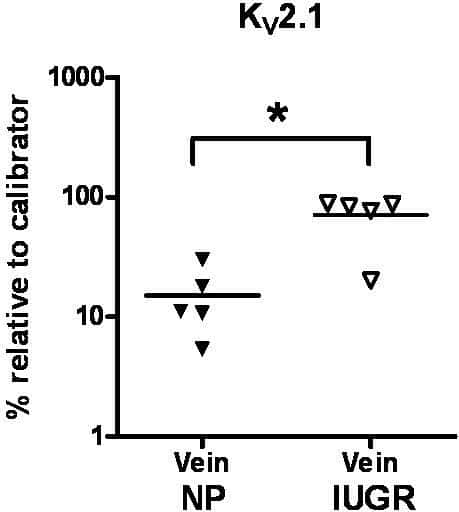
In normal pregnancy (NP), voltage [Kv] and ATP [KATP]-sensitive potassium (K) channel mRNA is expressed in the placental vasculature [1]. We have shown that K channels are important in the control of placental vascular reactivity in NP [2] and in pregnancies affected by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) [3]. However, there are no data on gene expression of K channels in the NP and IUGR placental vasculature. We aimed to determine K channel gene expression in NP and IUGR placental tissue. Placental homogenate, chorionic plate arteries and veins (NP; N=6: IUGR; N=5) were obtained after vaginal delivery or Caesarean section at term. Tissue sampling, total RNA isolation and cDNA production were performed as described previously [4]. K channel expression was assessed using SYBR Green 1 quantitative PCR. Channel sequences were derived from GenBank with reference to BLAST and primers designed with Beacon designer software. Each sample (1μl) was run as quadruplicate reactions with a passive reference dye. Quantification was performed using sample cycle threshold values to calculate initial input amounts from a standard curve of cDNA generated using a human reference RNA and normalised to a human reference cDNA calibrator. Expression was assessed relative to the calibrator. In IUGR placental chorionic plate arteries and veins showed similar expression levels of Kv2.1; placental homogenate expression was increased compared to arteries only. Similar expression patterns were seen for Kv9.3 and KIR6.1. In NP a similar pattern of expression was observed with Kv2.1; similar arterial and venous expression; raised expression in placental homogenate compared to arteries only. With Kv9.3 and KIR6.1, expression levels were similar in arteries, veins and placental homogenate. When comparing IUGR and NP gene expression directly, only venous expression of Kv2.1 was increased (Fig 1; P<0.05 Mann Whitney U test). We found variable placental K-channel expression in NP and IUGR. Only venous expression of Kv2.1 was increased in IUGR versus NP. Aberrant Kv channel expression may contribute to altered placental vascular resistance associated with IUGR pregnancies.
University College London 2006 (2006) Proc Physiol Soc 3, PC205
Poster Communications: Potassium channel gene expression in the human placental vasculature of normal and growth-restricted pregnancies
Jemma Corcoran1, Helen Lacey1, Philip N Baker1, Gregor K Fyfe1, Mark Wareing1
1. Maternal and Fetal Health Research Centre, The University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom.
View other abstracts by:
Figure 1
Where applicable, experiments conform with Society ethical requirements.