The induction of the antioxidant enzyme haem oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is a general response to oxidant stress in mammalian cells (Keyse and Tyrrell, 1989). Rothfuss et al. (2001) observed that an increase in HO-1 protein was associated with decreased oxidative DNA damage in lymphocytes exposed to hyperbaric oxygen. However, little is known about the time-course of HO-1 up-regulation in mononuclear cells. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to assess the HO-1 protein response over time in freshly harvested monocytes and lymphocytes exposed to oxidant stress in the form of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
After local ethical committee approval, seven male subjects (age 26 ± 2 years, height 1.77 ± 0.15 m, and body mass 80 ± 2 kg; mean ± S.E.M.) reported to the laboratory following an overnight fast. Subjects rested in a supine position for ten min prior to a venous blood sample (25ml) being taken. Subjects refrained from exercise, drinking alcohol and kept a record of their food and fluid intake for three days prior to blood sample collection. Mononuclear cells were isolated from peripheral blood and exposed to 50 µM H2O2 for 30 min at 37°C. Levels of HO-1 protein were analysed by flow cytometry (FACScan, Becton Dickinson, USA) using a monoclonal antibody (Stressgen, Canada) and fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated secondary antibody (FITC) (Sigma, UK) at 4, 6, 24 and 48 h after treatment. HO-1 protein was expressed as the percentage change from the initial baseline value using the median fluorescence intensities of the treated and corresponding sham-treated controls. Data were analysed at each timepoint using a one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test where appropriate. Statistical significance was accepted at P < 0.05.
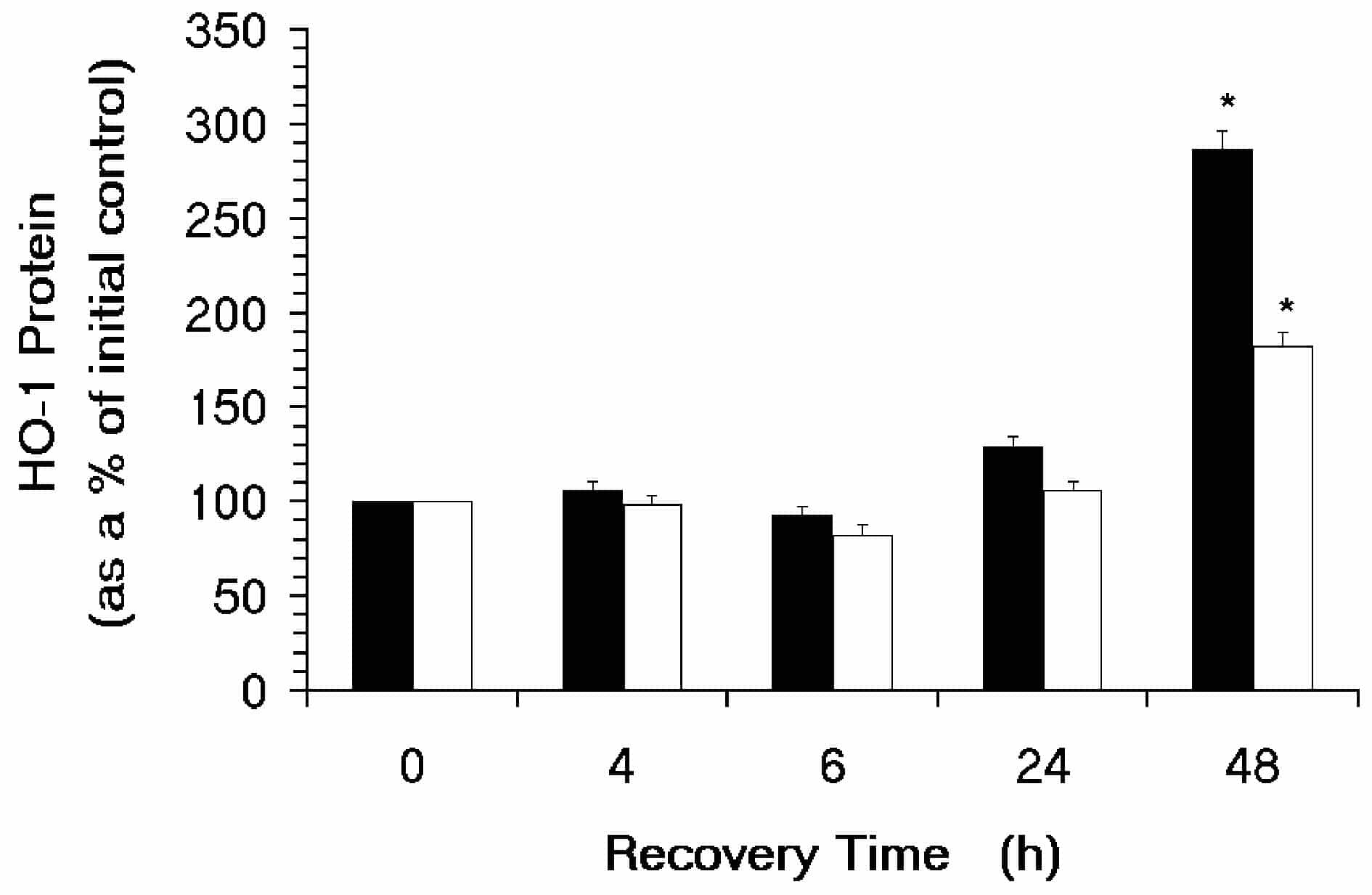
There was a significant increase in HO-1 protein over time in both cell types (P < 0.01). The change in HO-1 protein was 287 ± 10 % and 183 ± 7 % at 48 h post treatment in lymphocytes and monocytes, respectively.
Maximum levels of HO-1 protein were observed in every subject at 48 h post H2O2 treatment in both lymphocytes and monocytes. There was very little variability in the HO-1 response at this timepoint.