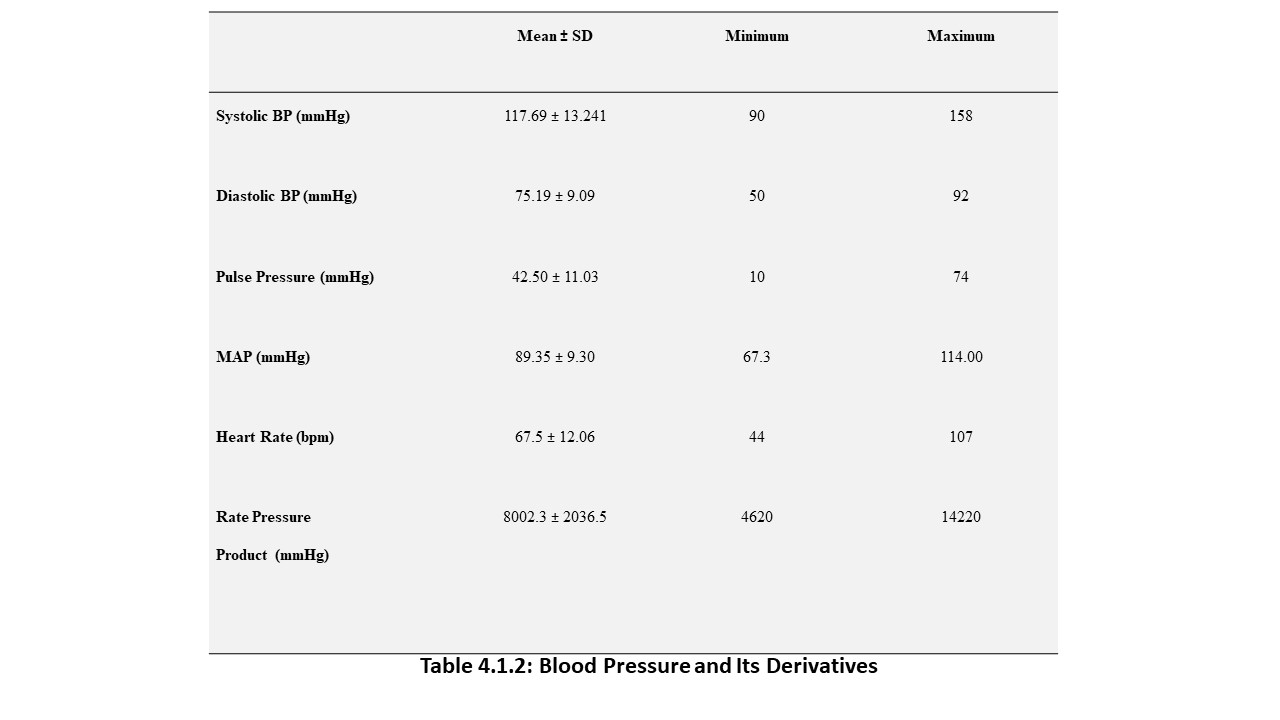
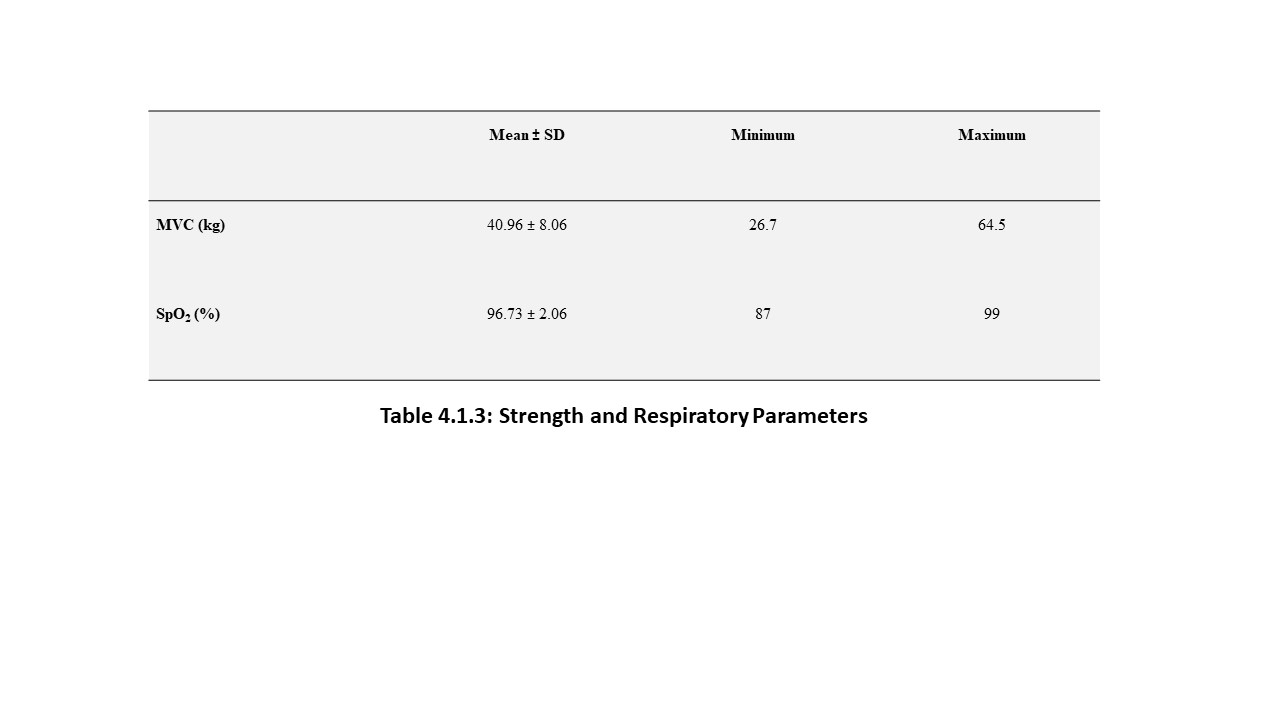
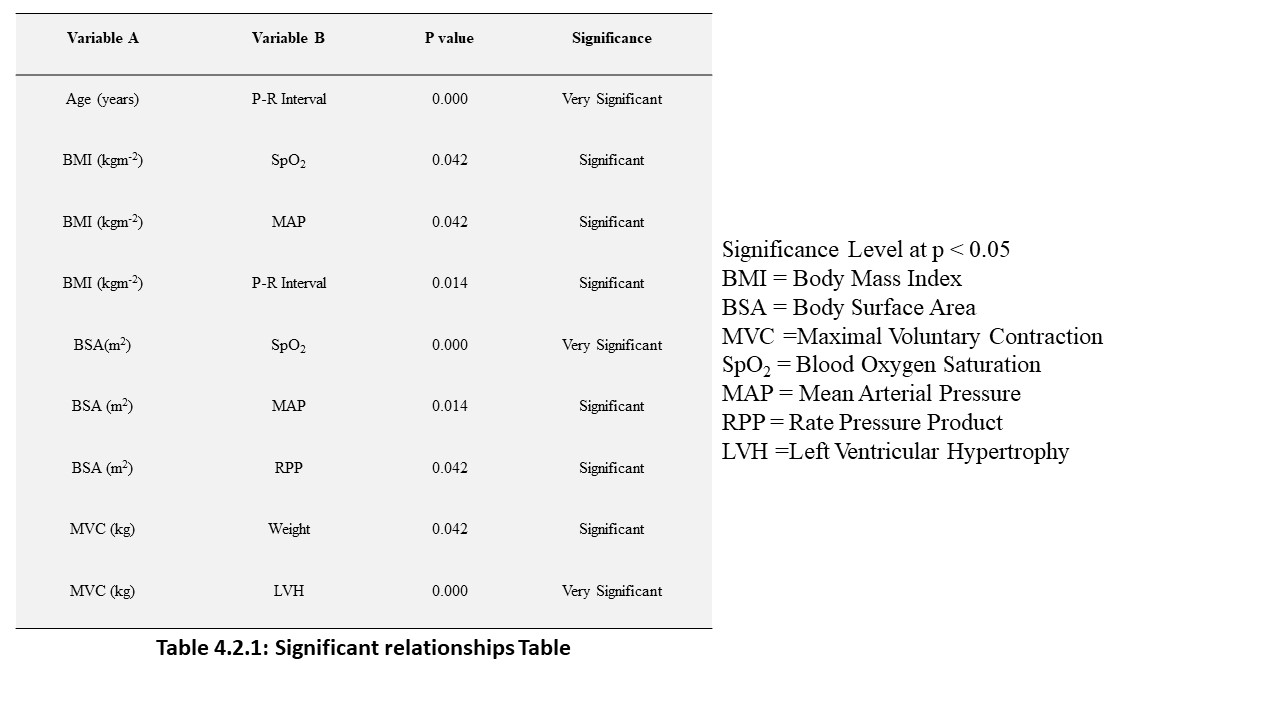
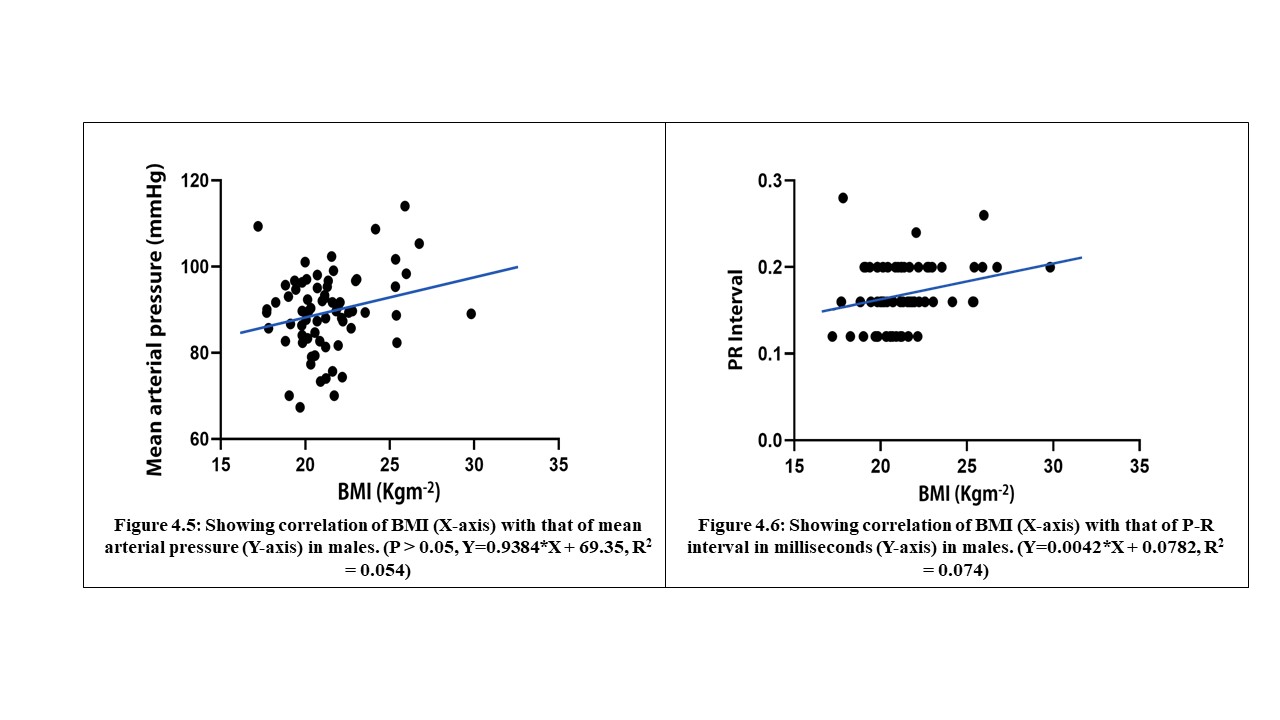
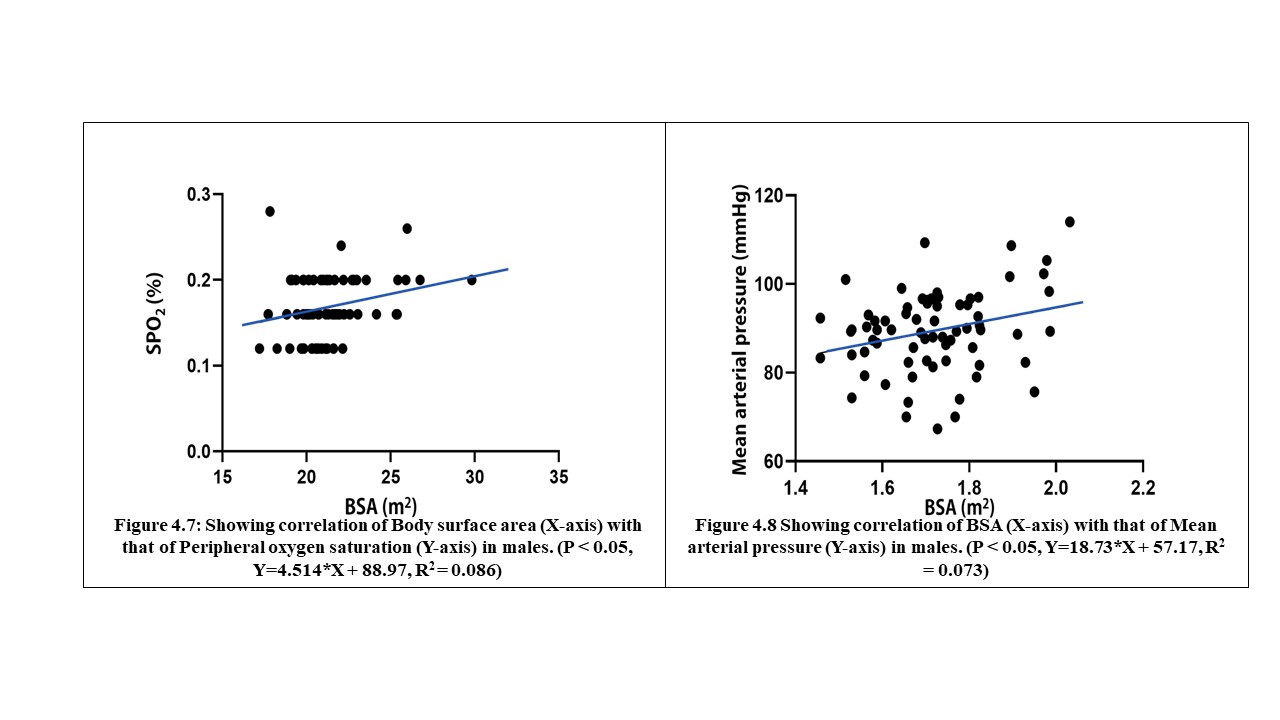
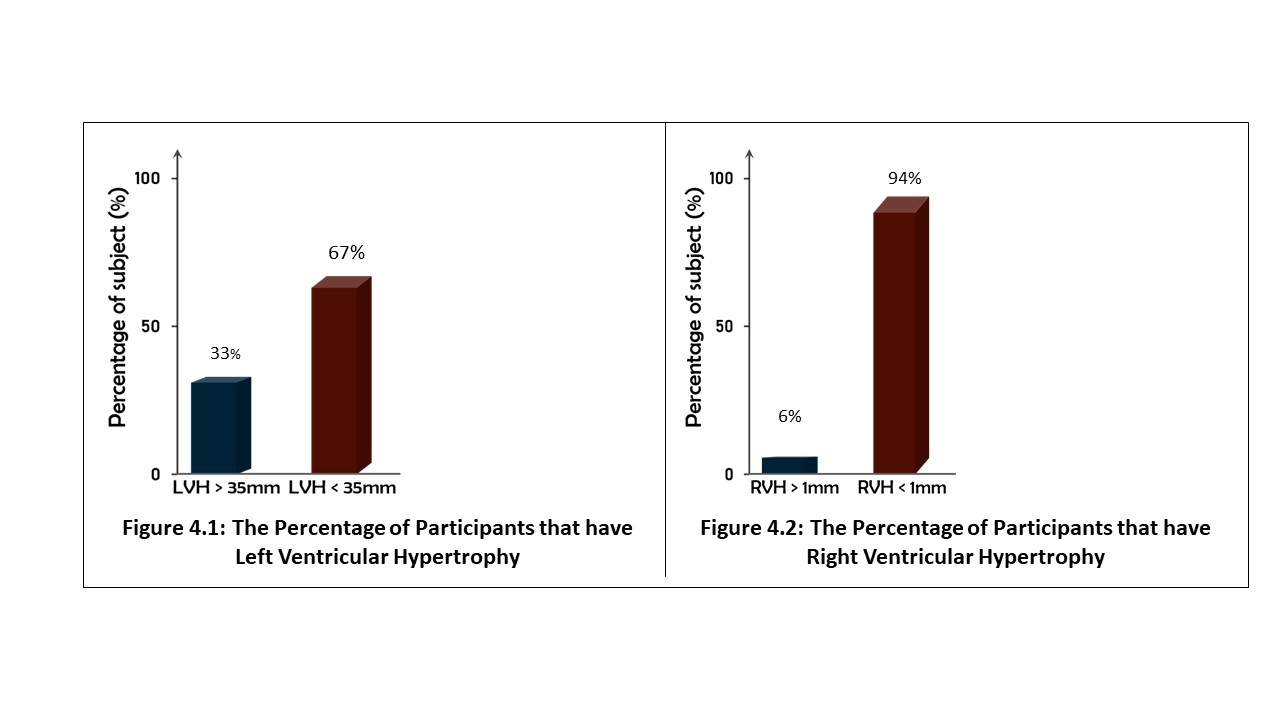
