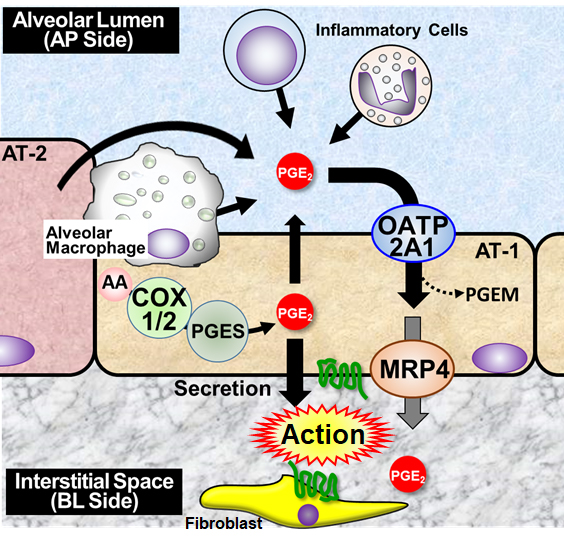
Solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 2A1 (SLCO2A1) is a plasma membrane transporter consisting of 12 transmembrane domains and mediates cellular uptake of major prostaglandins (PGE2, PGF2α, and PGD2) and, to a lesser extent, thromboxanes (e.g., TxB2). Recent whole-exome analyses demonstrated that recessive inheritance of SLCO2A1 mutations causes primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (PHO) and chronic enteropathy associated with SLCO2A1 (CEAS), suggesting that impaired function of SLCO2A1 is associated with a disorder of PG metabolism (1). In the lungs, there is significant evidence that the anti-fibrotic action of PGE2 results in the increased sensitivity of fibroblasts to apoptosis. Although the importance of PG biosynthesis synthase and signaling is well established, much less is known about the contribution of transporters to PGE2 action in the respiratory regions. Our laboratory has been investigating the role of SLCO2A1 in actions of PGE2 in the lungs since we observed more severe pulmonary fibrosis in bleomycin-treated Slco2a1-deficient mice (Slco2a1(-/-)) (2). This study aimed to understand the pathophysiological significance of SLCO2A1 in pulmonary inflammation. We conducted immunohistochemistry and transport studies using type 1 alveolar epithelial cell-like (AT1-L) cells transdifferentiated from type 2 alveolar epithelial cells prepared from rats and mice. Anti-Slco2a1 immunoreactivity was detected mainly in the alveolar epithelium. Slco2a1 deficiency remarkably reduced cellular uptake of PGE2 by AT1-L cells and increased PGE2 in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid of mice. Transcellular transport of PGE2 across the monolayer of rat AT1-L cells from the alveolar lumen (AP side) to the interstitial space (BL side) was greater than that in the BL-to-AP direction (3). Permeation coefficient of PGE2 was significantly reduced in the presence of SLCO2A1 inhibitors and, to a lesser extent, ceefourin-1 (an MRP4 inhibitor), suggesting that SLCO2A1 transports PGE2 from alveolar lumen to stromal tissues in cooperation with MRP4 (Figure 1). We further investigated the impact of SLCO2A1 on lung inflammation. BAL fluid cell analysis indicated more severe inflammation occurred in Slco2a1(-/-) on day 5 after BLM intratracheal instillation, and Slco2a1 deletion increased mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Tnf-α and Il-1β) and chemokine (Ccl5) in BAL cells (4). Male Slco2a1(-/-) exhibited significantly higher amounts of released Il-1β and PGE2 concentration in BAL fluid than female Slco2a1(-/-). Thus, Slco2a1-deficient male mice are likely more susceptible to airway inflammation. This observation is consistent with our recent report of NLRP3 inflammasome activation caused by increased peripheral PGE2 level in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mouse model (5). Finally, we found that cigarette smoke extracts (CSE) significantly reduced SLCO2A1-mediated PGE2 uptake; therefore, SLCO2A1 inhibition by xenobiotics is considered a new rationale for lung toxicity. In conclusion, excess amount of PGE2 due to impaired function of SLCO2A1 in the alveolar fluid may contribute to activation of inflammasomes in alveolar macrophages, resulting in aggravated lung inflammation. These results suggest that SLCO2A1 regulating PGE2 biodistribution in the respiratory region is essential for lung homeostasis.
Physiology 2021 (2021) Proc Physiol Soc 48, SA52
Research Symposium: Pathophysiological significance of the prostaglandin transporter SLCO2A1 in lung inflammation
Takeo Nakanishi1
1 Takasaki University of Health and Welfare, Takasaki , Japan
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.