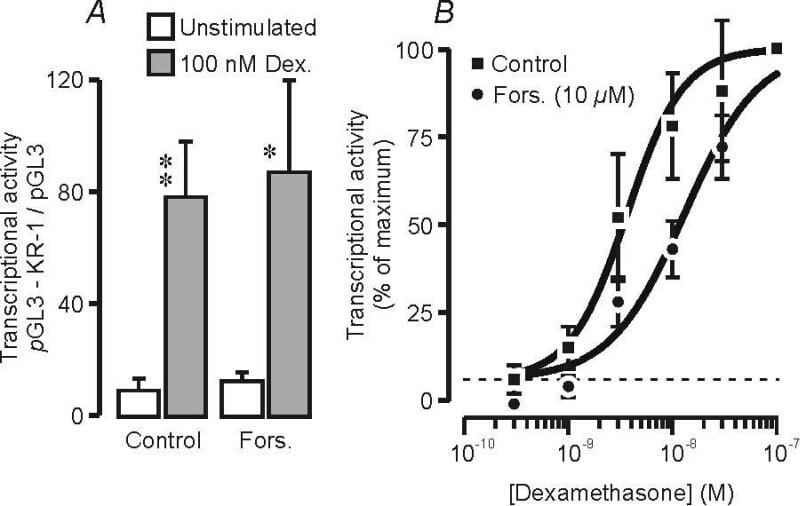
Glucocorticoids activate the promoter region of the epithelial Na+ channel α subunit (α-ENaC) gene (e.g. Sayegh et al., 1999; Richard et al., 2004) and, in the lung, this response may be important to the development of the Na+ absorbing phenotype that normally becomes apparent at the time of birth. This transcriptional response is mediated by glucocorticoid response elements in the upstream region of the α-ENaC gene and, although this gene region also contains putative cAMP response elements, signalling via the cAMP / PKA-dependent pathway does not seem to evoke transcription (e.g. Sayegh et al., 1999). However, the possibility that signalling via cAMP / PKA may modify the transcriptional response to glucocorticoids has not been explored and so the present study explores the effects of forskolin, an alkaloid that evokes cAMP formation, upon the glucocorticoid-induced activation of a reporter construct (KR-1-pGL3) containing the 2.2 kb upstream region of the human α-ENaC gene (Sayegh et al., 1999; Richard et al., 2004). Initial studies confirmed that forskolin does not induce transcription or modify the response to a maximally effective concentration of dexamethasone (Fig 1A). However, experiments that explored the effects of a range of dexamethasone concentrations (Fig 1B) showed that forskolin shifted the concentration – effect curve for dexamethasone to the right (control EC50: 3.6 ± 0.5 nM; forskolin EC50: 13.0 ± 2.5 nM, P < 0.001, Student's t test). This suggests strongly that signalling via cAMP / PKA may desensitise the α-ENaC promoter to dexamethasone.
King's College London (2005) J Physiol 565P, PC45
Communications: Forskolin desensitises the human α-ENaC gene promoter to dexamethasone
Ramminger, Sarah J; Forsyth, Laura ; Richard, Kerry ; Burchell, Ann ; Olver, Richard E; Wilson, Stuart M;
1. Lung Membrane Transport Group, Division of Maternal and Child Health Sciences,, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, University of Dundee, Dundee, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Fig. 1. H441 cells were transfected with the KR-1-pGL3 construct or the empty pGL3 vector and h) before transcriptional activity was assayed (Richard et al. 2004). (A) A strictly paired experimental design (n = 5) was used to explore the effects of forskolin (10 µM) upon transcriptional activity (mean ± s.e.m) in unstimulated cells and cells exposed to a maximally effective concentration of dexamethasone (100 nM); asterixis denote significant responses to dexamethasone (Student’s paired t test * P <0.05; ** P < 0.02). (B) Concentration-response curves showing the dexamethasone induced activation of KR-1-pGL3 in control and forskolin-treated (10 µM) cells (n = 5). The sigmoid curves were fitted to the experimental data by least squares regression.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.