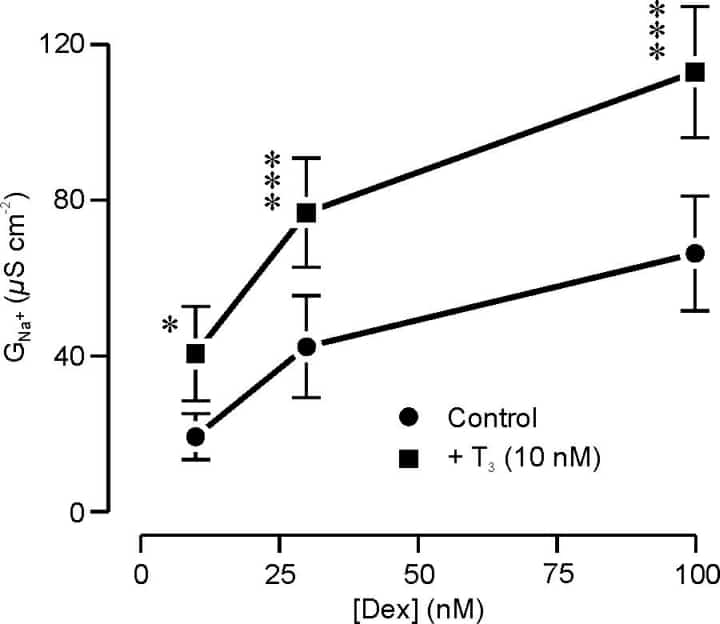
Studies of fetal lambs have shown that thyroidectomy abolishes the adrenaline-evoked absorption of lung liquid that is normally seen during labour and birth. However, whilst this effect can be reversed by exogenous T3,delivering T3 to immature fetuses does not cause precocious absorption of lung liquid unless it is given with a glucocorticoid (Barker et al., 1991). As this absorptive process is driven by active Na transport (Olver et al., 2004), it thus appears that thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones are both important to the initiation and maintenance of the adult lungs’ absorptive phenotype.Our earlier work shows that H441 distal airway epithelial cells do not transport Na if maintained in the absence of such hormones, but that 0.2 µM dexamethasone, a synthetic glucocorticoid, stimulates electrogenic Na transport by evoking expression of a selective apical Na conductance (Ramminger et al., 2003). The present study therefore explored the possibility that T3 may also play a role in this process and our data (Fig 1) show clearly that T3 potentiates the dexamethasone-induced increase in GNa.T3 thus appear to be involved in the control of epithelial Na absorption (see also Pachá et al., 1996), which may explain the abnormally high incidence of respiratory distress amongst congenitally hypothyroid infants (Cuestas et al., 1976).
University of Glasgow (2004) J Physiol 557P, C52
Communications: Thyroid hormone (T3) potentiates the glucocorticoid-evoked increase in apical Na conductance (GNa) in H441 distal airway epithelial cells
S.M. Wilson, S.J. Ramminger and R.E. Olver
Lung Membrane Transport Group, Division of Maternal and Child Health Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee, UK
View other abstracts by:
Fig. 1. H441 cells on Costar Snapwell membranes were grown for 7 days, by which time they had become incorporated into resistive epithelial sheets (Rt > 300 Ωcm2). The cells were then mounted in Ussing chambers, bathed in cytoplasmic solution and basolaterally permeabilised using nystatin (75 mM). Gcould then be quantified by measuring the amiloride-sensitive apical membrane currents evoked by imposing an inwardly directed Na gradient upon the permeabilised cells. The figure shows data (mean ± s.e.m., n = 5) for cells cultured in 10 nM, 30 nM or 100 nM dexamethasone, under control conditions and in the presence of 10 nM T3.The medium used contained insulin, but no other hormones or growth factors were present. Asterisks denote significant effects of T3 (* P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001, Student’s paired t test).
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.