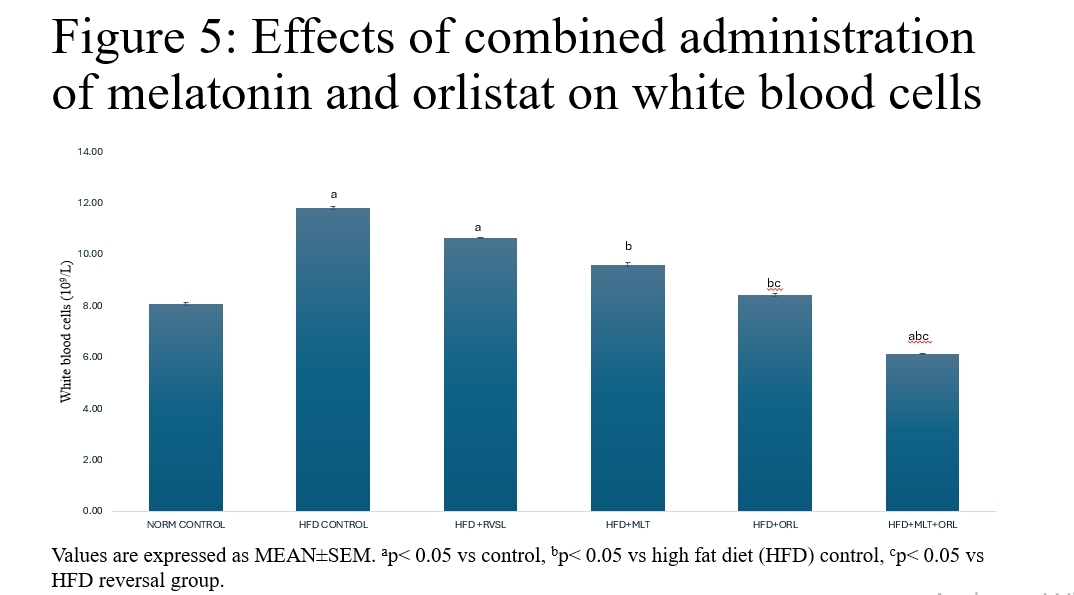
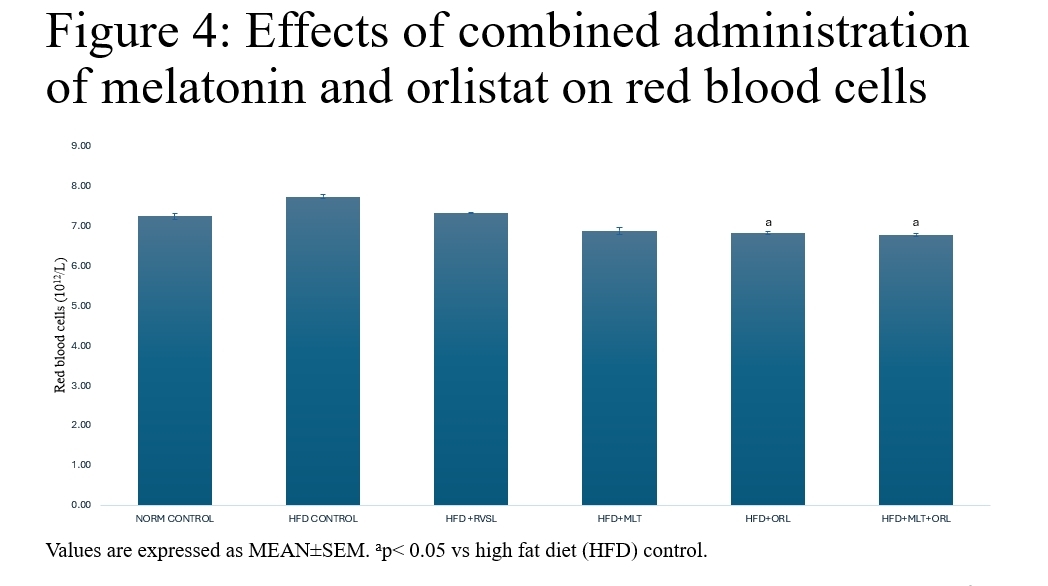
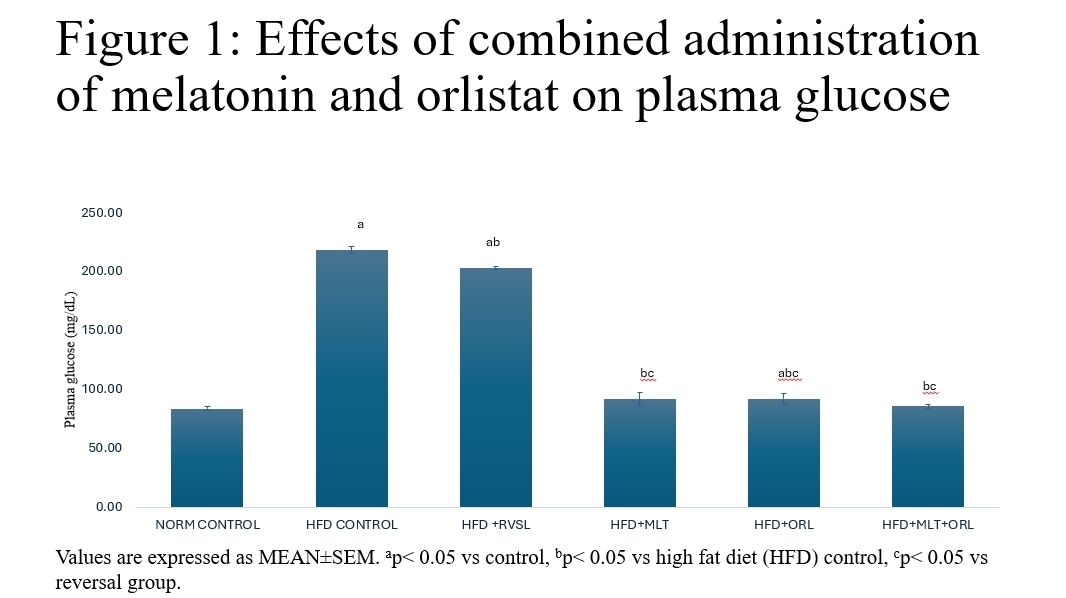
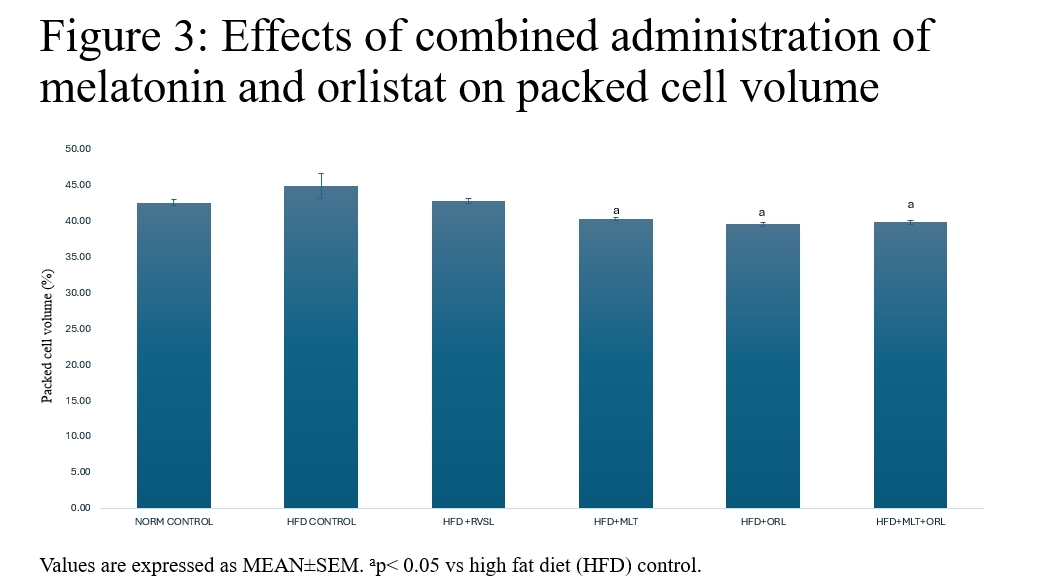
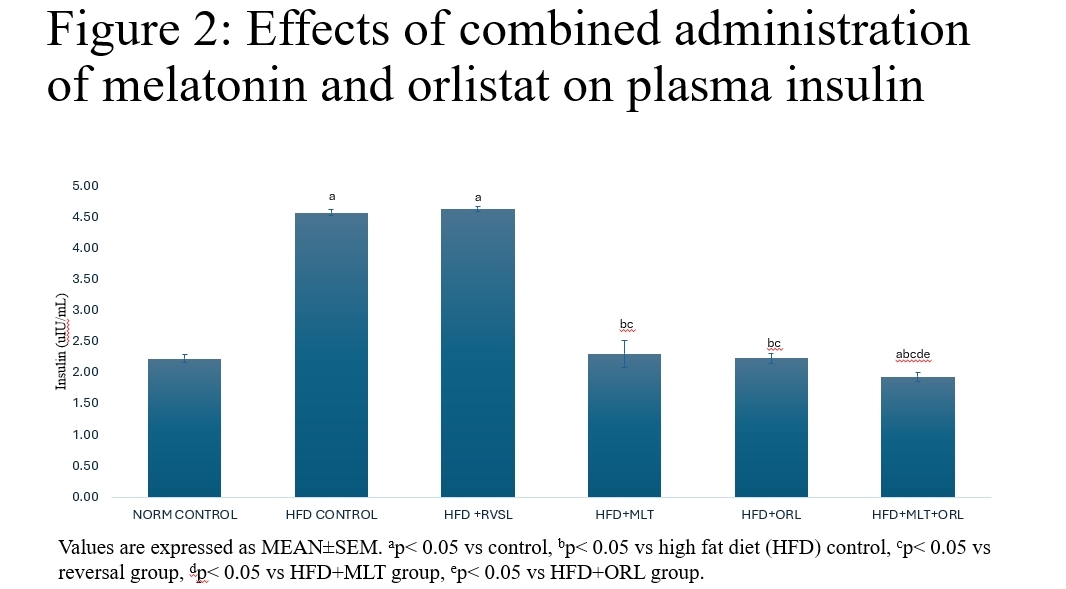
The prevalence of obesity, characterized as a metabolic disorder, has escalated to epidemic levels, posing significant public health challenges. Studies have demonstrated a direct correlation between increased body weight, altered haematological indices and elevated mortality rates. Despite concerted efforts, the persistent struggle against these conditions has prompted the exploration for innovative therapeutic interventions. For the treatment of obesity, the gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor orlistat has been suggested. Nonetheless, the majority of patients have been dissuaded from continuing to use it due to the gastrointestinal adverse effects. Therefore, a stronger medication with fewer adverse effects is required. It has been observed that melatonin, a commonly used alternative medication, effectively lowers body weight with very little