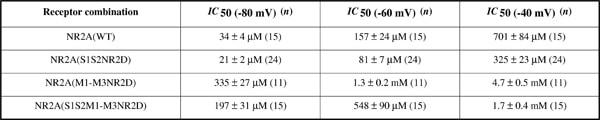
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) are composed of NR1 and NR2 subunits most likely arranged in a dimer of dimers configuration (Furukawa et al. 2005; reviewed in Chen & Wyllie, 2006). These receptor-channels exhibit characteristic voltage-dependent channel block by Mg2+ ions, the sensitivity of a particular receptor combination being determined by the identity of the NR2 subunits present, with NR2A-containing NMDARs being the most sensitive and NR2D-containing NMDARs being the least sensitive to Mg2+ block (Monyer et al. 1994; Kuner & Schoepfer, 1996). In this study we have examined voltage-dependent Mg2+ block using two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings from Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing wild-type NR2A subunits or chimaeric NR2A-NR2D subunits where either the S1 and S2 ligand-binding domains (LBD) of the NR2A subunit were replaced by the S1 and S2 LBDs of the NR2D subunit or the first three membrane associated regions of the NR2A subunit were replaced by the equivalent regions of the NR2D subunit. All NR2 subunit constructs were co-expressed with the NR1a subunit. Concentrations of Mg2+ ions required to inhibit glutamate-evoked responses by 50 % (IC50 values) at holding potentials of –80 mV, –60 mV and –40 mV were determined for wild-type and chimaeric receptor combinations and the results obtained shown in Table 1 below. The data indicate that when the M1-M3 regions of the NR2A subunit are substituted with the corresponding regions of the NR2D subunit there is a reduction in the sensitivity of such receptors to Mg2+ ions. Intriguingly, expression of the LBD of the NR2D subunit in the NR2A subunit increases Mg2+ potency compared to wild-type NR2A-containing NMDARs (P < 0.01). Current-voltage plots for glutamate-evoked currents, in the presence of 1 mM Mg2+, showed the typical J-shape profile for each of the constructs examined. Thus, in addition to the well-described role of the pore-forming regions, it appears that the LBD of different NMDAR subunits also influences the potency of Mg2+ block at these receptor-channels.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC149
Poster Communications: Properties of voltage-dependent Mg2+ block in rat recombinant chimaeric NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes
E. J. Baker1, D. C. Wrighton1, P. E. Chen1, D. J. Wyllie1
1. Centre for Neuroscience Research, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.