Introduction
Ficus exasperata has been reported to have several therapeutic potentials. However, there is paucity of reports on its effects on mRNA expression of genes associated with glycemic control in diabetic Wistar rats.
Aim/Objective
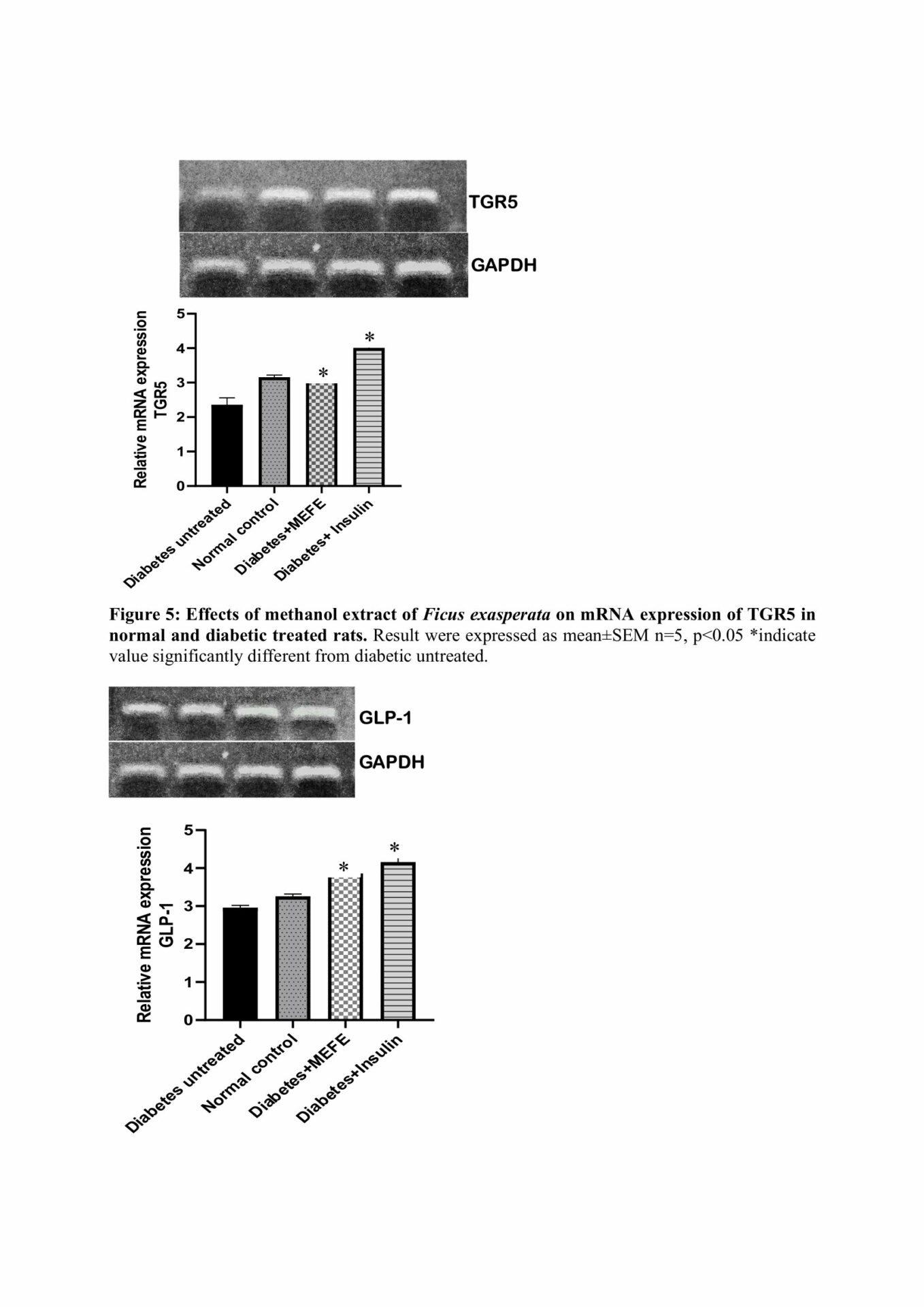
This study was designed to investigate the effects of methanol extract of Ficus exasperata (MEFE) on mRNA expression of Takeda G-protein coupled receptor 5 (TGR5), Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), Glucose dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and other glycemic indices in diabetic male Wistar rats.
