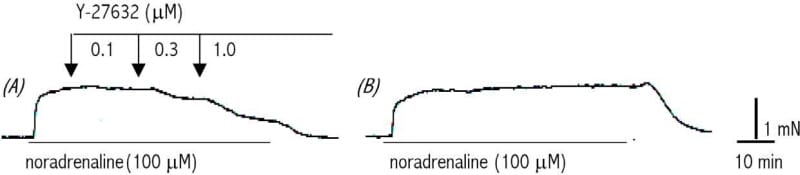
Noradrenaline (NA) elicits robust and sustained contractions of rat vas deferens in Ca2+-free/EGTA medium (Ashoori & Tomita, 1983). Agents that deplete intracellular Ca2+ stores or block its release or protein kinase C activation do not inhibit the Ca2+-free contraction (Amobi et al., 1999). In order to elucidate the excitation-contraction coupling pathway underlying the Ca2+-free response and the possible role of Rho kinase-mediated Ca2+sensitization, the effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors were investigated. The contribution of Ca2+sensitization to Ca2+-dependent contractions of both rat and human epididymal vas deferens were also evaluated. Male Sprague Dawley rats were killed humanely. Epididymal portions of isolated rat vas deferens, longitudinal muscle strips and rings of circular muscle from human vasectomy specimens (patient consent and College ethical approval obtained) were set up for tension recordings and superfused (2.5 ml min-1) with Krebs’-bicarbonate solution (36 oC). NA-induced Ca2+-free contraction of rat vas deferens was relaxed dose-dependently by Rho kinase inhibitors, Y-27632 (0.1-10 μM in different experiments, Fig. 1A) or HA 1077 (not shown). IC50 values (mean ± S.E.M.) were, respectively, 1.08 ± 0.13 μM (n=10) and 1.75 ± 0.43 μM (n=8) respectively. Exposure to Y-27632 (0.01-10 μM in different experiments) did not change basal tone but Y-27632 (0.01-3 μM) reduced the maximum of concentration-response curves to NA (0.1-300 μM) in Ca2+-free medium and Y-27632 (10 μM) abolished the response. In contrast, the NA response curve was unaffected by MLCK inhibitors, ML-9 (1-3μM) or wortmannin (1-3 μM) but the maximum was depressed by ML-9 (10 μM) or wortmannin (10 μM). Contractions of rat and human (longitudinal or circular muscle) vas deferens evoked in normal Krebs’ (Ca2+, 2.5 mM) by NA (100 μM) or high [K+]o (120 mM) were reliably depressed but not abolished by Y-27632 (1-10 μM). Abolition required the combination of Y-27632 (10 μM) and ML-9 (30 μM). These results suggest that Rho kinase-mediated Ca2+sensitization is the major mechanism underlying NA-induced Ca2+-free contraction of rat vas deferens and contributes to Ca2+-dependent contractions of both rat and human vas deferens.
King's College London (2005) J Physiol 565P, PC130
Communications: Effects of Rho-kinase inhibitors in rat and human epididymal vas deferens
Amobi, Nnaemeka I; Chung, I-Pang ; Smith, I Christopher;
1. Physiology, Division for Applied Biomedical Sciences Research, King's College, Guys Campus, London, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1. (A) Inhibition of NA-induced Caμμ2+2+-free/EGTA (1 mM) throughout out drug washout (90 min) and subsequent stimulation with NA.
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.