negative effects. Therefore, the present study investigated the haematological effects of melatonin administration in obesity model of male Wistar rats weighing between 120 – 140 g. It was hypothesized that combined administration of melatonin and orlistat are not anti-obesitogenic therapy on obese rat model. Sixty (60) rats of ten (10) animals per group were divided into the following: control (untreated); high fat diet (HFD); high fat diet recovery (hfd); HFD + melatonin (4 mg/kg); hfd + orlistat (30 mg/kg); and HFD + melatonin (4 mg/kg) + orlistat (30 mg/kg). Obesity was induced by exposing the rats to high fat diet for 16 weeks and confirmation was done using Lee index, which was determined by the formula: 4√body weight (g) / nose-anal length (cm) (Adeyemi et al., 2020). Rats with an index higher than 0.30 were considered obese and were used for the study. Diagnostic kits for the determination of the biomarkers were obtained from Abcam PLC, Cambridge, UK and the assays were performed according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and LSD post hoc test at 0.05 level of significance. The results showed that the induced obesity was accompanied with significant increases in plasma glucose, plasma insulin, packed cell volume (PCV), haemoglobin (HB), red blood cells (RBC) and white blood cells (WBC). Relative to the obese control, treatments with melatonin, orlistat and combined administration of both agents caused significant decrease in those parameters with the combined administration having a more potent effect. Hence, it was concluded that combined administration of melatonin and orlistat could be a better candidate in the management of haematological parameters in obese conditions.
Physiology in Focus 2024 (Northumbria University, UK) (2024) Proc Physiol Soc 59, PCB050
Poster Communications: HAEMATOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF MELATONIN ADMINISTRATION ON OBESE WISTAR RATS: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
Tahir Abdussalam1, Luqman Olayaki1,
1University of Ilorin Ilorin Nigeria, 2University of Ilorin Ilorin Nigeria,
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.