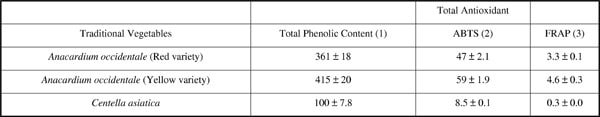
Anacardium occidentale and Centella asiatica, among the most popular Malaysian traditional vegetables, locally known as ‘gajus’ and ‘pegaga’ were screened for phenolics and analysed for the quantification of individual compounds by reverse-phased high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (RP-HPLC-MS2). Yellow variety of Anacardium occidentale showed the highest total phenolic content of 415 ± 20 mg GAE per kg fw. to that of red variety (361 ± 18 mg GAE per kg fresh weight, fw.) respectively measured using Folin-ciocalteu assay [1]. However, Centella asiatica had shown lower phenolic content of 100 ± 7.8 mg GAE per kg fw. compared to Anacardium occidentale. 15 phenolic compounds in red and yellow varieties of Anacardium occidentale and 11 phenolic compounds in Centella asiatica mainly flavonol glycosides and chlorogenic acids were identified and quantified. The antioxidant activities were measured using two different assays, an on-line high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method in conjunction with the analysis of the 2,2-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS+) assay [2] and Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Potential (FRAP) assay [3]. The yellow variety of Anacardium occidentale showed the highest antioxidant activities (59 ± 1.9 mM Trolox equivalent (TE) in ABTS+ assay and 4.6 ± 0.3 mM Fe2+ in FRAP assay) to that of red variety (47 ± 2.1 mM TE and 3.3 ± 0.1 mM Fe2+) and Centella asiatica (8.5 ± 0.1 mM TE and 0.3 ± 0.0 mM Fe2+). The antioxidant activity are correlated with the total phenolic content and contributions from other compounds such as vitamin C, carotenoids and triterpenes to the total antioxidant activity should also be considered. However, the level of carotenoids in this study did not show any correlation to total antioxidant activities of these two plant species.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC571
Poster Communications: Reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (RP-HPLC-MS) analysis of phenolics in selected Malaysian traditional vegetables and their total antioxidant activities
M. Mat Ali1, A. Crozier1
1. Environmental & Evolutionary Biology, Glasgow University, Glasgow , United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Total phenolic content and total antioxidant activities in Anacardium occidentale and Centella asiatica
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.