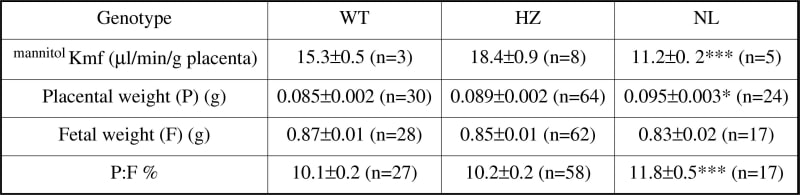
PTHrP plays an important role in fetal growth and skeletal development, regulating trophoblast and placental differentiation and placental calcium transport (Clemens et al. 2001). We have previously shown that the unidirectional maternofetal clearance of calcium is raised across the placenta of the PTHrP-/- (NL) fetuses when compared with their PTHrP+/+ (WT) and PTHrP+/- (HZ) counterparts, suggesting placental transport function is altered (Bond et al. 2004). Here we test the hypothesis that there is altered passive permeability across the NL placenta. Using a technique recently devised for artificially perfusing the fetal circulation of the mouse placenta (Bond et al. 2006) we measured unidirectional maternofetal clearance of 14C-mannitol (mannitolKmf), an inert hydrophilic tracer, across NL, WT and HZ placentas. Heterozygote mice were mated and on day 18 of gestation (term=19-20d) were anaesthetised (i.p. fentanyl citrate/fluanisone: 24 and 750µg) and the uterus delivered into a saline bath at 40°C. A fetus was randomly selected, the umbilical artery and vein catheterised and perfused with Krebs Ringer (pH 7.4) at 60 μl/min. 14C-mannitol (5µCi/50 µl saline) was injected via a maternal tail vein. Perfusate samples were collected every 5 min for 45 min. mannitolKmf was calculated as: perfusate [14C-mannitol] x perfusion rate/maternal plasma [14C-mannitol] x placental weight. Data for mannitolKmf are calculated as mean value over 45 min perfusion. Results are given in Table 1, expressed as mean±SEM. Statistical analysis used was one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. mannitolKmf was significantly reduced across the placenta(***P<0.001), whilst placental weight and P:F weight ratio were increased (*P<0.05; ***P<0.001 respectively), in the NL relative to WT and HZ. There was no significant reduction in NL fetal weight. These data suggest that in conceptuses lacking PTHrP the passive permeability of the placenta is reduced. This provides evidence that PTHrP may have an important role in determining placental exchange barrier properties as well as trophoblast growth.
University of Manchester (2006) Proc Physiol Soc 2, PC19
Poster Communications: Passive permeability of the mouse placenta to mannitol is reduced in parathyroid hormone related protein (PTHrP) null conceptuses
Helen Bond1, B Baker1, R Boyd1, E Cowley1, J Glazier1, C Sibley1, B Ward1, S Husain2
1. Division of Human Development, The University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom. 2. Queen Mary College, University of London, London, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.