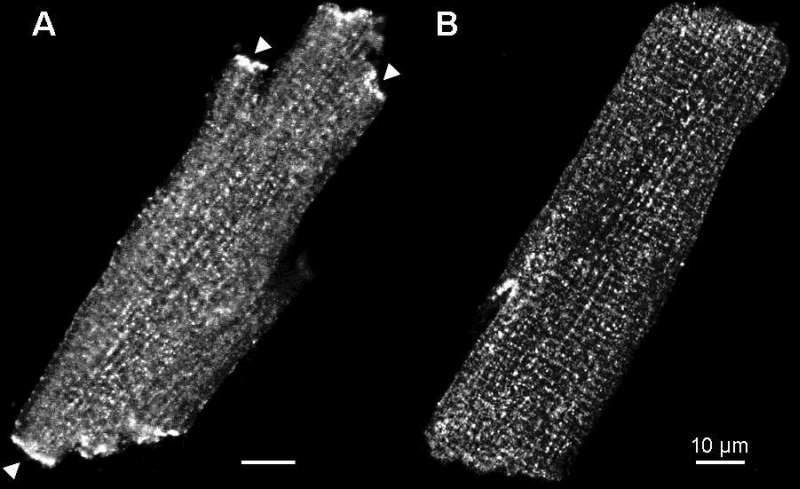
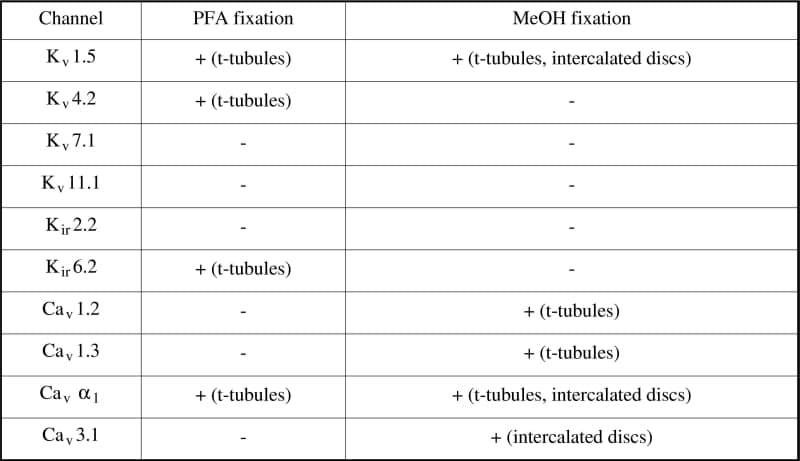
Immunocytochemistry is an established method to identify the localization of cellular proteins. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of different fixation treatments on immunocytochemical labelling of ion channels in enzymatically isolated rat ventricular myocytes from humanely killed rats. Two different fixation protocols were employed. In the first fixation protocol, cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde (PFA, 4%) for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS (which permeabilizes surface membranes as well as those of intracellular organelles). With the second fixation protocol, fixation and permeabilization was performed by incubating cells with ice-cold 100% methanol (MeOH) for 5 min at -20°C. After PFA or MeOH fixation all cells were subjected to the same protocol. They were washed in PBS and blocked with 10% donkey serum in PBS. Following 14-22 h incubation with primary antibodies at 4°C, cells were washed in PBS, incubated with secondary antibodies conjugated to FITC and visualized using laser scanning confocal microscopy. With these two fixation protocols, labelling of various ion channels was investigated: Kv1.5 (responsible for IKur, Fig. 1), Kv4.2 (responsible for Ito), Kv7.1 (KvLQT1, responsible for IKs), Kv11.1 (ERG, responsible for IKr), Kir2.2 (responsible for IK1), Kir6.2 (responsible for IKATP), Cav1.2 (α1C, responsible for ICaL), Cav1.3 (α1D, responsible for ICaL), Cavα1 (α1C and α1D) and Cav3.1 (α1G, responsible for ICaT). With PFA fixation, there was a distinct and strong striated pattern of labelling (presumably corresponding to t-tubules) of Kv4.2, Kir6.2 and Cavα1 and a weak striated pattern of labelling of Kv1.5 (Fig. 1), but no labelling of other ion channels. With MeOH fixation, there was a distinct and strong striated pattern of labelling of Cav1.2, Cav1.3 and Cavα1, a weak striated pattern of labelling of Kv1.5 and labelling at intercalated discs in the case of Kv1.5 (Fig. 1), Cavα1 and Cav3.1, but no labelling of other ion channels. Results are summarised in Table 1. This study clearly demonstrates the importance of different fixation protocols on the labelling of ion channel proteins in myocytes. It is concluded that, to visualise ion channels in the heart using immunolabelling, the results obtained from both PFA and MeOH fixation protocols should be compared.
University of Bristol (2005) J Physiol 567P, PC28
Poster Communications: The effect of different fixation protocols on immunocytochemical labelling of ion channels in rat ventricular myocytes
Yamanushi, Tomoko T; Boyett, Mark R; Dobrzynski, Halina;
1. Kagawa Prefectural College of Health Sciences, Kagawa, Japan. 2. Cardiovascular and Endocrine Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester , United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1. The effect of two different fixation treatments on immunolabelling of Kv1.5. A strong labelling at intercalated discs (e.g. at arrow) with MeOH fixation. B weak striated pattern of labelling with PFA fixation. Using a different Kv1.5 antibody and MeOH fixation strong labelling of Kv1.5 at the intercalated disc was previously observed in rat ventricular myocytes (Dobrzynski et al. 2000).
Table 1. Effect of two different fixation protocols on immunolabelling of ion channels.The presence (+) or absence (-) of labelling and the site of labelling if present is noted. For each fixation protocol and channel studied immunolabelling was imaged in three cells (except in cases in which there was no labelling); in all cases the pattern of labelling in the cells imaged was typical.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.