Methods
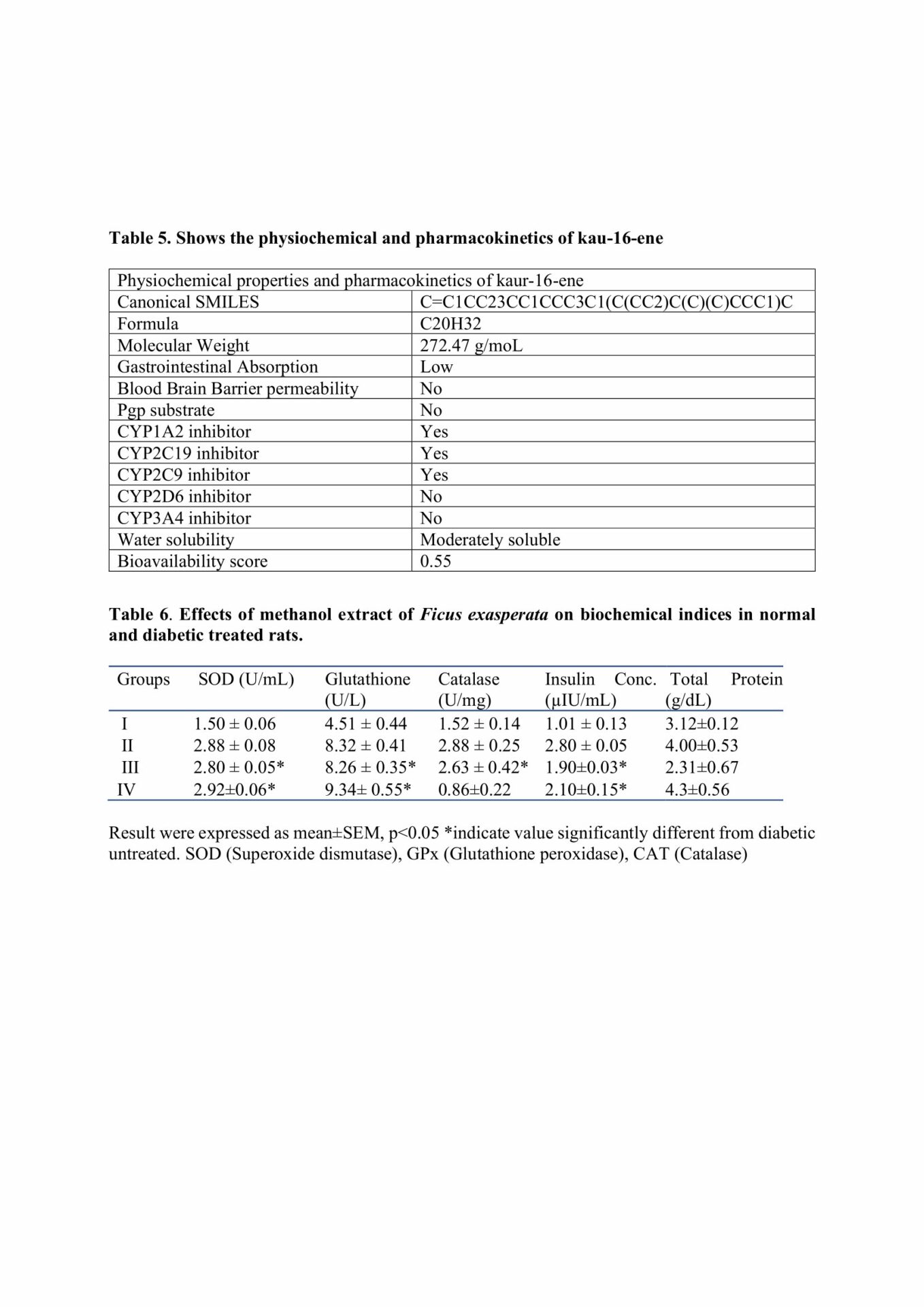
Fresh leaves of Ficus exasperata were gotten from Ondo State and authenticated at the Department of Botany, University of Ibadan, Nigeria with voucher specimen number (UIH: 240407). It was extracted using methanol and characterized using GCMS analysis. Twenty (20) rats were divided into four (4) groups (n=5) as follows: Group I (Diabetic Untreated), Group II (Normal control), Group III (diabetes + 200 mg/kg MEFE), and Group IV (diabetes + 0.3 units Insulin). Diabetes was induced via single intraperitoneal injection of alloxan monohydrate (150 mg/kg). Treatments were administered daily for 28 days. Thereafter, the rats were anesthetized using ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg) for blood collection and tissue harvesting (Beeton, 2007). The blood glucose and insulin concentration were assessed by glucose oxidase and ELISA method while superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and total protein were evaluated using commercially available randox kits. GLP-1, TGR5 and GIP expression were quantified using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). In-silico docking of MEFE compounds to P2Y1 receptor was done using Cavity-detection guided blind-docking software. Histology of the pancreatic islets were examined using hematoxylin and eosin stains. Data were analyzed using graphpad prism, p<0.05 was statistically significant. All procedures involving the use of animals were performed according to ethics and guidelines for animal care and use for research by University of Medical Sciences Ethical Review Committee and also in compliance with the guidelines provided by the Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on ethical principles for medical research involving experimental animals [World Medical Association, 2013].
