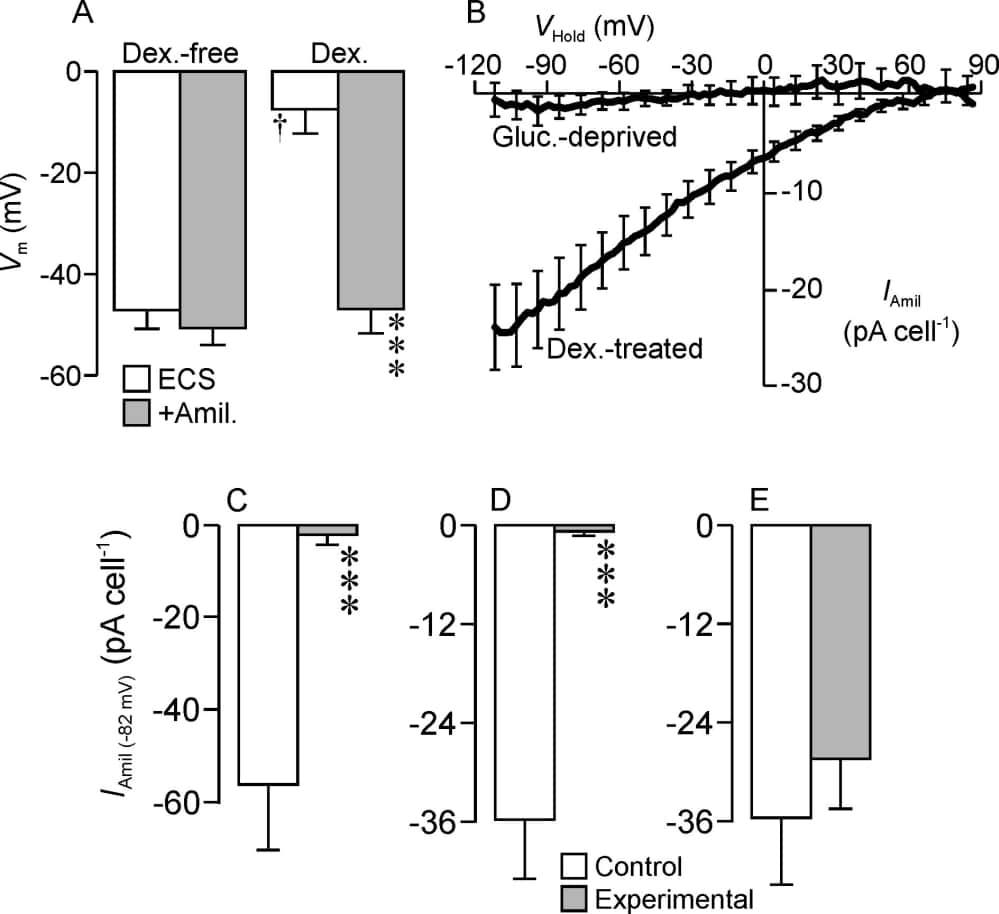
Airway function is dependent upon the absorption of Na+ from the airway surface liquid and this ENaC-dependent process is regulated by glucocorticoids. These hormones induce expression SGK1 (see e.g. Cohen & Lang, 2001), a regulatory kinase that seems to stimulate Na+ transport by increasing the surface abundance of ENaC subunits. The catalytic activity of SGK1 is dependent upon the phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)-controlled phosphorylation of SGK1-Ser422 by the mammalian target of rapamycin signalling complex 2 (TORC2) (García-Martínez & Alessi, 2008) and, to clarify the mechanism that allows gluccorticoids to control ENaC, we now explore the effects of inhibitors of TORC2 (TORIN1) and SGK1 (GSK650394) upon the glucocorticoid-induced epithelial Na+ current (Clunes et al., 2004) and SGK1 activity (assayed by monitoring the phosphorylation of NDRG1-Thr346/356/366, an endogenous SGK1 substrate, see Inglis et al. 1999) in H441 cells. Initial studies confirmed (see Clunes et al., 2004) that ~24 h exposure to 0.2 µM dexamethasone depolarizes Vm (Fig 1A) by inducing amiloride-sensitive Na+current(Fig. 1B). This glucocorticoid-induced current was abolished by TORIN1 (Fig. 1C) or GSK650394 (Fig 1D). Although TORIN1 inhibits TORC1 as well as TORC2, this cannot explain the present effect since rapamycin, a selective TORC1 inhibitor, had no effect (Fig. 1E). Analyses of extracted proteins (n = 4) showed that TORIN1 (0.1 µM, 3 h) and GSK650394 (10 µM, 3 h), but not rapamycin (0.1 µM, 3 h), also blocked NDRG1-Thr346/356/366 phosphorylation indicating inactivation of this kinase. These compounds did not, however, suppress the PI3K-dependent phosphorylation of protein kinase B-Thr308 demonstrating that PI3K activity is retained. Glucocorticoid-induced ENaC activity in H441 cells is therefore dependent upon TORC2 / SGK1 but, despite this finding, subsequent studies showed that dexamethasone (0.2 µM, ~24 h, n = 5) did not stimulate NDRG1-Thr346/356/366 phosphorylation. Moreover, whilst increased phosphorylation of this SGK1 substrate was evident in cells exposed to dexamethasone 3 h, brief (3 – 4 h) exposure to dexamethasone did not alter the electrical properties of H441 cells (n = 5). The glucocorticoid-induced Na+ currents in these cells thus develop relatively slowly but are maintained whilst SGK1 activation is more rapid and transient. It is therefore clear that hormone-induced ENaC activation does not coincide with the increased activity of SGK1 and so, whilst SGK1 is clearly important, our data suggest that the role of this kinase is permissive.
Durham University (2010) Proc Physiol Soc 21, PC23
Poster Communications: Glucocorticoid-induced activation of epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC) in H441 human airway epithelial cells does not coincide with increased activity of serum and glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 (SGK1)
G. B. Watt1, S. C. Land1, S. M. Wilson1
1. Centre for Cardiovascular and Lung Biology, University of Dundee, Dundee, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1. Membrane currents evoked by ramp changes in holding potential (VHold) were recorded in the perforated patch configuration during exposure to standard extracellular saline (ECS) and during exposure to 10 µM amiloride (+Amil). (A) Effects of amiloride upon Vm in glucocorticoid-deprived and dexamethasone-treated (0.2 µM, ~24 h) cells. (B) Effects of dexamethasone (0.2 µM, ~24 h) upon the amiloride-sensitive component of the membrane current (IAmil). The amiloride sensitive current flowing at -82 mV (IAmil(-82 mV)) was quantified in dexamethasone-treated (0.2 µM, ~24 h) control cells and in cells exposed (3 h) to 0.1 µM TORIN1 (C), 10 µM GSK650394) (D) or 0.1 µM rapamycin (E). All data are mean ± s.e.m and n > 4. Asterixes denote significant differences between control and experimental data (P < 0.001, Student’s paired t test), the dagger denotes a statistically significant effect of dexamethasone (P< 0.05, ANOVA).
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.