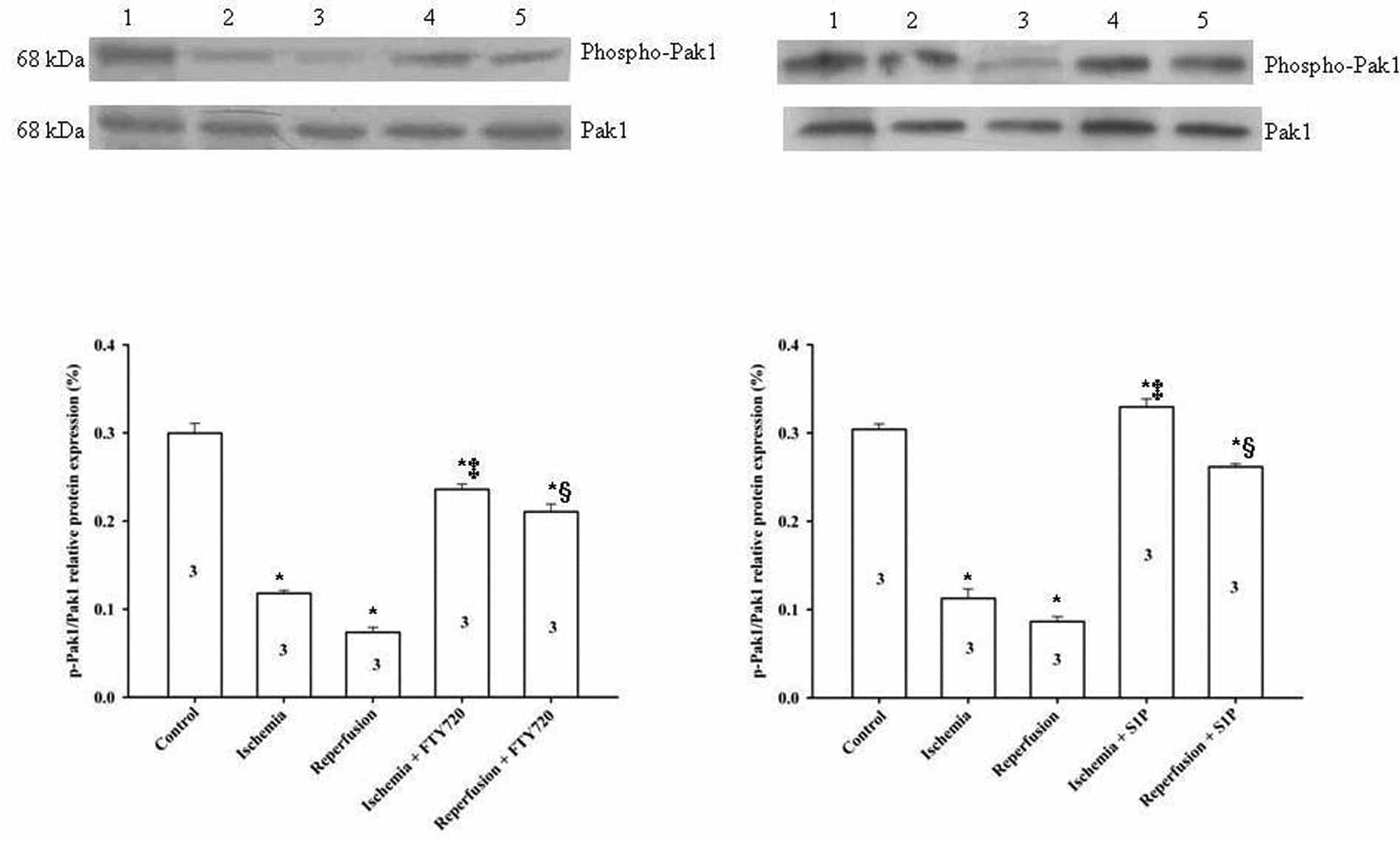
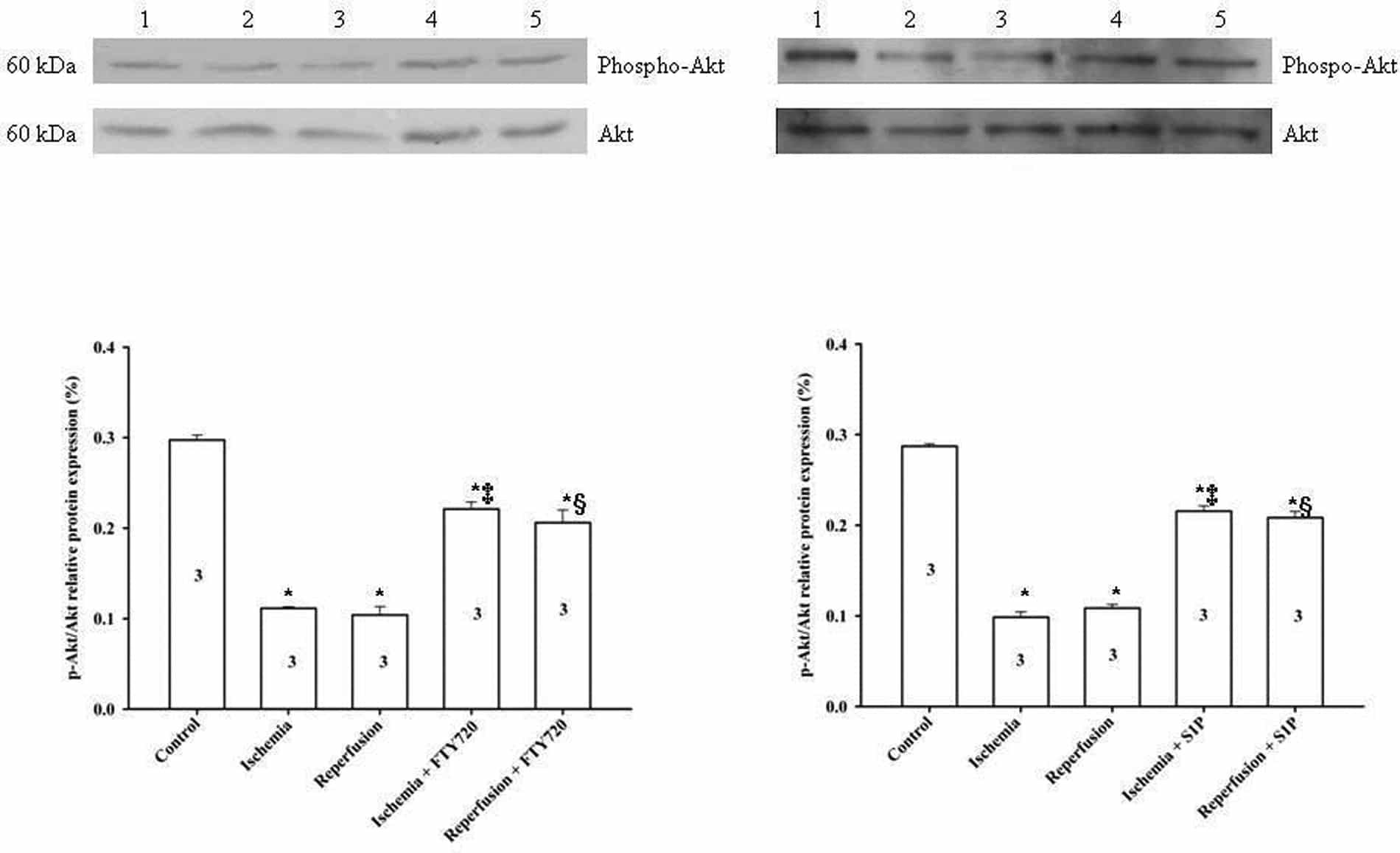
Recent studies demonstrated a role of Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) in protection against the stress of ischemia/reperfusion injury (I/RI). In experiments reported here, we have investigated the signaling through the S1P cascade by FTY720, a sphingolipid drug candidate displaying structural similarity to S1P, underlying the S1P cardio-protective effect. In ex vivo rat heart and isolated sino-atrial node models, FTY720 significantly prevented I/RI induced arrhythmic events including premature ventricular beats, VT and sinus bradycardia as well as A-V conduction block. Real-time PCR and Western blot analysis demonstrated the expression of the S1P receptor transcript pools and corresponding proteins including S1P1, S1P2 and S1P3 in tissues dissected from sino-atrial node, atrium and ventricle. FTY 720 (25 nM) significantly blunted the depression of the levels of phospho-Pak1 and phospho-Akt with ischemia and with reperfusion. There was a significant increase in phospho-Pak1 levels by 35%, 199%, 205% after 5, 10 and 15 mins of treatment with 25 nM FTY720 compared with control non-treated myocytes. However, there was no significant difference in the levels non-phospho-Pak1 expression between non-treated and FTY720 treated. Phospho-Akt levels were increased by 44%, 63%, and 61% after 5, 10 and 15 min of treatment with 25 nM FTY720 respectively. Our data provide the first evidence that FTY720 prevents the arrhythmias induced by I/RI, and indicate its potential significance as an important and new agent protecting against ischemia/reperfusion induced arrhythmias. The cardio-protective effect of FTY720 is likely to involve activation of signalling through the Pak1 and Akt cascade.
University College Dublin (2009) Proc Physiol Soc 15, C75
Oral Communications: FTY720, a sphingosine 1-phosphate analogue, prevents ischemic/reperfusion-induced cardiac arrhythmias in an ex vivo rat heart model via activation of p21-activated kinase/protein kinase Akt signaling
E. Eroume A Egom1, Y. Ke2, H. Musa1, T. Mohamed1, T. Wang1, E. Cartwright1, R. Solaro2, M. Lei1
1. Division of Cardiovascular and Endocrine Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom. 2. Department of Physiology and Biophysics, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, Illinois, USA.
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.