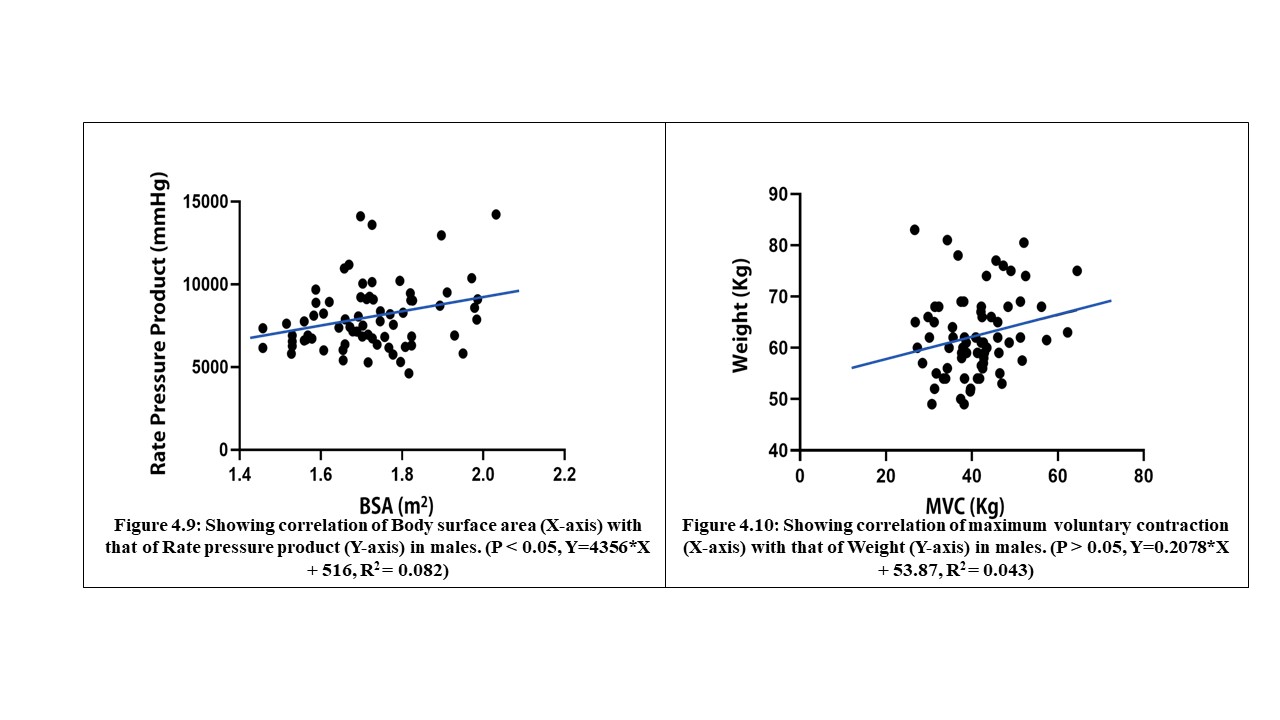
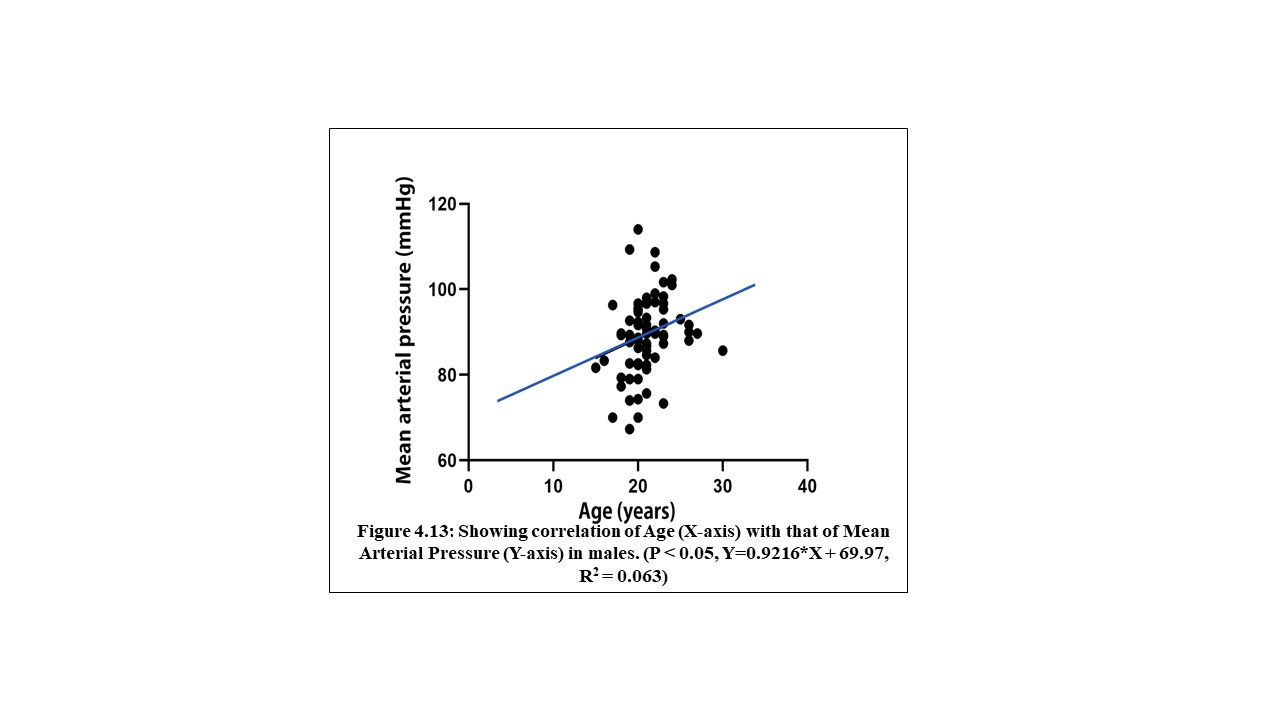
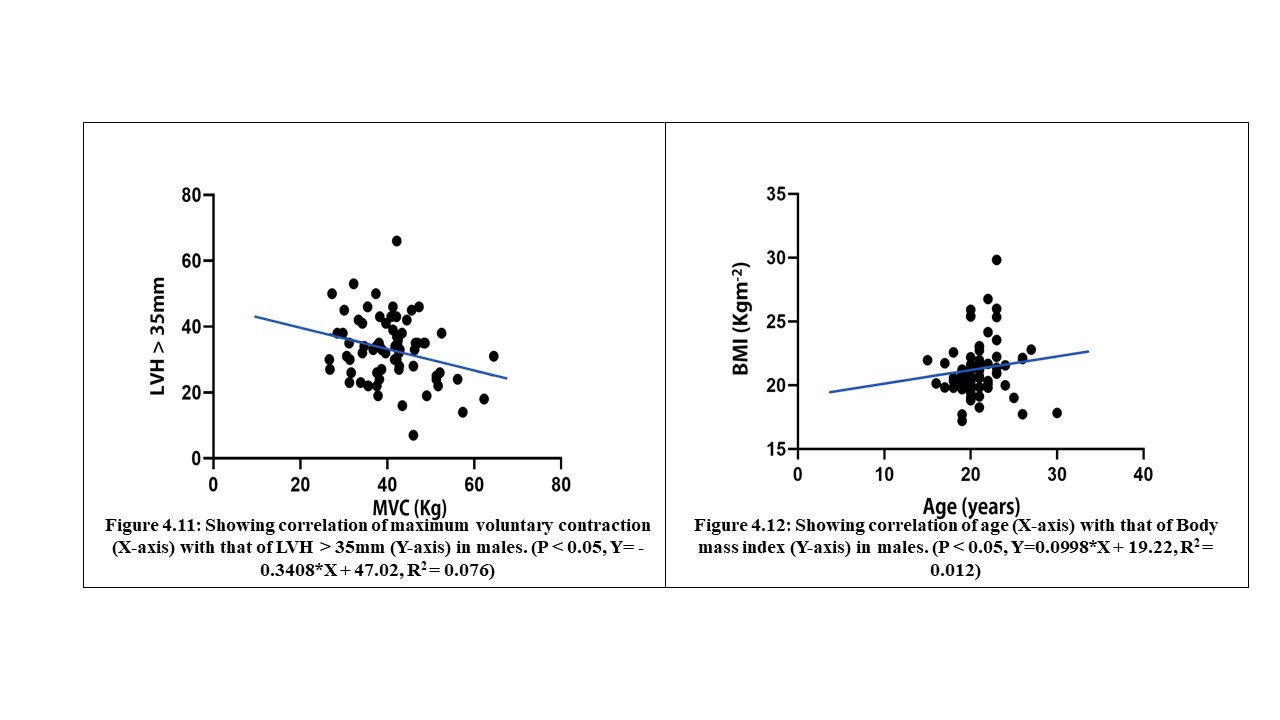
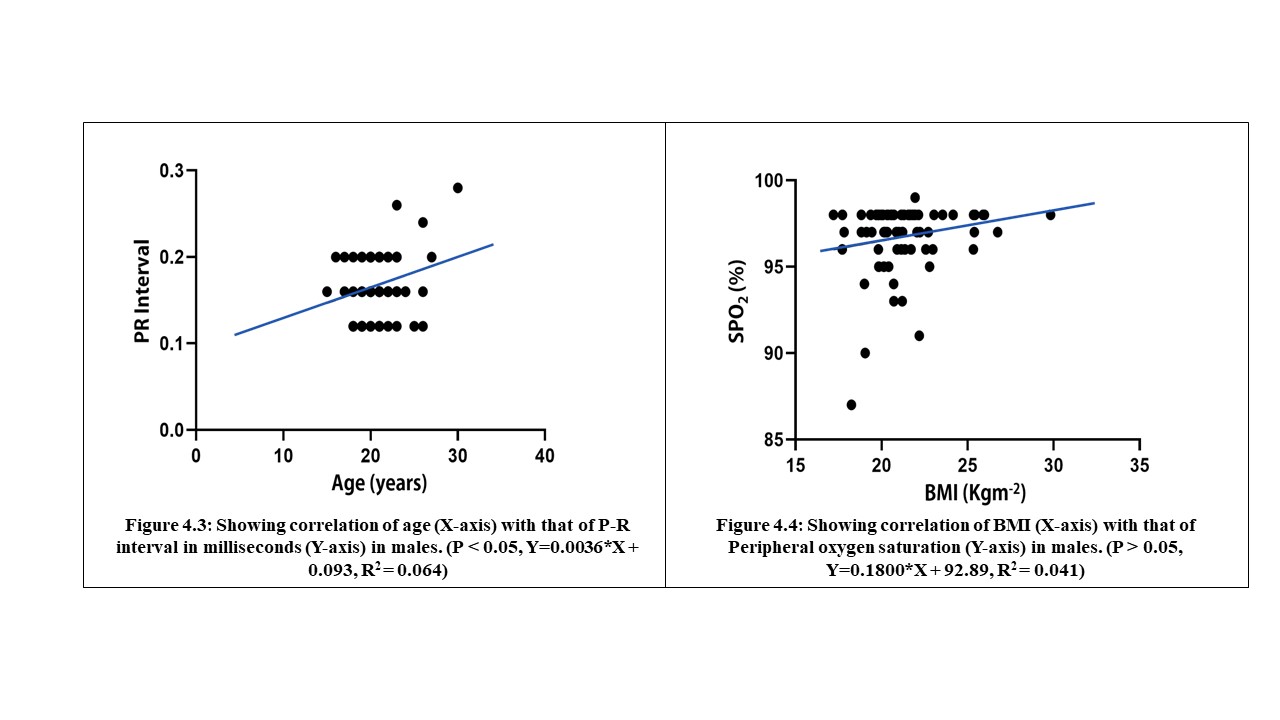
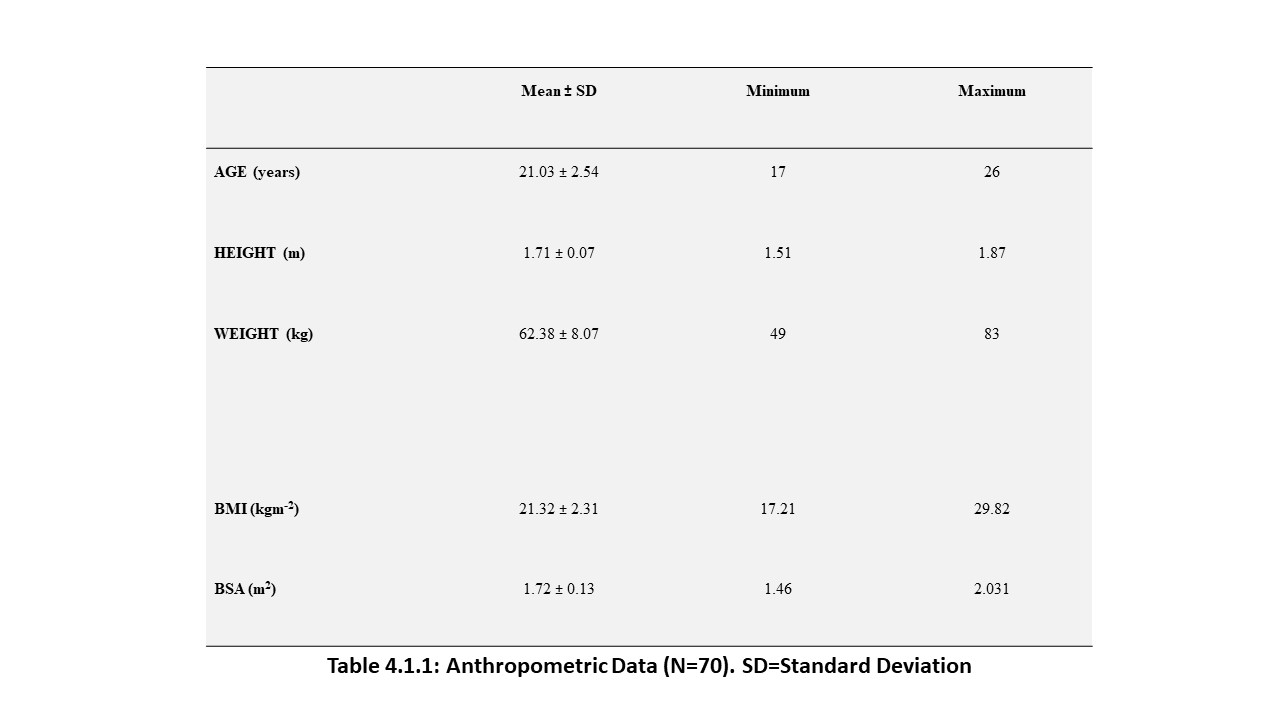
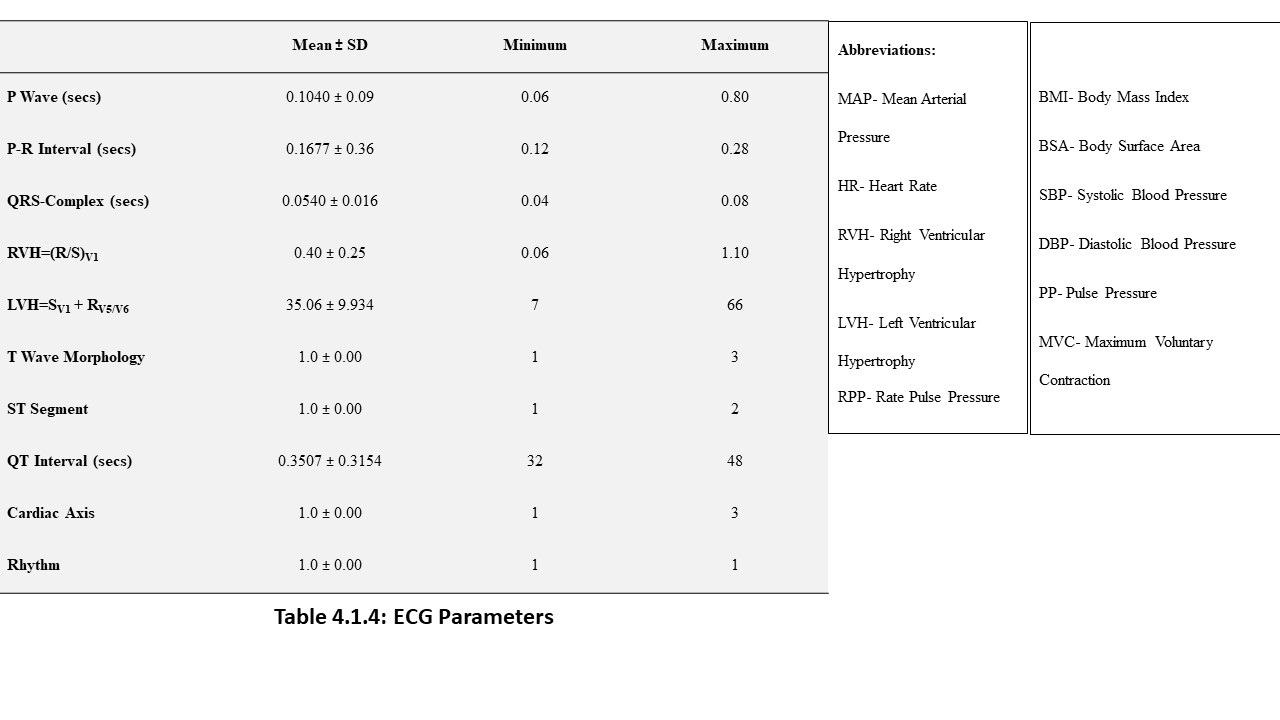
