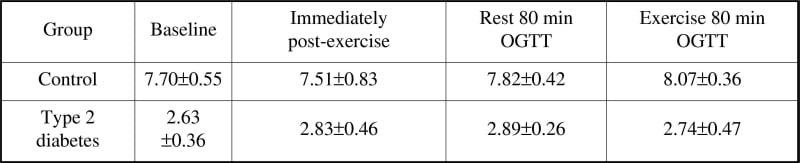
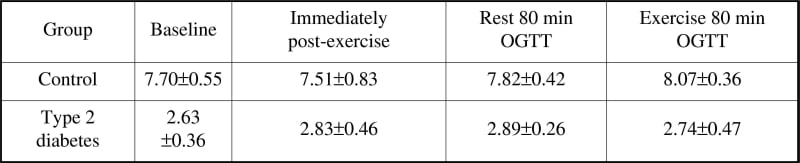
Adiponectin is a protein exclusively secreted by adipocytes (Scherer et al. 1995). Circulating adiponectin concentrations are inversely related to obesity and Type 2 diabetes (Weyer et al. 2001) and a regulatory role in glucose metabolism has been suggested (Tsao et al. 2002). Plasma adiponectin concentrations increase ~4 fold, reaching a peak at ~60 minutes postprandially in obese individuals, yet do not change in lean healthy individuals (English et al. 2003) or during exercise (Ferguson et al. 2004). The aim of this study was to measure the effects of a glucose meal or exercise on adiponectin levels on Type 2 diabetic subjects. Six (5 male) obese dietary controlled type 2 diabetic individuals (age, 57.8±3.9yr, BMI, 31.9±1.4kg/m2, HbA1c, 8.4±0.7%, mean±SD) and six (male) age matched lean, non-diabetic controls (age 52.1±3.6yr, BMI 24.8±0.7kg/m2, HbA1c 4.5±0.6%) were recruited for this study. Approval was granted by the East Sussex Local Research Ethics Committee. Each subject was given a 75g Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) at rest and following one hour of exercise (~50% VO2max) on separate occasions. Whole blood samples were immediately analysed for glucose concentrations via the glucose oxidase reaction and plasma analysed for adiponectin and insulin using the ELISA method. A repeated measures ANOVA was used to determine statistical differences between groups and across time. Adiponectin concentrations were lower in the Type 2 diabetes group when compared with the control group (P=0.042) and fasting adiponectin concentrations were inversely (r=-0.54) related to insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR = fasting glucose (mmol/l) x fasting insulin (μU/ml)/22.5), both group data combined. Exercise (P=0.371) or glucose ingestion (P=0.898) had no effect on fasting plasma adiponectin concentrations in either group (Table 1). Adiponectin concentrations do not seem to be affected acutely by exercise or a glucose meal in Type 2 diabetic or non-diabetic individuals.
King's College London (2005) J Physiol 565P, PC30
Communications: Exercise and Glucose Ingestion does not influence Adiponectin concentrations in Type 2 Diabetes
Macdonald, Adam L; Andrew, Philp ; Moira, Harrison ; Bone, Adrian J; Watt, Peter W;
1. School of Pharmacy and Biomolecular Sciences, University of Brighton, Brighton, East Sussex, United Kingdom. 2. Chelsea School , University of Brighton, Brighton, East Sussex, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1: Adiponectin concentrations (μ g/ml) at baseline immediately post exercise and 80 min post glucose ingestion at rest and following exercise
Table 1: Adiponectin concentrations (μ g/ml) at baseline immediately post exercise and 80 min post glucose ingestion at rest and following exercise
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.