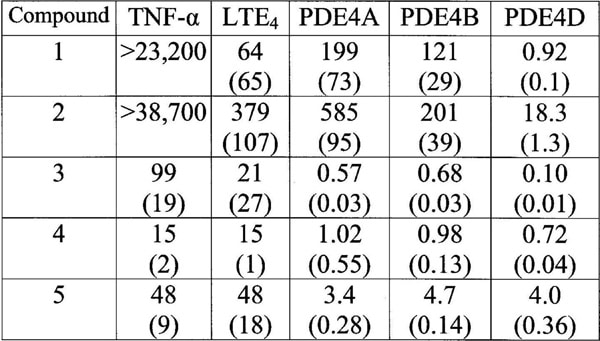
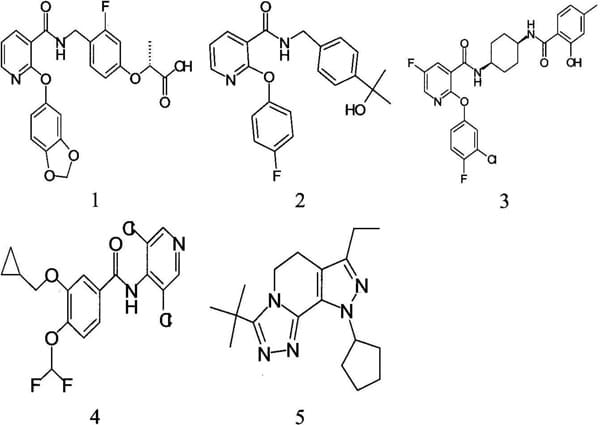
Inhibitors of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) developed to treat asthma and COPD have so far met with limited clinical success, often due to gastrointestinal side-effects. This may reflect inhibition of the PDE4D isoform (Robichaud et al, 2002). We have investigated whether human whole blood (HWB) assays for release of LTE4 and TNF-α can discriminate compounds that are selective for PDE4D from those with a more balanced isozyme inhibition profile that may have a better therapeutic index. HWB was incubated at 37oC with compound (0.3nM – 100µM) for 30 min prior to addition of LPS (100ng/ml). The assay mixtures were incubated for a further 24 h and TNF-α then determined by specific ELISA. A similar protocol was used for monitoring LTE4 release, except that the HWB was treated with sephadex G15 beads (15mg/ml) and PGE1 (1µM). Recombinant human PDE4A, B and D were expressed in Sf9 insect cells. PDE activity was monitored by following the conversion of [3H]cAMP (0.5µM) to [3H]5’AMP using a scintillation proximity assay (Amersham UK). IC50s (concentrations reducing stimulated cytokine release or [3H]5’AMP formation by 50%) were determined using a sigmoidal curve fit algorithm. The PDE4 inhibitors differed in their relative potency to inhibit LTE4 release and TNF-α release in HWB (Table). Overall, the rank order of selectivity for inhibition of LTE4 release (IC50 ratio TNF-α / LTE4) mirrored that for inhibition of PDE4D (IC50 ratio PDE4A or B / PDE4D); compound 1>2>3>4 and 5. Compounds 1 and 2 showed significantly greater potency against LTE4 release (>360-fold and >100-fold respectively, P<0.001) and this was associated with selective inhibition of PDE4D (≥130-fold and ≥11-fold respectively, P<0.001). Compound 3 showed a trend for selective inhibition of LTE4 release (5-fold, non-significant) and PDE4D (≥6 fold; P<0.001). In contrast, compound 4 (roflumilast) and compound 5 showed no significant selectivity for LTE4 release or for PDE4D inhibition. Our data support the proposal that sephadex-stimulated release of LTE4 and LPS-stimulated release of TNF-α in HWB are functional correlates for PDE4D and PDE4B (±4A) inhibition, respectively. Furthermore, when used together, these assays may have utility in clinical trials of PDE4 inhibitors as ex vivo biomarkers for efficacy and toleration. Roflumilast (4), which has shown efficacy in asthma and COPD at tolerated doses (Lipworth, 2005), has a balanced profile for inhibition of PDE4 isozymes and for LTE4 vs. TNF-α release in whole blood. In contrast, poor toleration might be anticipated for compounds 1 and 2 which are both highly selective for PDE4D inhibition and LTE4 release.
Life Sciences 2007 (2007) Proc Life Sciences, PC124
Poster Communications: Whole blood cytokine release assays differentiate PDE4 enzyme inhibitors: implications for safety and toleration
A. Barnard1, M. Trevethick1, S. Ballard1
1. Allergy and Respiratory, Pfizer, Sandwich, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table: IC50s for inhibition of TNF-α and LTE4 release in HWB plus PDE4A B & D. Data are geometric mean with s.e.m in parentheses (n≥3).
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.