70 young adults were assessed in FUTA south-gate community, Nigeria, to evaluate the relationship between some cardiovascular, anthropometric and strength variables. These participants were apparently healthy and were assessed by evaluating their electrocardiographic parameters, body mass index, body surface area and maximum voluntary contraction (MVC). The results analysed by descriptive and inferential statistics showed that despite the narrow age range of 15 to 30 years, the age of the subjects had significant relationship with the PR-intervals (p<0.05). Also, the BMI had correlation with the SpO2 values, mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) as well as their PR-intervals. Furthermore, the BSA had significant influence on the SpO2 values, MAP and the Rate Pressure Product (RPP) of the subjects. Moreover, the MVC also correlated with weight and may predict left ventricular hypertrophy in young adults. These results advocate that adequate knowledge of differences between people will enhance the methods and strategies of treating associated disorders.
Future Physiology 2020 (Virutal) (2020) Proc Physiol Soc 46, PC0111
Poster Communications: EVALUATION OF CARDIOVASCULAR, ANTHROPOMETRIC AND STRENGTH VARIABLES' RELATIONSHIP IN APPARENTLY HEALTHY MALE SUBJECTS IN FUTA SOUTH-GATE COMMUNITY
Success Ajayi1, Olusoji Adalumo1
1 Department of Physiology, School, of Health and Health Technology, Federal University of Technology, Akure, Nigeria
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.