital, i.v.) and stored at -80°C. All animal procedures complied with Home Office regulations. Total RNA was extracted from muscle samples and expression of MuRF1 and MAFbx determined by real-time PCR. The results are presented in Figure 1. There was upregulation of MAFbx and MuRF1 mRNA in skeletal muscle within 6 hours after onset of LPS infusion. Interestingly, the increase in MAFbx was restricted to the EDL, while expression of MuRF1 showed a time-dependent increase in soleus and EDL. LPS had no effect on MAFbx or MuRF1 expression in myocardium (Figure 1). These findings are in agreement with evidence implicating a central role for MuRF1 and MAFbx in skeletal muscle atrophy of various catabolic conditions (Lecker et al. 2004).
King's College London (2005) J Physiol 565P, C98
Communications: Effect of lipopolysaccharide infusion on mRNA expression of two, muscle-specific, ubiquitin ligases in myocardium, soleus and extensor digitorum longus of the rat
Murton, A J; Alamdari, N ; Constantin-Teodosiu, D ; Gardiner, S M; Bennett, T ; Layfield, R ; Greenhaff, P L;
1. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1. Fold changes in A) MuRF1 and B) MAFbx mRNA expression from corresponding control value in myocardium soleus and EDL muscles in response to LPS. Values represent mean ± S.E. ‡ Indicates different from corresponding control (P<0.05 MANOVA); * different from 2 hour LPS-treated muscle (P<0.05 MANOVA LSD post-hoc); †different from 6 hour LPS-treated muscle (P<0.05 MANOVA LSD post-hoc).
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.