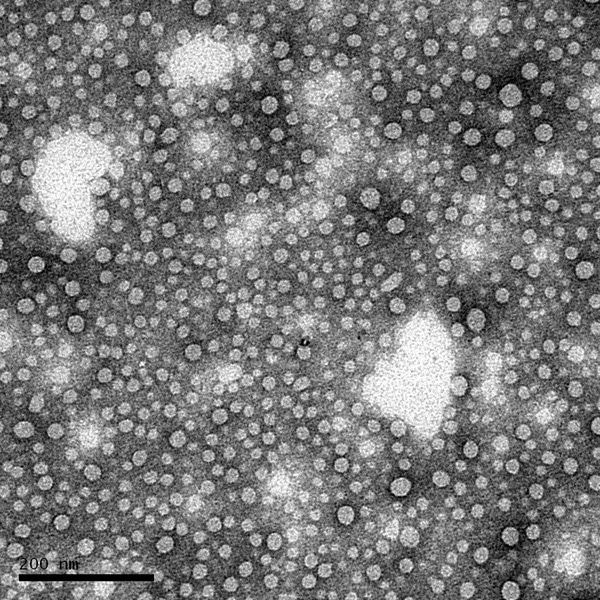
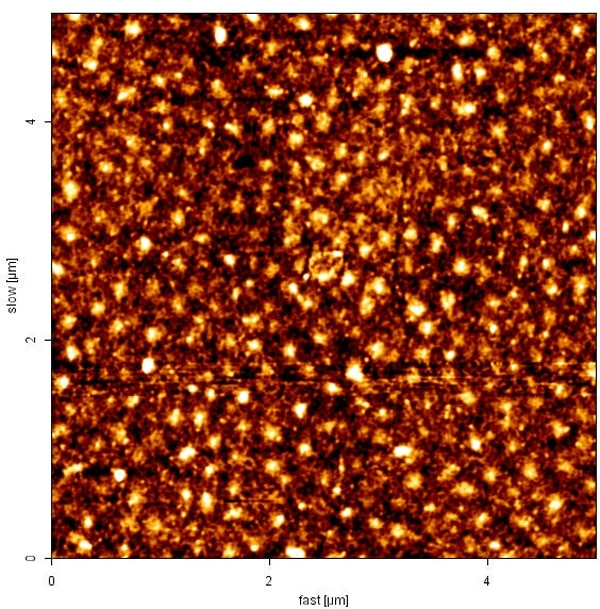
The hepatitis C virus core protein is the main consistent of nucleocapsid [1] and exhibits multiple functions involving in cellular growth, signaling and others[2-5]. In this study, we successfully overexpressed and purified the N-terminal 1-116 core protein, and assembled them into capsid-like particles. Using gel-filtration and sucrose-gradient assays, we characterized the molecular weight of the HCV core particle to be 180mers (~2400 kDa) and T=3. We studied the structural properties of the assembled core proteins using CD spectroscopy, AFM and TEM. The secondary structure of core assemblies contains 23% α-helix, 34% β-sheet and 47% random coil. The structure of this assembled core protein is hardly affected by pH, urea and ionic strength revealed by CD and AFM. Furthermore, the 3D image of virus like particle was constructed by EM.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC595
Poster Communications: Structural properties of hepatitis C virus core protein assembling
S. Lin1, Y. Chen1, 2, T. Lin3, J. Liou4, S. Lo2
1. Institute of life science, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan. 2. Institute of Medical Science, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan. 3. Department of Medical Research and Education, Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan. 4. Department of Biochemistry, Tzu Chi University, Hualien, Taiwan.
View other abstracts by:
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.