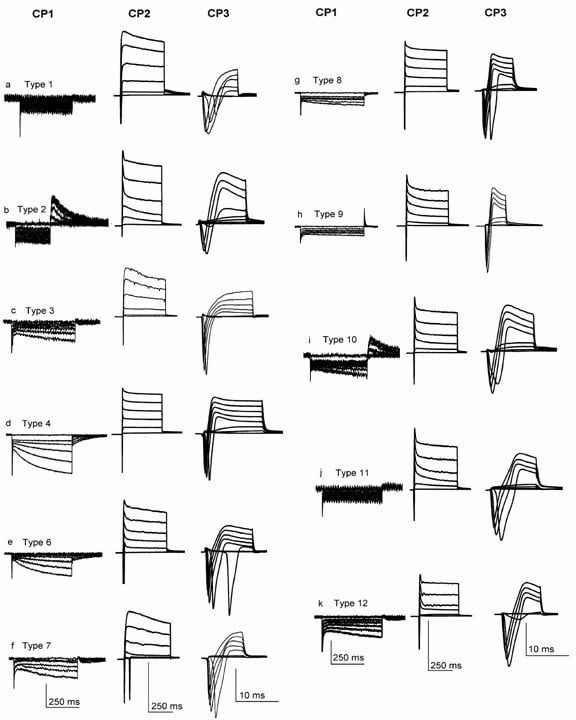
Here we present the classification and algesic profile of newborn Wistar rat neurons from acute and organotypic dorsal root ganglia (DRG) slices, using previously defined electrophysiology protocols (1), with slight changes. Newborn rats (3-5 days) were anaesthetized on ice, decapitated and dissected in ice-cold bicarbonate Ringer. Both acute and cultured DRG slice protocols were described in our previous study (2). Whole cell recordings were performed during the same day for acute DRG slices and during the second day for cultured DRG slices. 114 acute DRG slice neurons and 111 organotypic DRG slice neurons were recorded and classified into 11 and 12 different types, respectively. Cell types 3, 5, and 7 were absent in acute DRG slices while cell types 2 and 9 were present only in acute DRG slices, and three other cell types (10, 11 and 12) were added to the classification (1). Concerning the algesic profile, we noticed increased capsaicin-activated currents (pA/pF) in culture vs. acute slices for type cells 1 (58.59 ± 4.06 vs. 30.36 ± 2.51) and 6 (29.21 ± 1.68 vs. 14.88 ± 2.69) and decreased for type cell 11 (38.51 ± 3.57 vs. 15.92 ± 0.56). Acid-activated transient currents (pA/pF) in organotypic slice neurons decreased for all type cells (type 4: 17.72 ± 2.74 vs. 7.54 ± 1.65, type 6: 64.12 ± 4.43 vs. 22.01 ± 0.83, type 8: 37.18 ± 6.41 vs. 2.48 ± 0.07 and type 11: 60.39 ± 6.51 vs. 4.01 ± 0.27), excepting type cell 1 where was observed an increase (3.8 ± 0.41 vs. 15.84 ± 1.22). ATP-evoked density currents remained unchanged in both acute and culture slices. In conclusion, data presented within the current report show differences in phenotype and excitability of cultured versus acute DRG slice neurons from newborn rat. Moreover, acute DRG slices offer an in vitro model closer to in vivo conditions, neurons in slices remaining in contact with other neurons and glial cells, like in ganglia of living animals.
University of Cambridge (2008) Proc Physiol Soc 11, PC71
Poster Communications: Electrophysiology of newborn rat primary sensory neurons in acute and organotypic dorsal root ganglia slices
P. Nicoleta1, A. Bogdan1, F. Maria Luisa1
1. Animal Physiology and Biophysics, University of Bucharest, Faculty of Biology, Bucharest, Romania.
View other abstracts by:
Current signatures of neurons in newborn rat acute and organotypic DRG slices. Using very small (<22 µm) small (24-32 µm) and medium (32-45 µm) DRG neurons from acute and organotypic slices twelve different types were identified. CP1 and CP2 protocols were sufficient to distinguish types 1 2 4 6 and 10. CP3 was used to distinguish between types 3 and 7 9 and 11 8 and 12. Vertical scale bars: for CP1: 250 pA (a) 150 pA (b) 150 pA (c) 500 pA (d) 100 pA (f) 200 pA(g) 150 pA (h) 250 pA (i) 100 pA (j) 100 pA (k) 300 pA (l); for CP2: 4000 pA (a) 6000 pA (b) 2500 pA (c) 4500 pA (d) 3000 pA (f) 4000 pA (g) 4000 pA (h) 5000 pA (i) 6000 pA (j) 7000 pA (k) 5000 pA (l); for CP3: 8000 pA (a) 6000 pA (b) 4000 pA (c) 4000 pA (d) 5000 pA (f) 7500 pA (g) 5000 pA (h) 5000 pA (i) 3000 pA (j) 4000 pA (k) 6000 pA (l).
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.