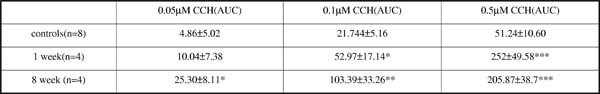
The myogenic basis of bladder overactivity has recently become a focus of interest and may involve increased detrusor muscle spontaneous activity (Brading, 1997) and changes in potassium (K) channel function (Andersson, 1992). The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying this remain unclear. This study aims to assess the spontaneous phasic activity (SA) in the detrusor muscle of bladders from a diabetic rat model. Male Wistar rats (200-250g) were administered streptozotocin (STZ, 65mgkg-1, i.p.). Strips of detrusor smooth muscle were isolated from bladder of rats 1, 4, 8 and 12 weeks after STZ or from weight matched controls. Tissues were mounted in tissue baths containing Krebs-bicarbonate solution (in mM, 118.3 NaCl, 11.7 D-Glucose, 24.9 NaHCO3, 4.7 KCl, 1.15 MgSO4, 1.15 KH2PO4, 1.9 CaCl2) with 5µM indomethacin at 37°C and gassed with 95% O2/5% CO2. Isometric tension was measured, via UF1 force transducers connected to a Powerlab using Chart software. After equilibration (2g of tension, 60 minutes), tissues were assessed for changes in basal SA expressed as mean area under the curve (AUC) and the effect of muscarinic modulation with carbachol (CCH) (0.05-0.5μM) was analysed. The effects of the large conductance Ca2+ activated K channel (BK) opener, NS1619 (1-30μM), on the SA in presence of 0.5uM CCH (1-30μM) of this drug was assessed. Then the effects of K channel blockers, iberiotoxin (IBTX) (BK channel blocker) TRAM34 (IK channel blocker), apamin (SK channel blocker) (0.01-0.1μM) and glibenclamide (KATP channel blocker) (1-10μM) were tested on the basal SA. Differences between control and diabetic tissues were analysed using Students t-test. Basal SA was seen in over 50% of the detrusor strips from 1 (AUC= 98.321±12.53, p<0.05), 4 (AUC=119.29±17.86, p<0.05) and 8 weeks (AUC=112.23± 24, p<0.05) diabetic rats compared to controls (AUC=59.56±5.52), but not in strips from 12 week diabetic rats. Initial results in 1-week and 8-week diabetic tissues show significantly higher SA to muscarinic modulation compared to controls (table 1) NS1619 (30μM) showed reduced AUC (%) at 1 (44.25±5.1%) and 8 weeks (19.65±17.1) similar to control (31.7±10.4%). IBTX on its own was the only K channel blocker which could increase basal SA. In conclusion, detrusor muscle from STZ diabetic rat bladders shows increased SA up to 8 weeks following induction of diabetes. The SA can be modulated by muscarinic stimulation and diabetic bladders are more sensitive to this. BK channels also appear to be involved in the SA, but further investigation is needed.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC177
Poster Communications: Increased spontaneous activity in diabetic overactive bladder
B. Vahabi1, K. Lawson1, D. Sellers1, N. McKay1
1. HWB,Biomedical Research Center, Sheffield Hallam University, Sheffield, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.