Introduction
Traditionally, muscle quality has been defined as the strength generated by muscle mass. Nowadays, we are able to look more deeply into the physiological and body composition mechanisms that determine muscle quality1.
Intracellular water content (ICW) has been shown to be a useful indicator of strength-related muscle quality in the elderly, as this is the population group that is the most compromised at the water level2. In high-performance sport, ICW has been found to be closely related to physical performance3. Phase angle (PhA) has also become an objective indicator of cellular health and functionality4.
For this reason, the aim is to obtain bioelectrical impedance (BIA) values of both PhA and muscle quality related to hydric parameters.
Methods
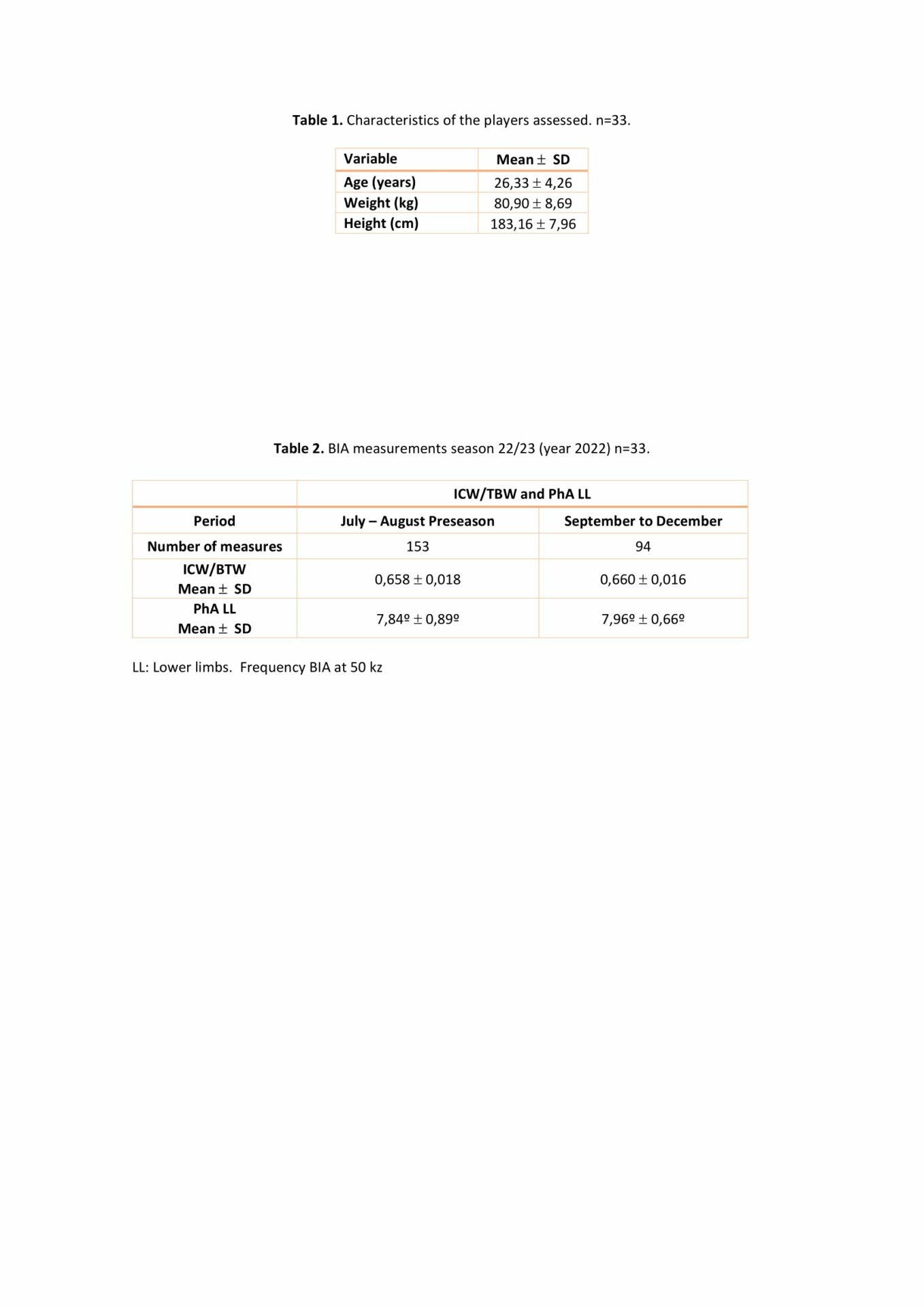
The sample of this longitudinal study was 33 professional football players (Table 1), from the first team of Watford FC (England). The measurements were taken during the competitive stage of the 22/23 season (year 2022).
Table 1. Characteristics of the players assessed. n=33.
|
Variable |
Mean ± SD |
|
Age (years) |
26,33 ± 4,26 |
|
Weight (kg) |
80,90 ± 8,69 |
|
Height (cm) |
183,16 ± 7,96 |
Players were assessed by multifrequency BIA model Tanita MC-780 MA under fasting conditions, without having exercised in the previous twelve hours and having emptied the bladder before the test. A total of 247 measurements were obtained where the water component and muscle quality were analysed using the AIC/ACT index (intracellular water/total body water) and lower limb PhA, both at 50 KhZ. Injured players were excluded from the total sample.
This work was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Pablo de Olavide University.
Results
In our group, we obtained mean reference values for the AIC/ACT index of 0.661 ± 0.017, and for the lower limb PhA of 7.8° ± 0.72°. Approximately 70% of the players are in the AIC/ACT (x±SD ) range of 0.644-0.678 and PhA of 7.08-8.52º, below which we estimate muscle quality deficits in relation to hydration and muscle quality. Approximately 96% of our players are in the interval of AIC/ACT (x±2SD ) of 0.627-0.695 and PhA of 6.36-9.44º, below which we estimate as low muscle quality.
The evolution of this index and PhA during the 22/23 season is shown in table 2.
Table 2. BIA measurements season 22/23 (year 2022) n=33.
|
ICW/TBW and PhA LL |
||
|
Period |
July – August Preseason |
September to December |
|
Number of measures |
153 |
94 |
|
ICW/BTW Mean ± SD |
0,658 ± 0,018 |
0,660 ± 0,016 |
|
PhA LL Mean ± SD |
7,84º ± 0,89º |
7,96º ± 0,66º |
LL: Lower limbs. Frequency BIA at 50 kz
Conclusions
We consider the muscle quality index and the PhA to be very useful for analysis by the technical and health staff of a professional football club. Our data on the 70% range can serve as a reference, below which there is a deficit in muscle quality. However, it would be advisable for each club to obtain the average values of the index and PhA in order to be able to compare and analyse their athletes.