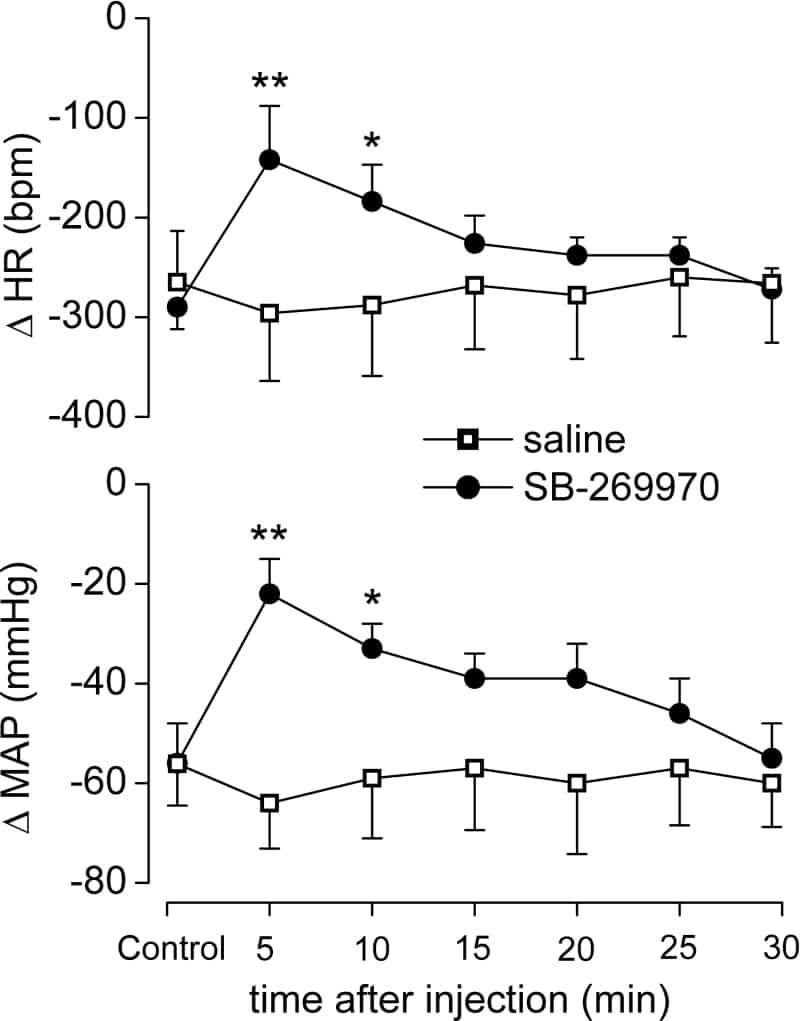
In anaesthetised rats, central 5-HT7 receptors play an important facilitatory role in cardiopulmonary, baro- and chemoreflex vagal bradycardia (Kellett et al. 2005). The present study investigated the involvement of central 5-HT7 receptors in the cardiopulmonary reflex responses in freely moving awake rats, using the selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB-269970 (Hagan et al. 2000). Adult male Wistar rats (280-330 g) were implanted with intracisternal (i.c.; Michelini & Bonagamba, 1988) 23-gauge guide cannulae under tribromoethanol anaesthesia (250 mg kg-1; i.p.). After 72 h recovery, rats were re-anaesthetised and implanted with femoral arterial and venous polythene catheters. Experiments commenced 24 h later. Pulsatile arterial pressure and HR were measured from the arterial line, and cardiopulmonary afferents were stimulated with 5-HT (1 – 3 μg; i.v.) under freely moving conditions as previously described (Chianca & Machado, 1996). After at least two stable (< 10% change) control reflexes, either the 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB-269970 (100 μg kg-1) or its vehicle (saline), was injected i.c. (5 μl) and reflexes stimulated every 5 min. Absolute changes in HR and MAP were analysed by 2-way ANOVA and Fisher’s least significant difference test. At the end of the experiment animals were humanely killed with an overdose of thiopentone sodium. Both reflex bradycardia and hypotension were significantly attenuated by SB-269970 within 5 min of administration (see Fig. 1), and there was rapid recovery from this effect. Neither SB-269970 nor saline significantly altered baseline MAP or HR (control baselines were 104 ± 4 mmHg and 376 ± 17 bpm, respectively). Pontamine sky blue dye given i.c. caused the densest staining in the dorsal medulla. The data demonstrate that the important facilitatory action of brainstem 5-HT7 receptors on cardiopulmonary reflex responses can also be observed in awake rats.
University of Bristol (2005) J Physiol 567P, PC32
Poster Communications: The cardiopulmonary reflex recruits central 5-HT7 receptors in awake rats
Kellett, Daniel O; Damaso, Enio L; Bonagamba, Leni G; Machado, Benedito H; Jordan, David; Ramage, Andrew G;
1. Physiology, University College London, London, United Kingdom. 2. Pharmacology, University College London, London, United Kingdom. 3. Physiology, University of Sao Paulo, Ribeirao Preto, Brazil.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1. Mean (± s.e.m.) cardiopulmonary reflex-evoked changes (Δ) in HR and MAP in awake rats treated with i.c. saline (5 μl) or SB-269970 (100 μg kg-1; n = 5). * P < 0.05 ** P < 0.01 (cf. saline).
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.