Results
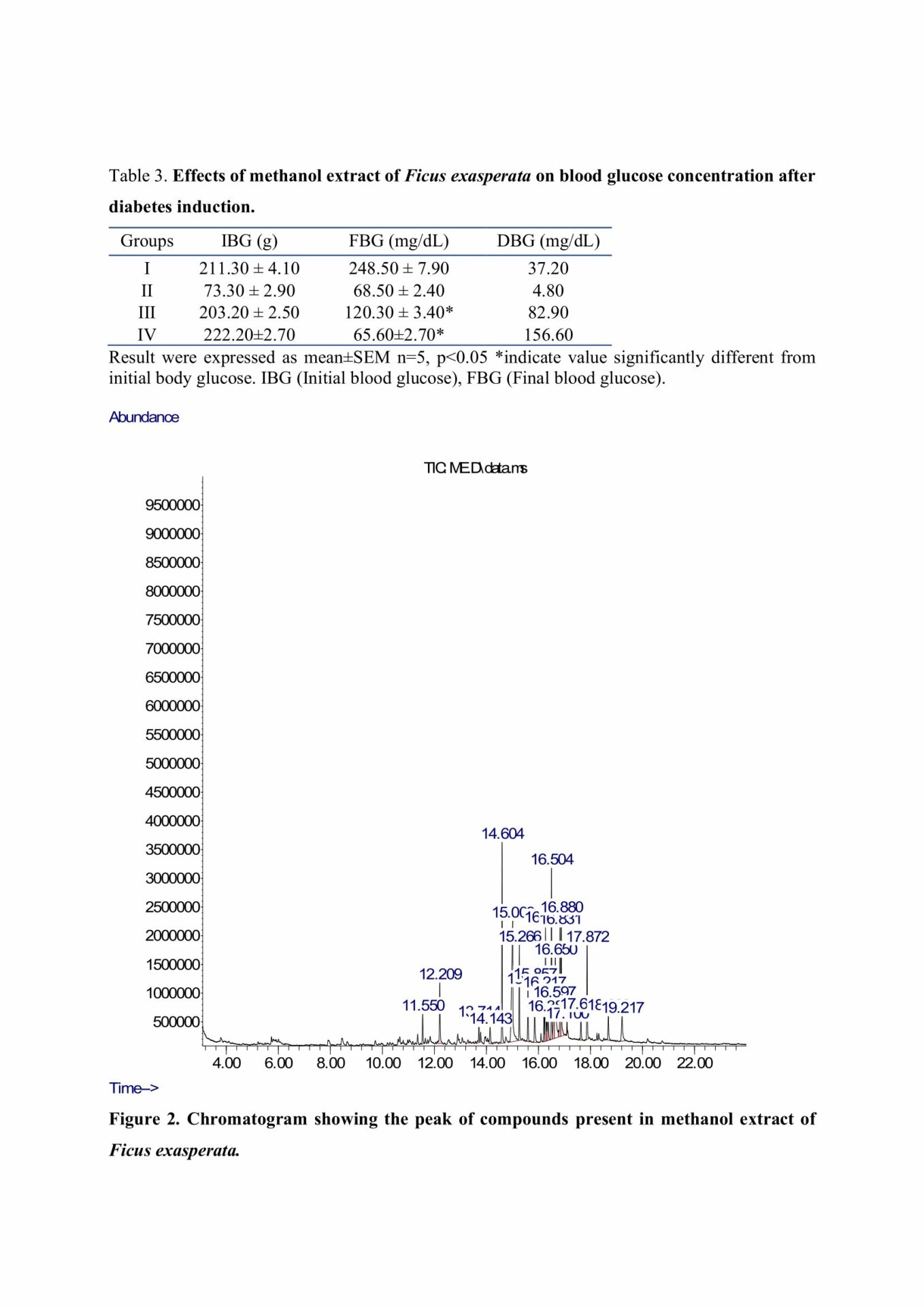
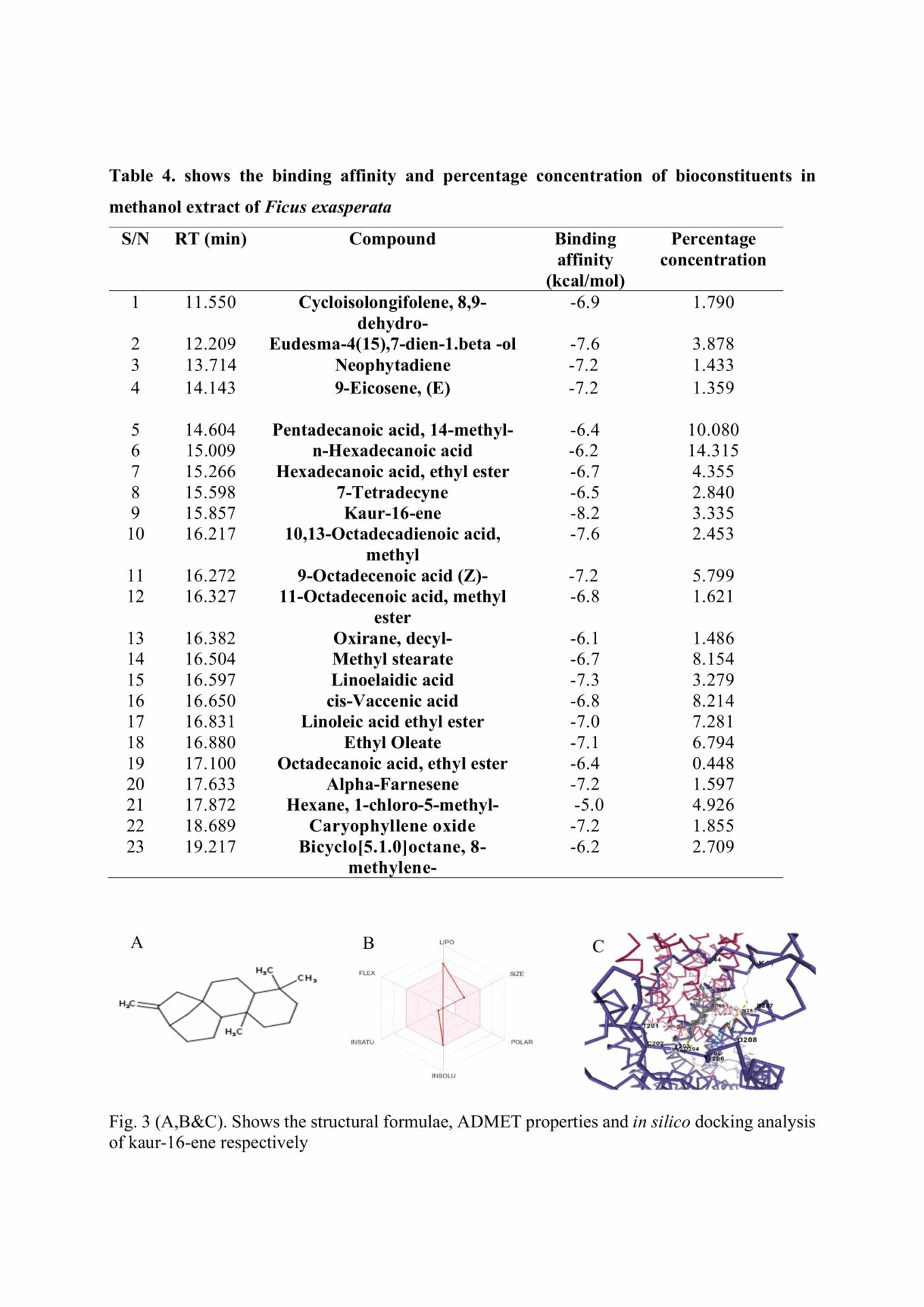
GC-MS result revealed the presence of 23 constituents with kaur-16-ene having the highest binding affinity (-8.2 Kcal) against P2Y1 receptor on islet cells. There was a significant decrease in blood glucose in diabetes+ MEFE (200 mg/kg) compared to DU. However, there was a significant increase in insulin, TGR5, GLP-1, and GIP expression, SOD, catalase and GPx in diabetes+ MEFE (200 mg/kg) compared to DU. The diabetic group + MEFE (200 mg/kg) showed regenerated islet cells compared to DU.
Conclusion
In diabetic rats, the observed results of MEFE suggest its antioxidative and stimulatory effects on genes that effectively controlled blood glucose levels.