Compelling evidence exists that prenatal serotonin (5-HT) plays a key role in CNS maturation. High endogenous levels of 5-HT resulting from monoamine oxidase A (MAOA) deficiency in the Tg8 transgenic strain of mice (created from the C3H/HeJ strain, C3H) alter the respiratory network maturation and the morphology of phrenic motoneurons (PhMns) (Cases et al. 1995; Bou-Flores et al. 2000). We compared neonatal C3H and Tg8 PhMns to know whether their 5-HT receptor expression was altered by prenatal 5-HT excess.
In ether-anaesthetised P0 neonates, brainstem and spinal cord were dissected, placed in vitro and the phrenic root was sucked within a rhodamine-filled suction electrode to label the PhrMns. Immunoreactivity of rhodamine-labelled PhMns was analysed by simple fluorescence and confocal microscopy with 5-HT2A and 5-HT1B receptor antibodies (Diasorin and Pharmigen, respectively).
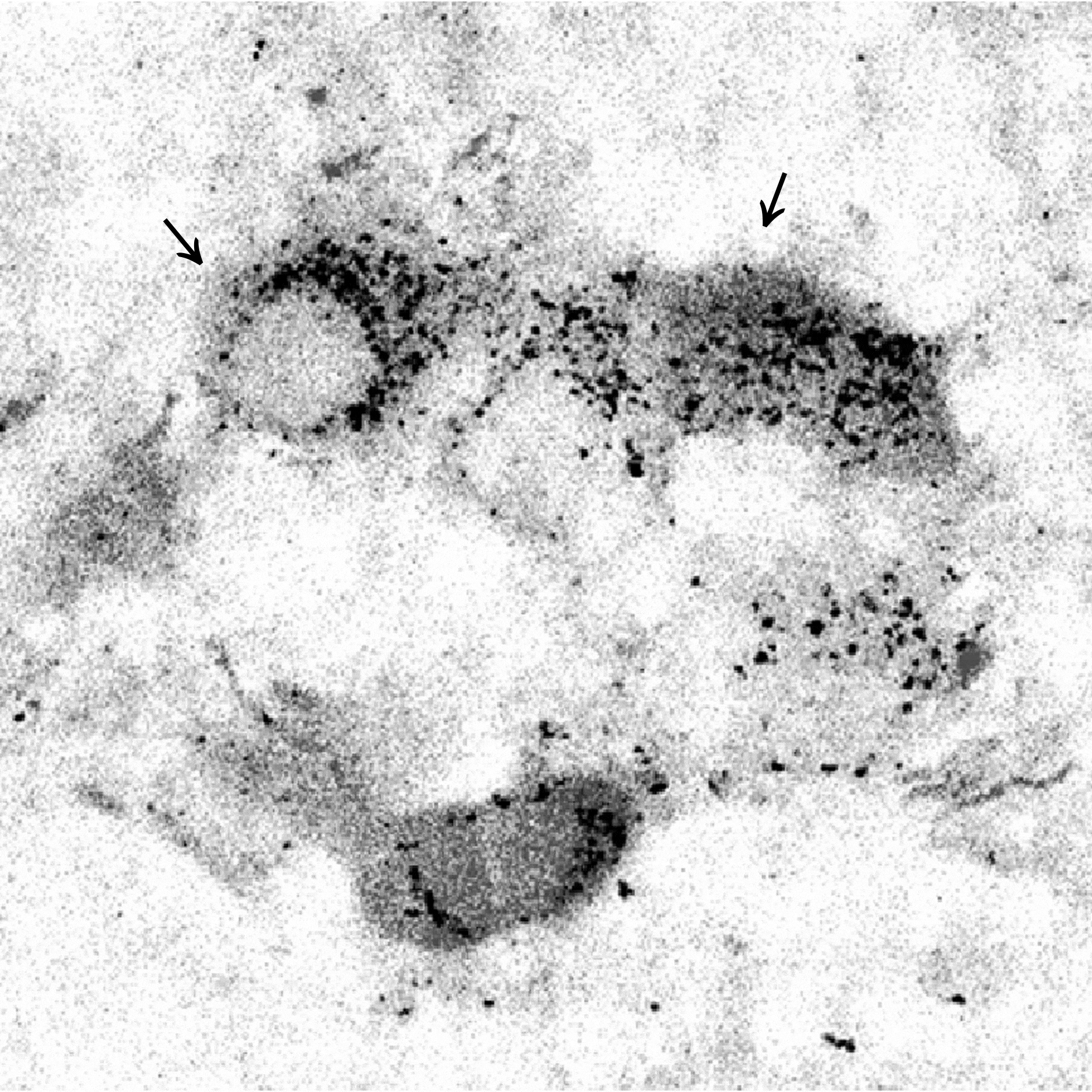
In five C3H and seven Tg8 pups, respectively 38 and 32 PhMns showed red-stained and well-defined somata, primary and some distal dendrites. As reported (Bou-Flores et al. 2000), the number of primary dendrites was in the same range in both strains (4-6 per soma) but Tg8 distal dendrites showed frequent branching and varicosity-like profiles. 5-HT2A immunoreactivity occurred in 24/38 C3H and 19/32 Tg8 somata, without obvious interstrain difference. The 5-HT1B immunoreactivity was weak and diffusely distributed, without any relation to distinct cellular profiles in C3H whereas 14/32 Tg8 somata were clearly immunoreactive (Fig. 1). Finally, we analysed nine PhMns of C3H pups born from dams which received daily injections of the 5-HT2A receptor agonist DOI (50 mg kg-1 day-1 from E16 to delivery) to activate the 5-HT2A receptors of their fetuses. Two C3H PhMns expressed 5-HT1B immunoreactivity similar to Tg8 PhMns.
In conclusion, these results suggest that a high endogenous level of 5-HT induces 5-HT1B receptor expression, probably through 5-HT2A receptors, in neurons where they are normally not expressed.
This work was supported by P.A.I. Junta de Andalucía and D.G.I. BFI2002-02055.