A recent study has shown that Na+-K+-ATPase activity is present on the surface sarcolemma of cardiac ventricular myocytes (Fowler et al. 2003). However the fraction on the surface sarcolemma compared to that within the t-tubules is unknown. The aim of the present study was to investigate this distribution.
Wistar rats were anaesthetised by I.P. injection of Nembutal (1 mg g-1). The heart was removed and ventricular myocytes enzymatically isolated, and detubulated as described by Kawai et al. (1999). Na+-K+ pump current (Ipump) was measured, using the whole cell patch clamp technique, as the outward current activated by 4 mM K+ at a holding potential of -20 mV in the presence of inhibitors of contaminating currents. The same protocol, but using high resistance electrodes, was used to investigate the [Na+]i dependence of Ipump after ~10 min Na+-K+ pump inhibition, in cells loaded with sodium-binding benzofuran isophthalate (SBFI) to monitor [Na+]i (Despa et al. 2003). All experiments were performed at 23-25 °C.
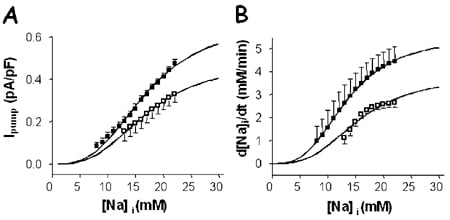
Detubulation induced a 32 % decrease in cell capacitance (control: 156 ± 7 pF, mean ± S.E.M., n = 24; detubulated: 106 ± 5 pF, n = 19; P < 0.05, Student’s unpaired t test) and a 39 % decrease in Ipump density (control: 0.28 ± 0.02 pA pF-1, n = 14; detubulated: 0.17 ± 0.03 pA pF-1, n = 16; P < 0.05), indicating concentration of Ipump in the t-tubules. Pump re-activation resulted in a rapid outward shift in the membrane current, followed by a decay. The initial rapid phase of this decay occurred with little decrease of bulk [Na+]i and may be due to local subsarcolemmal [Na+]i depletion by the pump (Despa et al. 2003). The subsequent slower phase was accompanied by a decrease of [Na+]i; detubulation decreased Ipump density and the rate of decrease of [Na+]i at a given [Na+]i during this phase (Fig. 1). Fitting these data using the Hill equation showed that detubulation decreased Vmax to ~70 % of control, but did not alter the Km for [Na+]i (control: 17.0 ± 0.3 mM, n = 7; detubulated: 16.9 ± 0.4 mM, n = 8; NS, unpaired t test).
We conclude that the functional density of Na+-K+ pump in the t-tubules is ~3-fold higher than in the surface sarcolemma, but that the Km,Na of the pump in the t-tubules is the same as that on the surface membrane.
This work was supported by the NIH and AHA (USA) and the Wellcome Trust (UK).