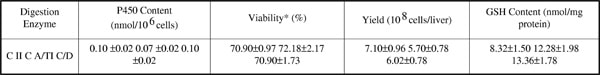
Isolated hepatocytes provide a useful whole cell in vitro system for the evaluation of xenobiotic metabolism and toxicity. Several modifications of the two-stage collagenase perfusion technique, originally described by Seglen1, have been reported for the preparation of hepatocytes. This study seeks to investigate the effect of digestion enzymes on the drug-metabolising activity of isolated rat hepatocytes in suspension. Hepatocytes were isolated from male Sprague Dawley rats (180-220 g) using collagenase type II (C II) as described previously2. Modifications of this technique using collagenase A/trypsin inhibitor (C A/TI) and collagenase/dispase (C/D) were also investigated. Hepatocytes prepared using the three different digestion enzymes were characterised based on cell yield, % viability (LDH leakage), cytochrome P450 and reduced glutathione (GSH) content, phase 1 metabolism (7-ethoxycoumarin o-deethylase activity (ECOD)) and phase 2 metabolism (glucuronidation and sulfation of 7-hydroxycoumarin (7HC)). For metabolic studies, incubations were performed over 120 min with a cell density of 2×106 viable cells/ml in Krebs Hepes buffer, pH 7.4, in rotating round bottomed flasks at 37oC under an atmosphere of 5% CO2/95% O2. Table 1 shows the parameters measured on initial isolation. There were no statistical differences in these parameters. However, at a substrate concentration of 100 µM the use of C A/TI results in a significant (p<0.05) increase in the capacity to form 7HC (3.32±0.25 nmol/106cells) compared with C II (1.30±0.23 nmol/106cells) and C/D (1.79±0.55 nmol/106cells). C A/TI also results in a significant (p<0.05) increase in the yield of 7HC glucuronide (94.0±9.5 nmol/106cells) compared with C/D (59.4±5.2 nmol/106cells) at a substrate concentration of 500 µM. These initial observations suggest that the use of trypsin inhibitor in perfusion solutions may be beneficial for the metabolic capacity of isolated rat hepatocytes.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC260
Poster Communications: The digestion enzyme used in isolation procedures influences metabolic capacity of hepatocytes
J. A. Sinclair1, C. Henderson1, I. J. Martin2, M. H. Grant1, J. N. Tettey1
1. Strathclyde University, Glasgow, United Kingdom. 2. Organon Laboratories Ltd, Motherwell, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1: Parameters measured on initial isolation (mean ± SEM n=5)
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.