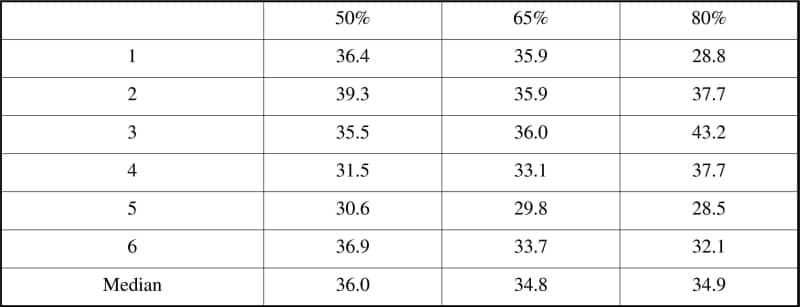
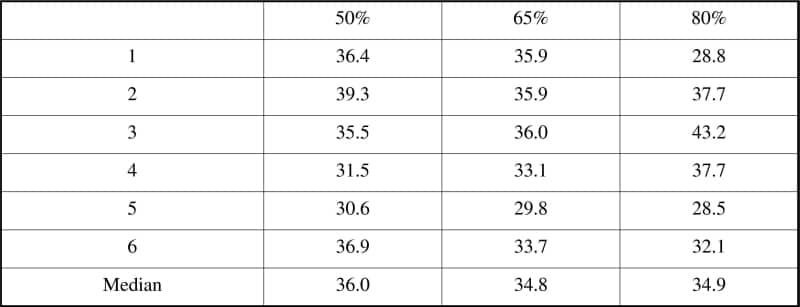
The study of oxygen uptake kinetics (tau values) using self-paced walking as the mode of exercise may provide a convenient indirect measure of aerobic fitness. However, one concern is the effect of inadvertent differences in exercise intensity between tests upon derived tau values. Previous studies report conflicting results. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of exercise intensity on tau values derived from treadmill walking. Six untrained healthy young (median age 22.5 years (21-24 years)) women underwent VO2max treadmill testing (visit 1) to permit calculation of sub-maximal work-rates of 50%, 65% and 80% VO2max. A familiarization bout (6 min at 65% VO2max) was performed at the start of the 2nd and 3rd visits and excluded from further analysis. Subjects then performed 9 bouts of exercise (3 bouts of each intensity) over the 2nd and 3rd visits. Each 6 min exercise bout was followed by ≥20 min of seated rest. Breath-by-breath data (with spurious breaths removed) were interpolated on a second-by-second basis and time aligned to exercise onset. Ensemble averaged datasets were fitted with a monoexponential model to derive a tau value for each intensity. Repeated measures ANOVA showed no significant linear trend (F(1,5) = 0.24, p=0.883). The within subjects coefficient of variation was 11.3% (Table 1). In this sample of young women of comparable age and fitness, variations in tau between these exercise intensities were not physiological significant. On the basis of these findings in young individuals, any unavoidable variations in exercise intensity between tests would be unlikely to mask intervention related effects on tau values.
King's College London (2005) J Physiol 565P, C36
Communications: The effect of exercise intensity on oxygen uptake kinetics in healthy young women
Fitzsimons, C F; Carnwath, A ; McLellan, S ; Young, A ; Greig, C A;
1. Geriatric Medicine, School of Clinical Sciences and Community Health, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom. 2. University Department of Anaesthetics, Critical Care & Pain Medicine, School of Clinical Sciences and Community Health, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Table 1. Tau values (s) corresponding to each exercise intensity (50% 65% and 80% VO 2max)
Table 1. Tau values (s) corresponding to each exercise intensity (50% 65% and 80% VO 2max)
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.