We have shown previously (Muzyamba & Gibson, 2001) that the oxidant phenazine methosulphate (phenazine) markedly stimulates the Ca2+-activated K+ pathway (or Gardos channel) in human red blood cells (RBCs). Stimulation is O2 dependent: perhaps paradoxically, it is increased when cells are deoxygenated. An increase in Gardos channel activity could be due to three effects, singly or in combination: (i) increased Ca2+ influx; (ii) decreased Ca2+ efflux via the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump (PMCA); or (iii) increased sensitivity of the channel to intracellular [Ca2+] ([Ca2+]i). The latter has been suggested from its effects on vesicles prepared from human RBCs (Alvarez et al. 1984).
In this communication, we concentrate on the effect of phenazine on Ca2+ fluxes, measuring transport with 45Ca2+, following the methodology established by Tiffert et al. (1993). Normal human RBCs were obtained from consenting donors under ethical permission. Ca2+ uptake was measured over 60 min in cells treated with vanadate (1 mM) to inhibit PMCA; maximal pump activity was estimated by determining the time course of Ca2+ efflux from cells loaded using A23187.
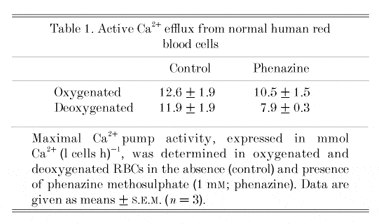
Results (Table 1) show that changing O2 tension in control cells had a small, but consistent, inhibitory effect on PCMA, in agreement with previous findings (Tiffert et al. 1993). Phenazine inhibited PMCA activity in both oxygenated and deoxygenated cells, but its effect was greater (Student’s paired t test) in the absence of O2 (inhibition of 33 ± 8 % in N2; 16 ± 5 % in air; means ± S.E.M., n = 3). Finally, in a typical experiment in N2, passive Ca2+ influx was 6.6 µmol (l cells h)-1 in control cells and 6.3 in the presence of phenazine.
Inhibition of the Ca2+ pump will increase [Ca2+]i and may account, at least in part, for activation of the Gardos channel. We hypothesise that the greater efficacy of phenazine in deoxygenated cells results from inhibition of the pentose-phosphate shunt in the absence of O2, thereby reducing the concentration of protective species such as NADPH.
We thank Action Research and The Wellcome Trust for financial support.