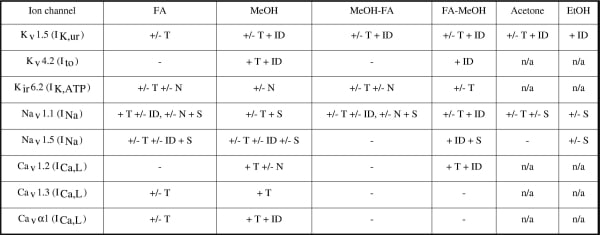
Immunocytochemistry with a standard formaldehyde fixation can pose difficulty in regard to sub-cellular localisation of ion channel proteins in cardiac cells. The aim of this study was to compare the effect of different fixatives on the expression and sub-cellular localisation of various ion channels in isolated ventricular cells from rats. Animals were killed humanely and cells isolated. Fixative used were: (1) aldehyde fixative (10% buffered formalin, FA); (2) non-aldehyde fixatives (a. 100 % methanol, MeOH, b. 100 % acetone and c. absolute ethanol, EtOH); (3) combination of fixatives (1) and (2a). After treatment with various fixatives, ventricular cells underwent a standard immunocytochemical protocol. In brief, cells were incubated with primary IgGs (raised against ion channel proteins listed in Table 1), and then incubated with secondary IgGs conjugated to either FITC or Cy3. Immunofluorescence signal was visualised with confocal microscopy. It is clear from Table 1., that the strength of immunofluorescnce signal of various channel proteins and their sub-cellular immunolocalisation in isolated ventricular myocytes varies amongst different fixation protocols. For example, a stronger intensity of immunolabelling of Kv1.5, Kv4.2, Cav1.2, Cav1.3 and Cavα1, was detected with the non-aldehyde fixative such MeOH (2a) than that with the aldehyde fixative (1). Conversely, immunofluorescence signals for Kir6.2, Nav1.1 and Nav1.5 were better detected with either the aldehyde fixative (1) or combination of fixatives (1) and (2a) than that non-aldehyde fixative (e.g., 2a). In addition, the sub-cellular localisation of ion channel proteins varied between the aldehyde fixative (1) and the non-aldehyde fixative (2a). With former fixative there was no immunosignal of e.g., Kv1.5 and Kv4.2 at the intercalated discs. Our data suggest that MeOH is the most suitable non-aldehyde fixative for the detection of ion channel proteins by immunocytochemistry.
University of Manchester (2007) Proc Physiol Soc 8, PC26
Poster Communications: The effect of different fixatives on immunodetection of ion channels in isolated rat ventricular cells
T. T. Yamanushi1, E. Hirakawa1, H. Ohsaki1, M. R. Boyett2, H. Dobrzynski2
1. Kagawa Prefectural College of Health Sciences, Takamatsu City, Japan. 2. Division of Cardiovascular and Endocrine Sciences, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1. T, t-tubules; ID, intercalated disks; N, nucleus; S, sarcolemma; n/a, not examined. Signal for each ion channel was collected from n=3 or more cells.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.